Comparing PRP and Stem Cell Therapy for Knee Pain: What You Need to Know

Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
Knee pain is a common ailment that affects millions of Americans each year. Whether caused by arthritis, sports injuries, or age-related wear and tear, finding effective treatment options can be life-changing. Two innovative approaches—Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy and Stem Cell Therapy—have gained significant attention as non-surgical alternatives for alleviating knee pain and promoting healing. But how do these treatments compare? Let’s break it down.
✍️ When it comes to prevention, early intervention is key. Read why starting PRP or topical hair treatments early can make a big difference in long-term outcomes.
Understanding PRP Therapy
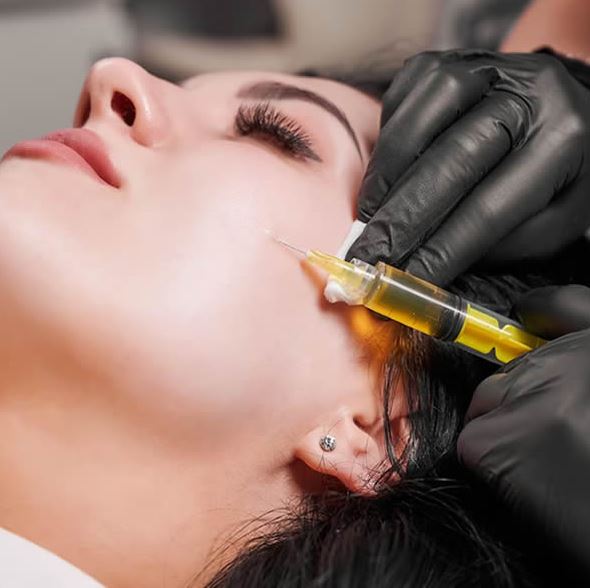
PRP therapy involves using the patient’s own blood to stimulate healing. The process starts with drawing a small amount of blood, which is then spun in a centrifuge to concentrate the platelets. These platelets, rich in growth factors, are injected into the injured or painful area of the knee.
Benefits of PRP Therapy:
- Non-Invasive: PRP therapy does not require surgery and has minimal downtime.
- Natural Healing: Since the treatment uses the patient’s own blood, the risk of adverse reactions is extremely low.
- Pain Management: PRP can reduce inflammation and pain associated with knee injuries and conditions like osteoarthritis.
Best Candidates for PRP Therapy:
- Individuals with mild to moderate knee osteoarthritis.
- Patients with ligament or tendon injuries.
- People looking for a natural alternative to corticosteroid injections.
Limitations of PRP Therapy:
- Results can vary depending on the severity of the condition.
- Multiple sessions may be required for optimal outcomes.
Understanding Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy harnesses the body’s regenerative power to repair damaged tissues. Stem cells, which can develop into various types of cells, are harvested from the patient’s bone marrow or fat tissue. Once prepared, these cells are injected into the knee to encourage tissue repair and reduce inflammation.
Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy:
- Regeneration Potential: Stem cells can regenerate cartilage and repair tissues, offering long-term relief.
- Versatility: It can treat a wide range of knee conditions, from severe arthritis to complex injuries.
- Reduced Inflammation: Stem cells release anti-inflammatory factors, helping alleviate pain and swelling.
Best Candidates for Stem Cell Therapy:
- Patients with moderate to severe knee arthritis.
- Individuals with chronic knee pain that has not responded to other treatments.
- Athletes or active individuals recovering from significant knee injuries.
Limitations of Stem Cell Therapy:
- The procedure is often more expensive than PRP therapy.
- Results can take longer to manifest, as tissue regeneration is a gradual process.
Choosing the Right Treatment for You
Deciding between PRP and stem cell therapy depends on several factors, including:
- Severity of the Condition: PRP is often more effective for mild to moderate issues, while stem cell therapy is ideal for more advanced conditions.
- Budget: PRP therapy tends to be more cost-effective, making it accessible to a broader range of patients.
- Desired Outcome: If your goal is to reduce inflammation and pain quickly, PRP might be the better option. For those seeking long-term tissue regeneration, stem cell therapy is more suitable.
- Medical Advice: Consulting with a specialist is crucial to determine which treatment aligns with your specific needs and health condition.
Are These Treatments Covered by Insurance?
In the United States, PRP and stem cell therapies are typically considered elective procedures, meaning they are not covered by most insurance plans. However, some clinics offer financing options to make these treatments more affordable.
Final Thoughts
Both PRP and stem cell therapy represent promising advancements in the treatment of knee pain, offering patients alternatives to surgery and long-term medication use. While PRP focuses on accelerating the body’s natural healing process, stem cell therapy dives deeper by regenerating damaged tissues.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.