How Human Tissue Allografts Are Changing Modern Medicine
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
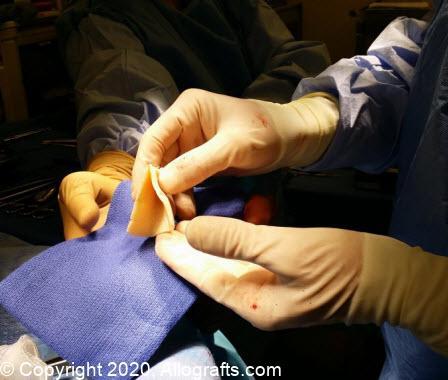
In the evolving world of modern healthcare, few innovations have been as transformative as the development of human tissue allograft. These biologically derived grafts are used across a wide range of clinical disciplines — from wound care and orthopedic surgery to reconstructive procedures. Whether you’re a clinician exploring treatment options or simply curious about how medicine is advancing, understanding how these grafts work is essential.
What Is a Human Tissue Allograft?
A human tissue allograft refers to tissue that is transplanted from one individual (the donor) to another (the recipient). Unlike autografts, which involve using the patient’s own tissue, allografts are sourced from donors — typically through accredited tissue banks. These grafts can include skin, tendons, ligaments, bone, or other soft tissues.
The donated tissue undergoes a stringent screening, sterilization, and processing protocol to ensure it is free from infectious diseases and biologically safe for clinical use. This process helps maintain the integrity of the tissue while minimizing the risk of immune rejection.
Key Applications of Human Tissue Allografts
Human tissue allografts are used in a wide range of medical settings. Some of the most common applications include:
1. Wound Care
Allografts are a valuable tool in treating chronic and non-healing wounds, such as:
- Diabetic foot ulcers
- Venous leg ulcers
- Pressure injuries
- Surgical or traumatic wounds
These grafts provide a scaffold for new tissue growth, helping accelerate healing in cases where the body struggles to regenerate on its own.
2. Burn Treatment
Severe burns that damage large areas of skin require immediate coverage. Allografts can serve as temporary biological dressings that protect the wound, reduce fluid loss, and lower the risk of infection while promoting recovery.
3. Orthopedic and Sports Medicine
In surgeries involving tendon or ligament reconstruction — such as ACL or rotator cuff repairs — human tissue allografts provide a strong, biocompatible alternative to autografts. This allows for shorter surgery times and quicker post-operative recovery.
4. Reconstructive and Plastic Surgery
Allografts play an essential role in reconstructive surgeries, especially when dealing with significant tissue loss or damage from trauma, cancer resections, or congenital deformities.
Benefits of Human Tissue Allografts
Healthcare providers often choose allografts over other grafting options for several compelling reasons:
No Donor Site Morbidity: Because the tissue is sourced from a donor, patients avoid the pain, scarring, and risk of complications that come with harvesting tissue from another part of their own body.
- Time and Cost Efficiency: Reducing the need for a second surgical site streamlines the procedure and lowers operative time.
- Natural Healing Support: These grafts integrate with the patient’s tissue and encourage natural regeneration, making them ideal for long-term healing.
- Availability and Versatility: Allografts are available in various sizes and configurations, making them adaptable to a wide range of clinical scenarios.
Ensuring Safety and Quality
Allograft safety is paramount. Tissue banks follow strict guidelines set by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the American Association of Tissue Banks (AATB), and other regulatory bodies. These include:
- Rigorous donor screening (medical history, blood tests, etc.)
- Advanced sterilization techniques (like gamma irradiation or chemical sterilization)
- Controlled storage conditions to maintain graft viability
By choosing reputable suppliers, healthcare providers can ensure the tissue products they use are both safe and effective.
Innovations in Tissue Grafting
Advancements in biotechnology have further enhanced the performance of human tissue allografts. Today, many products are engineered to retain the extracellular matrix (ECM), growth factors, and structural proteins needed for cellular migration and tissue regeneration.
Some allografts are even dehydrated or cryopreserved to extend shelf life without compromising efficacy — giving clinics more flexibility and access to life-saving materials.
Who Can Benefit from Allografts?
Human tissue allografts are not just for hospitals. Clinics, wound care centers, surgical centers, and outpatient practices regularly use them to support patients with:
- Complicated wounds
- Slow or stalled healing
- Surgical reconstruction needs
- Limited ability to tolerate more invasive procedures
For healthcare providers looking to improve healing outcomes and streamline surgical interventions, these grafts are a trusted solution.
If you're in search of clinically proven and well-regulated tissue products, visit our Human Tissue Allograft page to explore options tailored to wound care, surgery, and regenerative medicine.
Final Thoughts
The use of human tissue allografts has reshaped how medicine approaches healing. By leveraging donor tissue, clinicians can offer patients faster recovery, reduced pain, and improved outcomes — without the added risks of additional surgery. As the science behind these grafts continues to evolve, so does their potential to support healing across multiple specialties.
For clinics and providers focused on delivering the highest standard of care, human tissue allografts are more than just a tool — they are a bridge to better recovery and quality of life.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.



