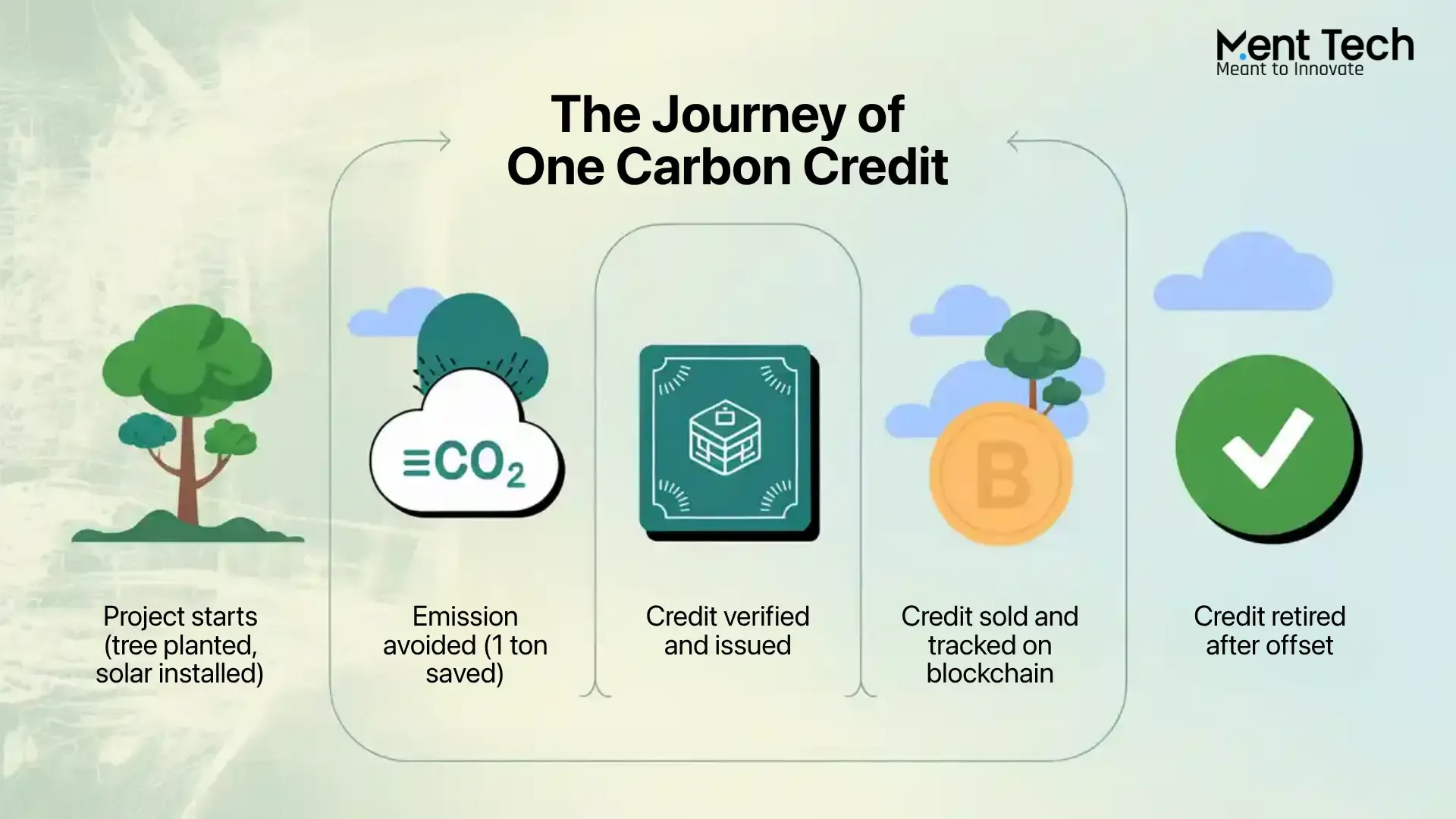
How Blockchain Can Bridge the Gap Between Consumers and Farmers

Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
Agriculture is the pillar of food security, economic stability, and contemporary society. And yet, despite its imperative role in society, consumer-farmer relations have not been going in the right direction for the last four decades. As a result of this gap typically, issues arise like mistrust, price manipulation, exploitation, and wastage in the food chain. While blockchain technology is moving at a hectic pace, agriculture too is in line for a revolution. Blockchain agriculture has been a likely game-changer that can be used as a middleman between producers and consumers to provide transparency, cost savings, and build trust in the food supply chain. Understanding Blockchain Technology
✍️ Curious about central bank digital currencies? Explore our resource on blockchain CBDCs to see how governments are adopting blockchain for financial innovation.
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that keeps data on numerous computers in a manner that makes it transparent, secure, and unalterable. Blockchain is decentralized, and no individual controls data, thus tamper-proof and forgery-proof. All transaction or data kept in a blockchain is time-stamped and appended to the previous one, thus making a chain of entries irreversible.
Although blockchain is mostly related to digital currencies such as Bitcoin, blockchain's uses are wider than digital currencies. Blockchain can have uses in agriculture for monitoring and verifying the movement of produce, opening up the food supply chain, and providing a secure and efficient platform for transactions.
