Acne-Prone Skin: Causes, Care Tips, and How to Manage It Effectively
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
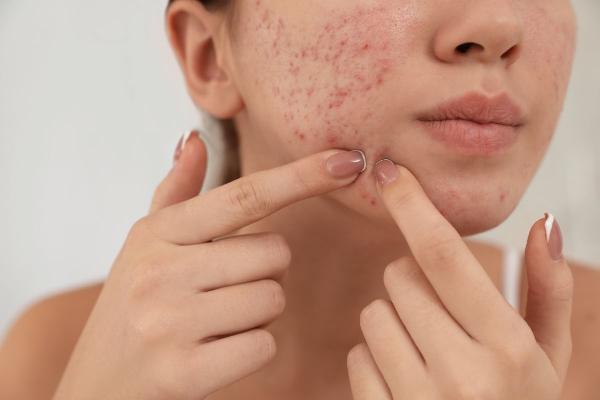
Dealing with frequent acne breakouts? If you have oily, acne-prone skin, you’re not alone. Unexpected acne breakouts can be frustrating and affect not only your skin but also your quality of life. Acne can lower self-esteem, making it important to understand the causes and find effective solutions.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore acne-prone skin in detail, covering the causes of acne, how to care for your skin, and the best ways to manage and treat it.
1. Understanding Acne-Prone Skin
Acne-prone skin refers to skin that is more susceptible to breakouts due to overactive oil glands. While every skin type can develop acne, individuals with acne-prone skin experience frequent breakouts because their oil glands produce excess sebum, leading to clogged pores and the formation of acne or Acne Vulgaris.
Acne is one of the most common skin conditions, affecting 80-95% of young men and 80-82% of young women. It typically begins during puberty and appears on areas such as the face, neck, chest, shoulders, and back. The intensity of acne can range from mild to severe, with various symptoms like:
- Small bumps
- Pus-filled spots
- Whiteheads
- Blackheads
- Oily skin
- Nodules or cysts
Types of Acne
Acne can be categorized into two broad types:
1. Non-Inflammatory Acne
This is the mildest form of acne, caused by clogged pores. Non-inflammatory acne includes blackheads and whiteheads. Blackheads appear dark and open at the skin's surface, while whiteheads are small, skin-colored bumps beneath the skin.
2. Inflammatory Acne
Inflammatory acne appears red and swollen due to clogged pores. Common types of inflammatory acne include:
- Papules: Small, red bumps
- Pustules: Small bumps containing pus
- Nodules: Larger, painful bumps
Other skin conditions, such as acne rosacea, can also cause acne-like breakouts. Rosacea is a sensitive skin condition that causes redness and papules or pustules on the face.
Severity Levels of Acne
- Mild Acne: Small whiteheads or blackheads and occasional irritated pimples.
- Moderate Acne: A mix of blackheads, whiteheads, pimples, and pustules on the face, sometimes leaving scars.
- Severe Acne: A significant number of blackheads, whiteheads, papules, pustules, and painful nodules that affect the face, back, and shoulders.
2. Causes of Acne
Acne occurs when the skin’s pores become clogged with excess sebum, dead skin cells, and bacteria. Acne-prone skin is more likely to experience these breakouts due to factors like:
a. Overproduction of Sebum
Sebum is the oil produced by the skin’s sebaceous glands. While sebum is essential for keeping the skin hydrated, excess sebum clogs pores and leads to acne.
b. Bacterial Buildup
When the skin’s pores are clogged, bacteria multiply, leading to inflammation and the development of acne lesions.
c. Dead Skin Cell Accumulation
Dead skin cells that accumulate on the surface of the skin can block pores, trapping oil and bacteria, which contributes to the formation of acne.
d. Inflammation
Inflammation occurs when the skin reacts to clogged pores or bacterial infections, resulting in red, swollen pimples or nodules.
Other factors that can trigger acne include:
- Poor skincare routines
- Greasy diets
- Hormonal fluctuations
- Stress
3. Symptoms of Acne-Prone Skin
If you have acne-prone skin, you might experience the following symptoms:
- Closed or open plugged pores (whiteheads or blackheads)
- Small, red papules
- Tender bumps or large nodules under the skin
- Pus-filled pimples or pustules
- Redness around affected areas
- Scarring from previous breakouts
4. Risk Factors for Acne Breakouts
Certain factors increase the risk of developing acne:
a. Age
Acne commonly affects teenagers and young adults but can occur at any age.
b. Genetics
Genetics play a significant role in determining skin type. If your parents had acne, you’re more likely to develop it due to genetic predisposition.
c. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes during puberty, the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and menopause can trigger excess oil production, leading to acne.
d. Medications
Certain medications, like corticosteroids or lithium, can cause or aggravate acne.
e. Diet
Foods with a high glycemic index (such as refined sugars and dairy) can trigger acne breakouts.
f. Stress
Stress increases oil production, which can worsen acne.
g. Smoking
Smoking affects sebum composition, causing oxidative stress that leads to more acne.
h. Inappropriate Skincare
Using harsh soaps, hot water, or chemical-laden skincare products can trigger or worsen acne.
i. Environmental Triggers
Factors like pollution, humidity, and sweating can cause acne breakouts. Poor lifestyle habits such as alcohol consumption and lack of sleep can also contribute to acne-prone skin.
