Do Riveted Joints Require Maintenance?
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
Riveted joints have long been a key component in engineering. They are known for their durability and strength. From aircraft to bridges, riveted joints are critical in holding structures together.
While they are designed to be robust, environmental factors and prolonged use can lead to wear, raising whether regular maintenance is necessary.
In this article, we'll examine what riveted joints are, discuss the necessity of their upkeep, and provide you with ten practical tips for maintaining them. Proper care ensures these joints continue to perform their vital functions safely and effectively.
What are Riveted Joints?
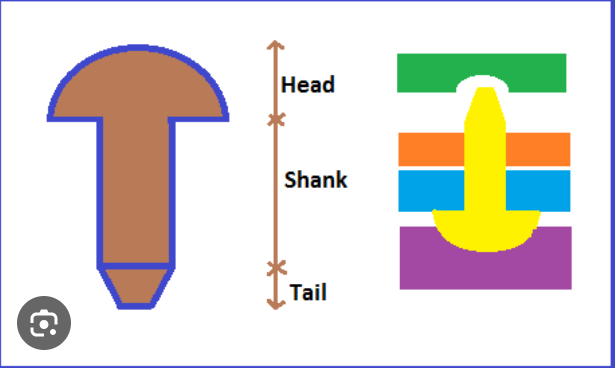
Riveted joints are permanent mechanical fastenings used to hold multiple components together. They consist of rivets, which are cylindrical metal shafts with a pre-formed head. During installation, the rivet is inserted into aligned holes in the pieces to be joined. The tail end is then deformed, creating a second head that secures the components.
The process of forming the second head is called riveting and can be done manually with a hammer or with a riveting gun. This creates strong, permanent joints that are highly resistant to shear forces. Due to their robustness, riveted joints are commonly used in applications that experience dynamic loads, such as aircraft structures, bridges, and heavy machinery.
Rivets are typically made from materials like steel, aluminum, or copper, chosen based on the specific application’s requirements. The strength of riveted joints makes them ideal for situations where welding might be impractical or undesirable. Understanding the construction of riveted joints is essential to appreciating their maintenance needs and ensuring these connections remain reliable under various conditions.
Do Riveted Joints Require Maintenance
Riveted joints, by nature, are designed to offer long-lasting durability without frequent maintenance. However, they are not entirely maintenance-free. The need for upkeep depends on factors such as environmental exposure, mechanical stress, and the materials used in their construction.
Over time, environmental conditions such as moisture, salt, and temperature fluctuations can lead to corrosion or weakening of the rivet or the bonded materials. Mechanical stresses, particularly in dynamic applications, can cause fatigue fractures or loosening. Therefore, regular maintenance is critical in preventing these issues, especially in safety-sensitive industries like aerospace and construction.
Periodic inspections help detect early signs of damage, such as rust, cracks, or movement in the joint, allowing for preventive measures before serious failures occur. Ensuring riveted joints remain in good condition is integral to the longevity and safety of the structures they form. Maintenance practices tailored to the joints’ specific stresses and conditions will help sustain their functionality and security.
Tips for Maintaining Riveted Joints
Conduct Regular Inspections
Regular inspections identify early signs of wear, corrosion, or structural damage in riveted joints. Visual inspections should be performed routinely, particularly in areas exposed to high stress or adverse environmental conditions. For critical applications, employ advanced imaging technologies like ultrasonic or radiographic testing. These methods provide a more in-depth assessment of the joint’s internal condition, allowing for the early detection of potential issues that might not be visible externally. Keeping a consistent schedule and adhering to inspection protocols will help prevent small problems from developing into significant safety concerns.
Protect Against Corrosion
Corrosion is one of the most common threats to the integrity of riveted joints. To combat this, protective coatings such as paints, sealants, or galvanization are applied to shield the rivets and connected materials from corrosive agents such as moisture and chemicals. Using corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel or aluminum for rivets can also increase durability. For structures exposed to particularly harsh environments, consider additional protective measures such as weatherproofing or using rust inhibitors to prolong the operational life of the joints.
Monitor for Fatigue
Fatigue can lead to the degradation of riveted joints, especially those subjected to repeated stress cycles. To monitor for signs of fatigue, regularly check for cracking, deformation, or movement in the joint. Implement non-destructive testing techniques such as dye penetrant inspections or magnetic particle testing to detect early signs of fatigue, thereby preventing unexpected failures. Establishing a fatigue monitoring program helps understand the joint’s stress history, enabling timely interventions and reinforcements where necessary.
Tighten Loose Rivets
Loose rivets can compromise the structural integrity of a joint, making it essential to address them promptly. Utilize appropriate tools, such as hydraulic tightening equipment, to re-secure any loose rivets without causing further damage to the surrounding materials. It’s important to ensure that the applied force is within the acceptable range during re-tightening to prevent over-tightening, which could lead to rivet or material failure. Regularly scheduled maintenance checks will help detect and correct such issues early.
Replace Damaged Rivets
Damaged rivets must be replaced to maintain joint strength due to corrosion, physical impact, or stress fatigue. When replacing a rivet, ensure that the new one matches the original’s size, material, and strength specifications to maintain the joint’s design integrity. Carefully remove the damaged rivet, not enlarging the original holes or damaging the surrounding materials. Properly fitted replacements will restore the joint’s stability and performance.
Use the Right Materials
The selection of materials for rivets and adjoining structures should consider the specific demands and environment of the application. Materials should be chosen for their ability to withstand the anticipated load stresses and environmental conditions. For example, materials with higher corrosion resistance are preferable in marine environments. Balancing material strength with cost and specific environmental resistances will help ensure the longevity and reliability of the riveted joints.
Ensure Proper Installation
Proper installation is pivotal in ensuring the effectiveness and longevity of riveted joints. Rivets should be installed using the correct methods and tools to create secure and reliable connections. This includes aligning holes accurately, using the right rivet size, and applying the correct riveting techniques to form sound joints. Adhering to established installation guidelines minimizes the potential for defects that could require costly rectifications later on.
Conclusion
Riveted joints remain a staple in industries requiring reliable structural connections. While designed to be durable, these joints benefit from regular maintenance, particularly in environments subject to harsh conditions or high mechanical stress. You can significantly extend the lifespan of riveted joints by conducting regular inspections, protecting against corrosion, and addressing any signs of fatigue or damage.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.







