How to Symptoms COVID-19 JN 1 Variant: Treatment and Prevention
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
The COVID-19 pandemic continues to evolve as new variants of the SARS-CoV-2 virus emerge. One such recent variant, known as JN.1, has gained attention due to its high transmissibility and potential to cause illness, even among vaccinated individuals. Understanding the symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures is crucial to protecting oneself and others. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the JN.1 variant of COVID-19, its symptoms, how it is treated, and how it can be prevented.
What is the JN.1 Variant of COVID-19?
The JN.1 variant is a sub-lineage of the Omicron strain, which has been the dominant variant globally for the past few years. Like its predecessors, JN.1 has several mutations that affect the spike protein of the virus, making it easier for it to spread and possibly evade parts of the immune response. Although initial reports suggest that it may not be significantly more deadly than previous strains, its increased transmissibility makes it a serious concern for healthcare systems and vulnerable populations.
Apple Strengthens Digital Safety with Enhanced Parental Controls for Kids and Teens
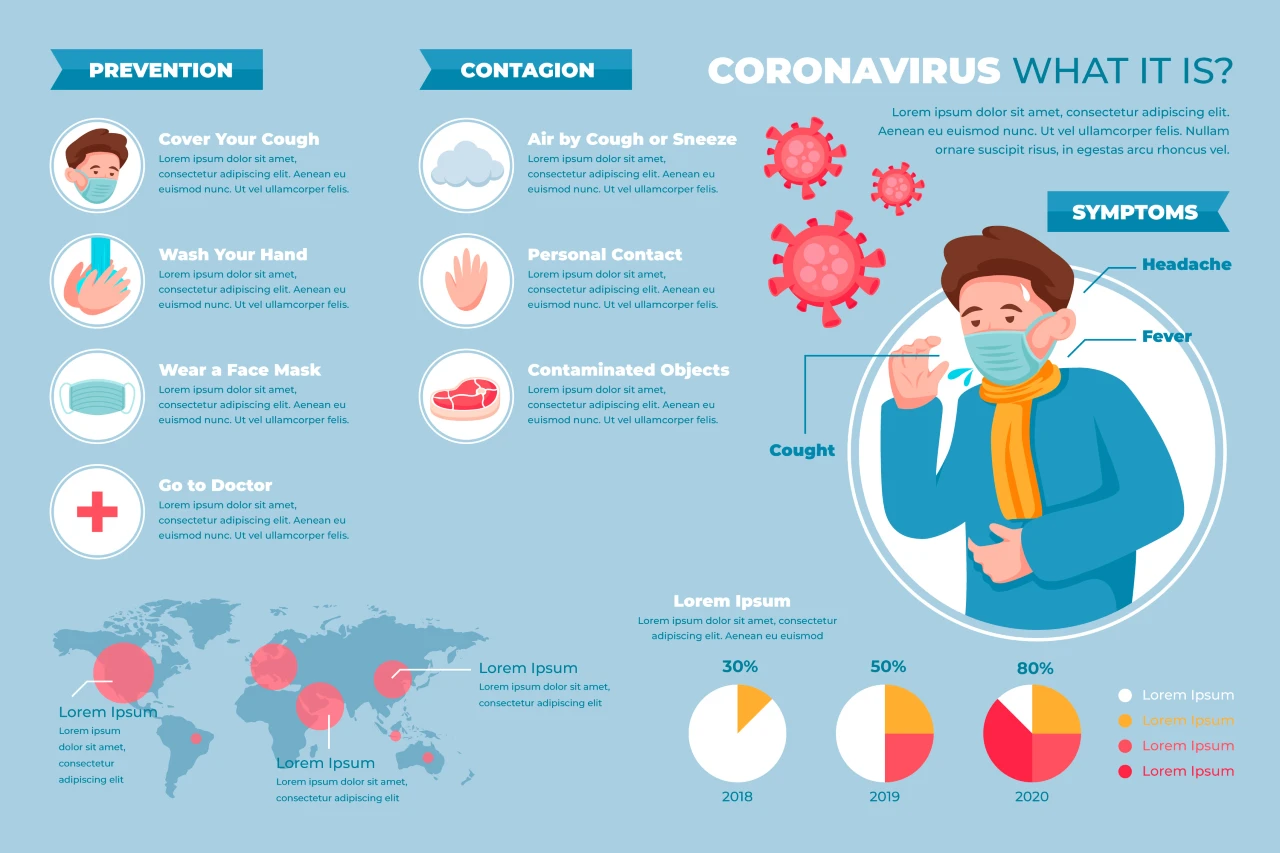
Common Symptoms of the JN.1 Variant
The symptoms of the JN.1 variant closely resemble those of previous Omicron subvariants. However, due to slight genetic differences, some individuals may experience a variation in symptom intensity and duration. Here are the most commonly observed symptoms:
1. Fever and Chills
A sudden onset of fever is often one of the earliest signs of JN.1 infection. This may be accompanied by chills, body aches, and general fatigue.
