From Production Process to Industrial Applications: A Deep Dive into Epoxy Resin (2023–2034)
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
Epoxy Resin, often perceived as a complex scientific compound, is surprisingly versatile, finding applications. This blog serves as your comprehensive guide to all things epoxies! In this blog we'll embark on a journey into the captivating realm of epoxy resin, dwelling into:
The Science: Unveiling the chemistry behind epoxy, we'll elucidate its remarkable properties as a potent adhesive, sealant, and casting material.
Industrial Applications: Exploring the extensive industrial uses of epoxy, we'll examine its role in constructing robust composite materials and safeguarding electrical components.
Manufacturing Process: Get super detailed information about the process that leads into the formation of this resin and gain knowledge about the feedstock used for its production.
Introduction
Epoxy Resin is a versatile synthetic polymer valued for its exceptional adhesive, mechanical, and electrical properties. Its widespread applications include serving as adhesives in construction, woodworking, and manufacturing industries due to its robust bonding capabilities and resistance to environmental factors like moisture, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations. Moreover, epoxy resin finds extensive use in coatings and sealants, providing corrosion and abrasion resistance in diverse sectors such as flooring, automotive, marine, and aerospace. It is also a crucial component in composite materials, contributing to the production of strong yet lightweight structures in aerospace, automotive, sports equipment, and construction. Additionally, its low viscosity makes it suitable for molding and casting various objects, prototypes, and architectural elements, allowing for precise reproduction of fine details in sculptures and models.
These versatile properties make epoxy resin indispensable across industries, driving innovation and enabling the creation of durable, high-performance products. Various types of epoxy resins are utilized across different sectors. These resins are Bisphenol A Based Resin, Bisphenol F Based Resin, Epoxy Phenol Novolac Based Resin, Cycloaliphatic Epoxy Based Resin, and Others. Bisphenol A Based Resin finds extensive use across diverse applications, spanning coatings, civil engineering, adhesives, electrical insulation materials, and reactive intermediates. The global Epoxy Resin market is likely to flourish at a moderate CAGR of 4.11% by the year 2034.
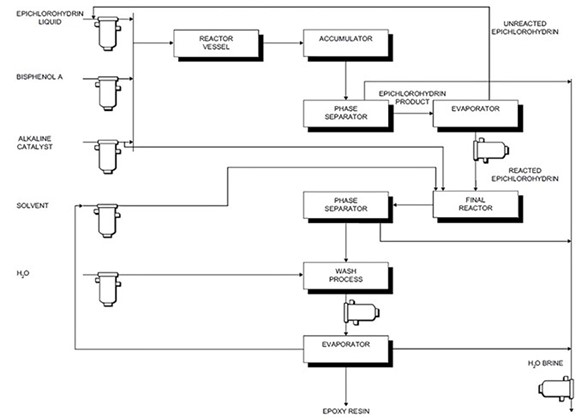
Manufacturing Process
Epoxy resins exhibit high viscosity levels and are typically molded. Catalysts or curing agents, such as accelerators or hardeners, can facilitate curing either through catalytic action or direct reaction with the resin. Epoxy resins are typically created through the reaction of compounds containing at least two active hydrogen atoms, including polyphenolic compounds, diamines, amino phenols, heterocyclic imides and amides, and aliphatic diols, with epichlorohydrin. The oxirane group within an epoxy monomer reacts with various curing agents such as aliphatic and aromatic amines, phenols, polyamides, amidoamines, anhydrides, thiols, and acids. These reactions lead to the formation of rigid thermosetting products through the combination with other suitable ring-opening compounds.
Epoxy resins are commonly synthesized through a reaction between epichlorohydrin (ECH) and Bisphenol-A (BPA), although alternative raw materials like Aliphatic Glycols, Phenol, And O-Cresol Novolacs. Initially, ECH and BPA are introduced into a reactor, followed by the addition of a caustic soda solution as the mixture reaches its boiling point. After unreacted ECH evaporates, the resulting phases are separated using an inert solvent such as Methyl Isobutyl Ketone (MIBK). Subsequently, the resin undergoes water washing, and solvent removal is accomplished via vacuum distillation. Producers then incorporate specific additives tailored to desired properties such as flexibility, viscosity, color, adhesiveness, and accelerated curing, depending on intended applications. These resins can be obtained in liquid or solid forms through similar processes. To transform epoxy resins into durable and rigid materials, curing with a hardener is an essential step. Primary and secondary amines are commonly employed as curing agents.