5. Preventing Acne Breakouts
Preventing acne is possible with a consistent skincare routine and healthy lifestyle. Here are some effective ways to reduce breakouts:
- Cleanse twice daily: Wash your face every morning and before bed to remove dirt, oil, and makeup.
- Use gentle, chemical-free skincare products: Avoid products with harsh ingredients that can irritate the skin.
- Avoid harsh scrubbing: Be gentle when cleansing your skin to avoid irritation.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water keeps your skin hydrated and healthy.
- Keep bedding and makeup tools clean: Wash pillowcases, towels, and makeup brushes regularly.
- Apply sunscreen: Protect your skin from UV damage by using a broad-spectrum sunscreen.
- Avoid popping pimples: Popping pimples can worsen inflammation and cause scarring.
- Consult a dermatologist: For persistent acne, consult a professional for personalized skincare advice.
6. Acne Treatment Options
Managing and treating acne-prone skin requires the right combination of treatments. If you're wondering, "What's the best acne treatment near me?" here are some common options:
a. Topical Treatments
Over-the-counter and prescription topical treatments help treat mild to moderate acne. Some effective ingredients include:
- Retinoids (tretinoin, adapalene): Help reduce clogged pores and prevent new breakouts.
- Antibiotics (clindamycin, erythromycin): Reduce bacteria and inflammation.
- Benzoyl Peroxide: Kills acne-causing bacteria and unclogs pores.
- Salicylic Acid: Exfoliates and helps remove dead skin cells.
b. Oral Medications
For more severe acne, oral medications may be prescribed:
- Antibiotics: Help reduce bacterial growth and inflammation.
- Oral Contraceptives: Can regulate hormones and reduce oil production in women.
- Isotretinoin: A powerful drug used to treat severe acne that doesn't respond to other treatments.
c. Professional Treatments
Dermatologists may recommend various treatments to manage acne-prone skin, such as:
- Chemical Peels: Help exfoliate the skin and reduce acne.
- Light Therapy: Targets bacteria that cause acne.
- Steroid Injections: Used to reduce inflammation in severe cases of acne.
7. Skincare Routine for Acne-Prone Skin
Establishing a consistent skincare routine is essential for managing acne-prone skin. Here's a step-by-step guide:
Morning Routine:
- Cleanser: Use a gentle cleanser to remove oil and impurities.
- Toner: Apply toner to balance skin pH and remove excess oil.
- Moisturizer: Hydrate your skin with an oil-free moisturizer.
- Sunscreen: Use broad-spectrum sunscreen to protect your skin from sun damage.
Evening Routine:
- Makeup Remover: Remove makeup before cleansing to prevent clogged pores.
- Cleanser: Cleanse your face to remove dirt and oil.
- Spot Treatment: Apply any prescribed acne treatment to target breakouts.
Weekly Routine:
- Exfoliation: Gently exfoliate your skin to remove dead skin cells and prevent clogged pores.
- Face Mask: Use a soothing face mask to calm the skin and reduce inflammation.
8. Natural Remedies for Acne-Prone Skin
While over-the-counter treatments can be effective, some natural remedies can also help manage acne. Here are some remedies to try:
a. Aloe Vera
Aloe vera gel has anti-inflammatory properties and can help soothe irritated skin and reduce acne.
b. Green Tea
The antioxidants in green tea help reduce oil production. Drinking or applying green tea to your skin can improve acne.
c. Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties that can reduce bacteria and inflammation around hair follicles.
d. Honey
Honey has antimicrobial properties and can be used as a face mask to hydrate and calm the skin.
9. When to See a Dermatologist
While many cases of acne can be treated at home with over-the-counter products, you should see a dermatologist if:
- Your acne is severe or painful.
- You are developing scars from past breakouts.
- Over-the-counter treatments haven’t worked after several weeks.
Dermatologists can provide advanced acne treatments and personalized advice. To find the best acne treatment near me, consult a specialist and begin your journey to clearer skin.
Final Thoughts
Managing acne-prone skin involves understanding the causes of acne, following a consistent skincare routine, and using the right acne treatments. Whether you prefer natural remedies, topical treatments, or professional help, it’s essential to stay patient and persistent, as clear skin takes time.
If you're struggling with acne-prone skin, seek advice from a qualified dermatologist. For more information or to schedule a consultation, visit MD.co.uk to start your journey to clearer, healthier skin.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.