The Current Challenges in the Agricultural Supply Chain
Farm-to-table food chain is complicated and usually opaque. It involves multiple stakeholders such as farmers, distributors, wholesalers, retailers, and consumers. These stakeholders may have competing interests, and information could be siloed or misrepresented for individual advantages. Consumers, therefore, could be unaware of the origin and production of food they consume and this raises concerns regarding food safety, quality, and sustainability.
Secondly, farmers, particularly small farmers, stand very little opportunity for good prices for their crops. Most of the time, middlemen, who in most cases have the power of control over the sale of the product, exploit the situation by charging high prices. The other variables like inefficiency in the distribution channel, inability to enter the market, and volatility in demand expose the farmer to volatile prices.
For consumers, it means that they truly don't know the environmental footprint, quality, or ethics that go into food that they buy. It links customers and farmers and both of them are losers in this disconnection.
How Blockchain in Agriculture Can Fix These Issues
Blockchain can solve the majority of problems encountered by farmers and consumers by bringing in transparency, avoiding inefficiencies, and enabling direct transactions between the producers and the consumers. Blockchain possesses some of the most important ways of bridging the consumer-farmer gap as elaborated below:
1. Transparency and Traceability
The best advantage of blockchain in agriculture is that it possesses the capability of tracking and authenticating every step of the supply chain.
With blockchain, all the production process, processing, and distribution can be traced and made available to consumers. For example, if consumers buy a product, they can scan with a QR tag or an application built on blockchain to see the complete background history of the product, from the farm where it was cultivated to the retail store where it is on sale. This transparency is able to derisk food safety issues by enabling the consumer to see where any contamination would have taken place in the supply chain. If a fault occurs, as a fault may through contamination and necessitate a recall, blockchain can provide an easier track back of where the fault happened, so it can be easier and more specific to respond.
For manufacturers, traceability can also assist them in demonstrating the quality and sustainability of their crops, which can sustain consumer trust and premium prices for ethically produced products.
2. Cutting Out Middlemen and Ensuring Reasonable Prices
Blockchain also has the ability to make the agri-supply chain more efficient by cutting out unnecessary middlemen like distributors, wholesalers, and brokers who overcharge and create inefficiencies. Farmers are able to directly sell their produce to consumers or retailers using smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps), in which they get a fair price for their crops without being exploited by middlemen.
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts that execute on instructions without human intervention after specific conditions are fulfilled. For agriculture, smart contracts can be employed in order to transfer funds to farmers for the produce once delivered to the buyer and only for produce with predetermined quality levels. Blockchain erases delay and theft as transactions are carried out automatically while reducing the role of humans so as to set up exchange processes quicker and more secure.
For shoppers, eliminating the middlemen equates to reduced expense and easier access to fresh, local fruits and vegetables. They also have a guarantee that their dollars have a clear shot to farmers who grew the produce themselves, resulting in a more balanced food system.
3. Increased Access to Credit for Farmers
Most small-scale farmers struggle to access finance since they have no credit history, adequate collateral, or high interest. Blockchain for agriculture can help by allowing farmers to build an open, unalterable record of how they farm and produce. This information can then be used to prove to investors or lenders that they are creditworthy.
Blockchain can also serve as a back for DeFi platforms providing microloans or crowdfunding facilities to farmers. Since blockchain is open and secure, the platforms can enjoy efficient money utilization and easy payment terms. Farmers, in contrast, get access to funds for funding their projects, raising yields, and living better lives.
4. Increased Sustainability and Ethical Practices
Increased pressure from customers has been present as far as the environmental and ethical condition of the bought products. Blockchain farming will be useful in addressing such issues in that it has a traceable history of product development, harvesting, and processing. The data can include information on the utilization of water, utilization of pesticides, carbon usage, labor standards, among others.
Farmers who adopt ethical and sustainable farming methods can utilize blockchain to demonstrate their environmental and labor integrity. This can make them stand out in a competitive market, attract consumers who care about sustainability, and even sell sustainable products at a premium.
5. Reducing Food Loss
Food loss is a huge global problem, and blockchain can reduce it by optimizing supply chains.
Blockchain may enable real-time monitoring of levels of inventory, demand variability, and shelf life, enabling manufacturers and retailers to better match demand and supply. This can reduce overproduction, avoid stockouts, and enable food to reach consumers in best condition, reducing the quantity of food that ends up unsold or wasted. 6. Building Trust between Consumers and Farmers
Trust is generally a big problem in agriculture because consumers and farmers are not connected with each other.
By using blockchain technology to develop an open and transparent supply chain, the producer and the consumer can both feel more secure that the product they are selling or buying is trustworthy. The customers will get information on where their produce comes from, how it is, and how sustainable, and the farmers will be in a position to show that they are committed to producing quality produce in an ethical and sustainable way. In general, blockchain has the ability to transform the agriculture industry by bridging the gap between the farmers and the consumers. With transparency, eliminating middlemen, offering good prices, and enabling sustainability, blockchain for agriculture can make the food supply more efficient, ethical, and trustworthy. The technology can offer more sustainable and fairer opportunities to consumers and farmers as it continues to develop.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.