How Can Anticoagulation Therapy Help Prevent Stroke and Clots?
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
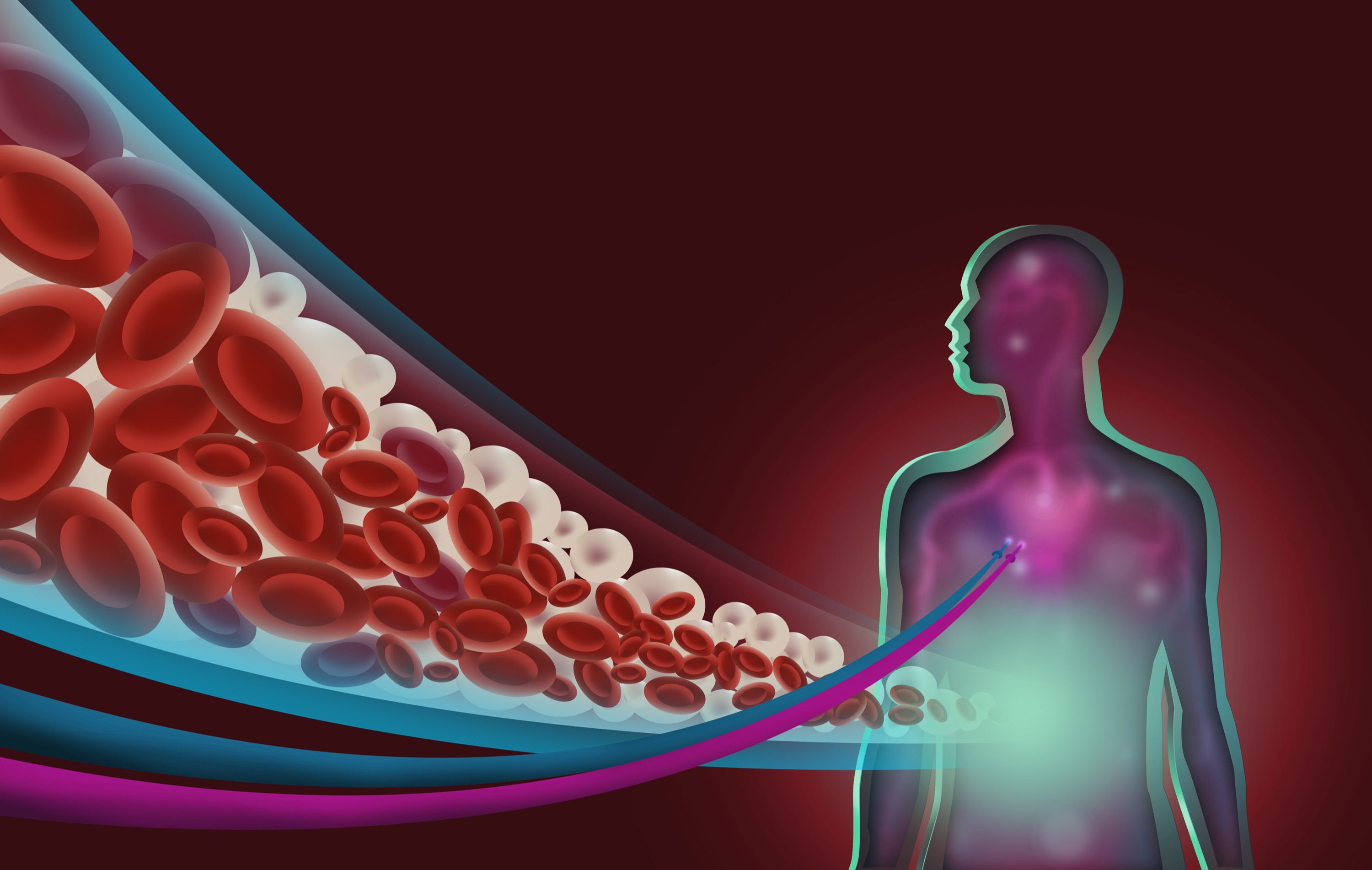
Nothing frightens people more about their health than a stroke or a blood clot. Both conditions can occur unexpectedly and affect how our bodies operate, often permanently impacting our lives. Is there, however, a method to prevent them? Of course, there is, and anticoagulation therapy in Los Angeles CA, commonly referred to as blood-thinning medication, plays a large part in reducing the risk of strokes and clots.
Anticoagulation therapy works by making the blood less likely to form dangerous clots. For individuals at high risk of blood clots, it can be a life-saving treatment. Let’s examine how anticoagulation therapy works, why it’s important, and how it helps protect our health. By the end of this post, you’ll better understand why blood thinners are essential in preventing strokes and clots.
What is Anticoagulation Therapy in Los Angeles CA?
Anticoagulation therapy is using drugs that help prevent blood from clotting too easily. While clotting is a natural process that helps to stop bleeding, some people's blood clots too much, and this may cause severe health issues like strokes and DVT.
