Carbon Fiber Injection Molding: Advanced Techniques and Applications

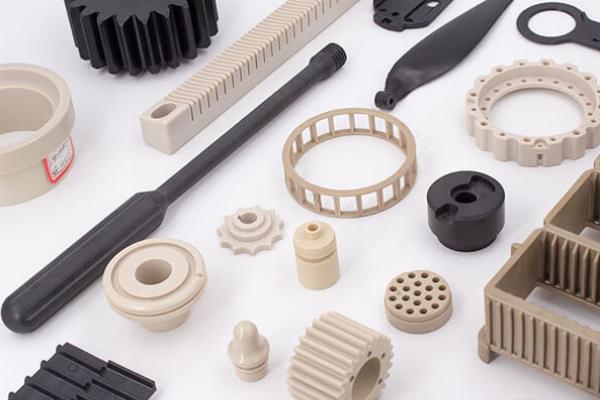
Carbon fiber injection molding is an advanced manufacturing process that combines the lightweight, high-strength properties of carbon fiber with the versatility and efficiency of injection molding. This method is increasingly popular in industries where performance, weight reduction, and production efficiency are critical. This article explores the intricacies of carbon fiber injection molding, its benefits, challenges, and its applications across various industries.
1. Understanding Carbon Fiber Injection Molding
What is Carbon Fiber?
Carbon fiber is a material composed of thin strands of carbon atoms bonded together in a crystalline structure. Each strand of carbon fiber is incredibly strong for its size, and when woven together, these fibers form a fabric that can be embedded in a resin matrix to create a composite material. The resulting composite is known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, stiffness, and resistance to environmental degradation.
What is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a manufacturing process in which molten material, typically plastic, is injected into a mold cavity. The material cools and solidifies within the mold, forming a part that can be complex in geometry. This process is widely used in mass production because of its ability to produce high volumes of parts with consistent quality.
Combining Carbon Fiber with Injection Molding:
Carbon fiber injection molding involves the incorporation of carbon fibers into a thermoplastic or thermosetting resin, which is then injected into a mold using standard injection molding techniques. The carbon fibers reinforce the plastic matrix, enhancing its mechanical properties while maintaining the advantages of the injection molding process, such as high production rates and design flexibility.
2. Process Overview
Material Preparation:
The first step in carbon fiber injection molding is preparing the material. This involves selecting a suitable resin, typically a thermoplastic like nylon, polycarbonate, or PEEK (polyether ether ketone), and mixing it with carbon fibers. The fibers can be short or long, depending on the desired properties of the final product. Short fibers are easier to process and more suitable for complex geometries, while long fibers provide superior mechanical strength.
Injection Molding Process:
Melting and Mixing: The carbon fiber-reinforced polymer (CFRP) pellets are fed into the injection molding machine, where they are heated to a molten state. The carbon fibers are evenly distributed throughout the resin during this phase.
Injection: The molten CFRP mixture is injected into a pre-designed mold cavity under high pressure. The mold is designed to the precise specifications of the final product, allowing for complex shapes and detailed features.
Cooling and Solidification: Once the mold is filled, the material is allowed to cool and solidify. The mold is then opened, and the part is ejected.
Post-Processing: Depending on the application, post-processing steps such as trimming, machining, or surface finishing may be required to achieve the desired final product.
3. Advantages of Carbon Fiber Injection Molding
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio:
One of the primary advantages of carbon fiber injection molding is the ability to produce parts with a high strength-to-weight ratio. Carbon fiber composites are significantly lighter than metals like steel or aluminum while offering comparable or superior strength and stiffness. This makes them ideal for applications where weight savings are crucial, such as in aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods.
Design Flexibility:
Injection molding allows for complex geometries and detailed features that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. This flexibility in design enables the creation of intricate parts that are both lightweight and strong, without the need for additional assembly or joining processes.