Applications of Epoxy Resin:
Paints & Coatings
Due to their exceptional bonding properties with metals, epoxy resins and amine curing agents exhibit outstanding anticorrosion characteristics when incorporated into coatings. When utilizing high molecular weight variants, these coatings display excellent secondary workability, rendering them ideal as PCM primers. Additionally, epoxy resins offer a diverse range of viscosities, spanning from solventless to solvent-based types, making them well-suited as ink components where viscosity attributes play a crucial role.
Adhesives
Epoxy resin is widely utilized as an adhesive due to its robust properties, particularly in structural and engineering applications. Its versatility extends across various industries, including vehicle construction, snowboard manufacturing, aircraft assembly, and bicycle production. Beyond structural uses, epoxy adhesives find application in virtually any scenario.
Electronics and Electrical Systems
Epoxy resins are integral to manufacture insulators, motors, transformers, and generators. Renowned for its exceptional insulating properties, epoxy resin provides effective safeguarding against dust, moisture, and short circuits, making it a prominent choice for circuitry production as well.
Repair Epoxy resins effectively blend with a range of materials such as latex, wood, metal, and various synthetic substances. Applying epoxy resin to delicate objects results in the formation of a thin, secure barrier that remains tightly adhered over extended periods, ensuring lasting stability and protection.
Market Outlook:
Epoxy resin, a thermosetting copolymer formed by the polymerization of epoxide and other monomers with hydroxyl groups, comprises a monomeric resin, accelerator, hardener, and plasticizer. Possessing corrosion resistance, thermal stability, mechanical strength, chemical resistance, durability, and adhesion, epoxy resins are utilized in paints, coatings, adhesives, composites, and electronic encapsulation across various sectors. Their applications span building and construction, automotive, industrial, and consumer goods and are likely to foster market growth. The global Epoxy Resin market is anticipated to reach approximately 6.2 million tonnes by 2034.
Epoxy Resin Major Manufacturers
Significant companies in the Global Epoxy Resin market are Olin Coporation, Huntsman Corporation, Nan Ya Plastics Co Ltd, Jiangsu Sanmu Group, Hexion Inc., Kumho P&B Chemicals, Nantong Xincheng Synthetic Material Co Ltd, Zhuhai Hongchang Electronic Material Co Ltd, Jiangsu Yangnong Kumho Chemical Co., Ltd., Kukdo Chemical Co., Ltd., Sinopec Baling Petrochemical Co., Ltd, and Others.
Challenges and Opportunities
The epoxy resin market faces several challenges, including environmental concerns regarding the production and disposal of epoxy resins, particularly due to the presence of harmful chemicals and potential emissions during manufacturing processes. Additionally, fluctuating raw material prices, such as those for bisphenol-A (BPA) and epichlorohydrin, can impact production costs and profit margins for epoxy resin manufacturers. Moreover, increasing regulatory scrutiny and stringent environmental regulations may require epoxy resin producers to invest in sustainable manufacturing practices and develop eco-friendly alternatives, which could pose challenges in terms of research and development costs and market adoption. Furthermore, competition from alternative materials and substitutes, such as bio-based resins and advanced polymers, presents a challenge for the epoxy resin market, necessitating innovation and differentiation to maintain market share and competitiveness.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Epoxy Resin market is poised for continued growth and evolution despite facing various challenges. PVC remains a widely used and versatile material with applications spanning across multiple industries, including construction, automotive, healthcare, and packaging. Epoxy resins have several key properties: high strength, minimal shrinkage, superb adhesion to diverse substrates, effective electrical insulation, resilience against chemicals and solvents, and affordability.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.