Blood clots form when the platelets in your blood stick together and make a plug. This is a beneficial process, most of the time. But it can be dangerous if such clots form in the wrong places, as in the heart, lungs, or brain. Anticoagulants stop this harmful clotting from taking place by blocking the formation of certain chemicals within your blood that cause clotting to occur.
Why do patients need blood thinners?
The condition in which these blood clots can be found is in some people suffering from certain kinds of health problems. These medical conditions may include atrial fibrillation, heart problems, or even a past surgery. In such individuals, these blood clots can occur inside the human body and reach the brain, leading to strokes.
Doctors frequently give the medication to a patient who is susceptible to forming blood clots in anticoagulation therapy in Los Angeles CA. These anticoagulants will stop clots from forming, thus preventing dangerous health conditions from developing. For one, patients suffering from AFib are five times more likely to have a stroke, but blood thinners can reduce that chance a lot.
How Do Anticoagulants Stop Strokes?
Anticoagulants cause decreased blood clotting capability. These will be important in AFib because their abnormal heart rhythm creates potential puddles in the inner aspect of the heart; if permitted, clots may eventually form. Once a clot leaves the heart, it can reach the head to cause a stroke.
Anticoagulants thin the blood, making these lethal clots less likely to form. This can prevent the clot from traveling to the brain and causing a stroke. Studies show that anticoagulation therapy reduces the risk of stroke by about 50 to 70% for people with AFib.
Common Types of Anticoagulant Medications
There are various types of anticoagulants, and all function differently. The two most commonly used are:
Warfarin is one of the oldest and most common blood thinners. Regular blood tests are needed to monitor the blood's ability to clot.
Direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs): These are newer drugs, such as rivaroxaban (Xarelto) and apixaban (Eliquis), which do not require routine blood tests.
Both of these drugs lower the risk of stroke and clots, but they are only prescribed according to individual needs. Doctors consider the use of other medications, lifestyle, and other medical conditions when choosing the appropriate blood thinner.
How Anticoagulants Help Prevent Clots in the Lungs and Legs
While strokes are the most dangerous risk of clots, anticoagulants prevent clots from occurring elsewhere in the body, such as in the lungs or legs.
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a life-threatening condition in which a blood clot travels to the lungs and causes an obstruction of the blood flow. It can be caused by clots in the legs that cause DVT or deep vein thrombosis and then travel to the lungs. Anticoagulants help prevent this.
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a clot forms in the deep veins of the legs. If not treated, it can break loose and move to the lungs or brain, which may lead to serious complications. Anticoagulants prevent clots from growing and moving to dangerous areas.
Anticoagulants reduce the potential occurrence of clots in such sites. Thus, anticoagulation therapy in Los Angeles CA can protect an individual from fatal conditions such as PE and DVT.
What are the Risks of Anticoagulation Therapy?
Although anticoagulants are life-saving drugs, they have a few risks associated with them. The first and foremost risk is bleeding. Because anticoagulants interfere with the blood's ability to clot, they can cause bleeding if an injury occurs. Doctors carefully monitor people on anticoagulation therapy and adjust doses accordingly.
Some of the common side effects are:
Easy bruising
Nosebleeds
Bleeding gums
It is sometimes responsible for extreme bleeding in the brain or gastrointestinal tract. The advantages of not allowing harmful clots to form often outweigh these risks. Doctors collaborate with the patient to ensure the treatment is as safe as possible.
How to Remain Safe During Anticoagulation Therapy
If you are under anticoagulation therapy in Los Angeles CA, there are a couple of things that you need to do. These include the following:
Regular check-ups: Visit your doctor regularly to ensure your medication works as intended.
Avoid risky activities: Since blood thinners make your blood thinner, it is advisable to avoid activities that might lead to injury.
Monitor for signs of bleeding: Look for any unusual bruising, nosebleeds, or blood in your stool or urine.
Maintain a healthy diet: Some foods, especially those high in vitamin K (like leafy greens), can affect how blood thinners work. Talk to your doctor about what foods to avoid.
Being proactive about your health can reduce risks and improve treatment when on blood thinners.
Unique Facts About Anticoagulation Therapy
Here are some interesting little-known facts about anticoagulation therapy:
In the US, over 2 million patients are prescribed anticoagulants for stroke prevention each year
Blood thinners can reduce the risk of stroke by as much as 70% in people affected by atrial fibrillation.
The first anticoagulant, warfarin, was discovered in the 1940s, but newer options have improved convenience and safety.
This therapy is not one size fits all but has been highly effective in the prevention of stroke and clots. If you or your loved one is at risk, then this therapy may mean all the difference between an inferior quality of life and excellent long-term health.
Conclusion
To summarize, anticoagulation therapy is the first form of stroke and blood clot prevention. It helps dilute the blood and lowers the risk of life-threatening conditions such as pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, and stroke. Although these medications can pose a risk of certain adverse effects, this risk is usually outweighed by the benefits, especially when a healthcare professional of anticoagulation therapy in Los Angeles CA, closely monitors the patient. If you are at risk for blood clots, discuss this with your physician to initiate an anticoagulant treatment for you.
Take charge and make both of you aware of the danger that may arise in terms of strokes and blood clots so you may be prepared for a safer future.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.