High Production Efficiency:
Injection molding is a highly efficient process, capable of producing large quantities of parts with consistent quality in a relatively short period. When combined with carbon fiber reinforcement, manufacturers can achieve high-performance parts at a lower cost per unit compared to traditional composite manufacturing methods like lay-up or filament winding.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance:
Carbon fiber-reinforced composites exhibit excellent resistance to high temperatures and chemical corrosion, making them suitable for demanding environments. This resistance extends the lifespan of components in harsh conditions, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
4. Challenges in Carbon Fiber Injection Molding
Fiber Orientation and Distribution:
One of the main challenges in carbon fiber injection molding is ensuring uniform fiber orientation and distribution within the part. During the injection process, fibers can become aligned in the flow direction, leading to anisotropy in the mechanical properties. This means that the part may exhibit different strengths in different directions, which can be a design consideration.
Tooling and Mold Design:
The design of molds for carbon fiber injection molding is more complex than for standard plastic injection molding. The molds must account for the higher stiffness and abrasive nature of the carbon fiber material, which can lead to increased wear and tear on the mold surfaces. Additionally, the mold must be designed to accommodate the specific flow characteristics of the carbon fiber-reinforced resin.
Cost Considerations:
While carbon fiber injection molding offers significant benefits, the cost of carbon fiber material is higher than that of standard plastics. This can make the process more expensive, especially for small production runs or low-volume applications. However, the cost is often justified by the performance benefits in critical applications.
5. Applications of Carbon Fiber Injection Molding
Automotive Industry:
Carbon fiber injection molding is increasingly used in the automotive industry to produce lightweight, high-strength components such as structural parts, interior panels, and under-the-hood components. The weight reduction achieved with carbon fiber composites contributes to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions in vehicles.
Aerospace Industry:
In aerospace, where every ounce of weight savings can translate into significant fuel savings, carbon fiber injection molding is used to produce components such as brackets, housings, and other structural parts. The high strength and thermal stability of carbon fiber composites make them ideal for use in aircraft and spacecraft.
Consumer Electronics:
The consumer electronics industry leverages carbon fiber injection molding to produce lightweight, durable, and aesthetically appealing components for smartphones, laptops, and other devices. The combination of strength and lightness helps improve the portability and durability of electronic devices.
Sporting Goods:
Carbon fiber composites are widely used in the sporting goods industry for manufacturing high-performance equipment such as tennis rackets, bicycle frames, and golf clubs. The injection molding process allows for the creation of complex shapes and fine-tuned designs that enhance the performance of athletes.
Medical Devices:
In the medical field, carbon fiber injection molding is used to create lightweight, durable, and radiolucent components for medical devices, such as imaging equipment and prosthetics. The biocompatibility of some carbon fiber composites also makes them suitable for use in implants.
6. Future Trends and Developments
Advanced Materials:
Research and development in the field of advanced materials are leading to the creation of new carbon fiber-reinforced polymers with improved properties. These materials are being designed to offer even better strength, stiffness, and thermal resistance, further expanding the potential applications of carbon fiber injection molding.
Sustainability:
As environmental concerns grow, the development of more sustainable carbon fiber production methods and the recycling of carbon fiber composites are becoming increasingly important. Innovations in these areas will help reduce the environmental impact of carbon fiber manufacturing and broaden its adoption across industries.
Automation and Industry 4.0:
The integration of automation and Industry 4.0 technologies into carbon fiber injection molding processes is expected to enhance production efficiency and quality control. Automated systems can optimize fiber orientation, monitor material properties in real-time, and reduce waste, making the process more cost-effective and sustainable.
Conclusion
Carbon fiber injection molding represents a powerful fusion of material science and advanced manufacturing techniques. It enables the production of lightweight, high-strength components with complex geometries, making it indispensable in industries where performance and weight reduction are paramount. While challenges such as fiber orientation, mold design, and cost must be managed, the advantages of carbon fiber injection molding ensure its continued growth and adoption in automotive, aerospace, consumer electronics, and beyond. As technology advances and sustainability becomes a greater focus, the future of carbon fiber injection molding promises even greater innovations and applications.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.