Gingivectomy for Periodontitis: A Clinical Perspective
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
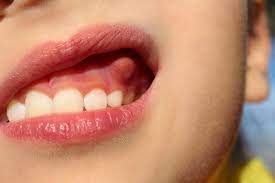
Gingivectomy for periodontitis: a clinical perspective is essential for understanding how surgical intervention plays a crucial role in managing advanced gum disease. Periodontitis is a progressive inflammatory condition caused by bacterial plaque, which leads to the destruction of the supporting structures around the teeth. When non-surgical treatments like scaling and root planing are no longer effective, Gingivectomy (Gum Tissue Removal) in Dubai becomes a valuable next step. This procedure is specifically designed to eliminate deep periodontal pockets and inflamed tissue, thereby halting the disease's progression and preserving the dentition.
Why Periodontitis Requires Surgical Intervention?
In its early stages, periodontitis can often be managed with non-surgical methods. However, when the condition advances and periodontal pockets deepen beyond the reach of daily hygiene, gingivectomy becomes necessary to access and remove infected tissue.
Deep pockets harbor aggressive bacteria that can’t be cleaned by brushing alone
Chronic inflammation leads to gum detachment and bone loss
Non-surgical methods are insufficient for pockets over 5mm deep
Gingivectomy surgically removes the diseased tissue to restore health
By reducing pocket depth and removing inflamed tissue, the gingivectomy procedure helps reestablish healthy gum contours and prevent further tissue damage.
The Clinical Indications for Gingivectomy:
A gingivectomy is not performed on all periodontitis cases—it’s reserved for specific clinical presentations where the benefits outweigh the risks. Dentists and periodontists evaluate the patient’s oral and systemic health before recommending surgery.
Persistent bleeding gums despite non-surgical care
Periodontal pockets not responding to root planing
Gingival overgrowth caused by medications or genetics
Cosmetic concerns due to irregular or enlarged gum margins
Clinicians also consider patient compliance, immune response, and the extent of bone loss before determining the appropriateness of gingivectomy for periodontitis management.
The Surgical Process and Techniques:
The gingivectomy procedure for periodontitis typically involves numbing the area, removing the infected gum tissue, and reshaping the remaining tissue to eliminate pockets. Precision and control are critical to the procedure’s success.
Local anesthesia ensures patient comfort during the procedure
A scalpel, laser, or electrosurgical tool is used to excise soft tissue
The gum is reshaped to create a new, shallower margin
The area is disinfected and sometimes dressed for healing
Lasers are increasingly used due to their ability to cauterize and reduce bleeding, enhancing patient recovery. The entire process can be completed in a single appointment, depending on the extent of disease.
Post-Operative Care and Healing in Periodontitis Cases:
Healing after a gingivectomy in periodontitis patients may take slightly longer than in cosmetic cases due to the inflammatory nature of the disease. However, with proper post-operative care, recovery is usually smooth and predictable.
Avoid spicy, hard, or hot foods for several days
Use antimicrobial mouth rinses as prescribed
Maintain gentle brushing and flossing habits
Attend follow-up visits to monitor tissue response
Avoid tobacco and alcohol to promote healing
Gum tissue typically heals within 1–2 weeks, but tissue stabilization and final contouring may continue for up to a month. Adherence to aftercare protocols is essential to long-term success.
Clinical Outcomes and Long-Term Benefits:
Clinicians recognize gingivectomy as a reliable treatment option for managing moderate to severe periodontitis, especially in localized cases. The outcomes are often positive when paired with strict maintenance and hygiene routines.
Significant reduction in pocket depth and bleeding on probing
Easier access for oral hygiene and professional cleaning
Decreased bacterial load and risk of reinfection
Improved patient motivation due to aesthetic and functional results
Gingivectomy for periodontitis: a clinical perspective reveals that when used appropriately, the procedure provides both therapeutic and preventive benefits. It empowers patients to regain control over their oral health while giving clinicians a valuable tool in managing chronic gum disease.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.