Everything You Need to Know about Dermatitis Eczema: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
Dermatitis Eczema: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments | Healthcare 360 Magazine
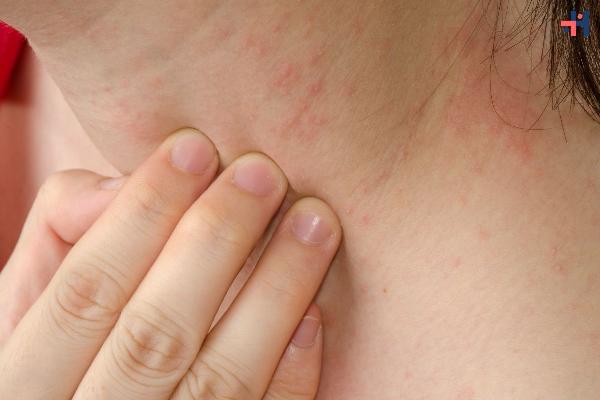
Dermatitis eczema is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by inflammation, redness, and itching, this condition can significantly impact one’s quality of life. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the different types of dermatitis eczema, their causes, symptoms, and the most effective treatments available today.
What is Dermatitis Eczema?
Dermatitis eczema is a general term for a range of skin conditions that cause inflammation and irritation. The term “eczema” is often used interchangeably with dermatitis, though it specifically refers to a type of dermatitis. These conditions share common features, such as itchy, red, and swollen skin, but differ in their triggers and treatments.
Types
Dermatitis Eczema: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments | Healthcare 360 Magazine
Atopic Dermatitis: This is the most common type of eczema, often starting in childhood. It is linked to a genetic predisposition and is commonly associated with other allergic conditions like asthma and hay fever.
Contact Dermatitis: This type occurs when the skin comes into contact with an irritant or allergen. It is classified into two main subtypes:
Irritant Contact Dermatitis: Triggered by direct contact with irritants like soaps, detergents, or acids.
Allergic Contact Dermatitis: Caused by an allergic reaction to substances such as nickel, fragrances, or certain preservatives.
Seborrheic Dermatitis: This type primarily affects oily areas of the body, such as the scalp, face, and upper chest. It is associated with an overgrowth of yeast on the skin and is often seen as dandruff or flaky patches.
Nummular Dermatitis: Characterized by coin-shaped patches of irritated skin, this type often develops after an injury or in dry weather conditions.
Stasis Dermatitis: This occurs on the lower legs and is related to poor circulation, often seen in individuals with chronic venous insufficiency.
Causes
Dermatitis eczema can arise from a variety of factors, including:
Genetics: A family history of eczema or other allergic conditions can increase the risk of developing dermatitis eczema.
Immune System: An overactive immune response can trigger inflammation and cause eczema symptoms.
Environmental Factors: Exposure to allergens, irritants, and pollutants can exacerbate symptoms. Common triggers include harsh soaps, detergents, and extreme weather conditions.
Stress: Emotional stress can worsen eczema symptoms, though it may not be the primary cause.
Skin Barrier Dysfunction: A weakened skin barrier can lead to increased water loss and susceptibility to irritants and allergens.
Symptoms
The symptoms of dermatitis eczema vary depending on the type and severity of the condition but typically include:
Dermatitis Eczema: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments | Healthcare 360 Magazine
Itching: One of the most common symptoms, itching can be intense and lead to scratching, which may further irritate the skin.
Redness and Inflammation: Affected areas often appear red, swollen, and inflamed.
Dry, Scaly Skin: The skin may become dry and scaly, sometimes leading to cracking and bleeding.
Blisters and Oozing: In some cases, blisters may form and ooze clear fluid.
Thickened Skin: Chronic scratching can lead to thickened, leathery skin known as lichenification.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing dermatitis eczema typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and sometimes patch testing. Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms, potential triggers, and family history of eczema or other allergic conditions. In some cases, a skin biopsy or patch test may be performed to rule out other conditions and identify specific allergens.
Treatment Options
Effective treatment of dermatitis eczema aims to reduce inflammation, relieve itching, and restore the skin barrier. Treatment options include:
Topical Medications:
Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory creams or ointments are commonly used to reduce inflammation and itching.
Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors: These medications, such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, can help control inflammation and are often used for sensitive areas like the face.
Moisturizers: Regular use of emollients and moisturizers helps to keep the skin hydrated and restore the skin barrier. Look for products labeled as fragrance-free and suitable for sensitive skin.
Avoidance of Triggers: Identifying and avoiding specific triggers, such as certain fabrics, soaps, or foods, can help prevent flare-ups. Patch testing may be useful for identifying allergens.
Phototherapy: For severe cases, phototherapy (exposure to ultraviolet light) can be effective in reducing inflammation and itching.
Systemic Medications:
Oral Corticosteroids: These are used for short-term management of severe flare-ups but are not recommended for long-term use due to potential side effects.
Oral Immunosuppressants: Medications such as cyclosporine or methotrexate may be prescribed for severe cases that do not respond to topical treatments.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies:
Bathing: Use lukewarm water and mild, fragrance-free soap. Avoid hot water, which can dry out the skin.
Humidifiers: Adding moisture to the air can help prevent dry skin, especially in winter months.
Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, or counseling can help manage stress and potentially reduce eczema flare-ups.
Living with Dermatitis
Managing dermatitis eczema requires ongoing care and attention. Here are some tips for living with the condition:
Dermatitis Eczema: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments | Healthcare 360 Magazine
Develop a Skincare Routine: Establish a consistent routine that includes moisturizing regularly and using prescribed medications as directed.
Wear Soft, Breathable Fabrics: Opt for clothing made of natural fibers, such as cotton, to reduce irritation.
Keep Your Environment Clean: Regularly wash bedding, towels, and clothing to minimize exposure to potential allergens and irritants.
Stay Informed: Keep up with the latest research and treatments for eczema to ensure you’re using the most effective strategies for managing your condition.
Seek Support: Joining support groups or seeking professional counseling can help you cope with the emotional impact of living with eczema.
Conclusion
Dermatitis eczema is a multifaceted condition that can significantly impact your daily life. By understanding the different types, causes, and symptoms of eczema, you can better manage your condition and improve your quality of life. Effective treatment involves a combination of medical interventions, lifestyle adjustments, and ongoing care. If you suspect you have dermatitis eczema, consult with a healthcare provider for a personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs.
With the right approach, you can control your symptoms and enjoy a more comfortable, eczema-free life.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.