2. Cough
A dry, persistent cough is a hallmark symptom. Some individuals may also develop a productive cough with mucus.
3. Sore Throat
A sore throat, sometimes severe enough to interfere with swallowing, is commonly reported.
See also What is Diabetes? Symptoms and Causes
4. Fatigue
Exhaustion and an overall lack of energy can last for several days and sometimes persist even after other symptoms have resolved.
5. Nasal Congestion or Runny Nose
These symptoms may mimic seasonal allergies or the common cold, making it difficult to distinguish without testing.
6. Headache
Moderate to severe headaches have been commonly reported with this variant.
7. Loss of Taste or Smell
While less common than in earlier variants, some people still experience a temporary loss of taste or smell.
Amazon CEO Foresees Workforce Reduction as AI Revolutionizes Operations
8. Shortness of Breath
This symptom is more likely in older adults or those with underlying health conditions. It may indicate the infection has reached the lungs.
9. Gastrointestinal Issues
Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea are sometimes reported, especially in younger patients.
Who is at Risk?
While anyone can become infected with the JN.1 variant, some groups are more vulnerable to severe illness:
Older adults (65+ years)
Individuals with weakened immune systems
People with chronic health conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, or lung disease
Unvaccinated individuals
Pregnant women
These individuals are advised to take extra precautions to reduce their exposure risk.
Diagnosis and Testing
To confirm infection with the JN.1 variant or any form of COVID-19, a laboratory test is necessary. Testing methods include:
PCR tests: Highly accurate and often used in hospitals or clinics.
Rapid antigen tests: Convenient and fast, but less accurate, especially during early stages of infection.
Home testing kits can be helpful but may not always detect the latest variant due to changes in the viral structure. If symptoms persist and a rapid test is negative, a follow-up PCR test is recommended.
Reddit Launches New Initiative to Convert Positive User Posts into Brand Advertisements
Treatment of COVID-19 JN.1 Variant
There is no specific antiviral treatment exclusively for the JN.1 variant, but the general treatment strategy remains consistent with other COVID-19 infections. Treatment depends on the severity of symptoms and the patient’s overall health.
Mild Cases
For mild to moderate illness, treatment focuses on symptom relief:
Rest and hydration
Over-the-counter medications such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen to reduce fever and aches
Steam inhalation or nasal sprays for congestion
Throat lozenges and warm fluids for sore throat
Moderate to Severe Cases
In more serious cases, especially those involving breathing difficulty or underlying health conditions:
Antiviral medications such as Paxlovid may be prescribed by healthcare professionals.
Oxygen support may be necessary for those with respiratory complications.
Hospitalization may be required for patients with low oxygen saturation, pneumonia, or organ dysfunction.
Post-COVID Care
Some patients may experience lingering symptoms for weeks or months, often referred to as “Long COVID.” Fatigue, brain fog, chest pain, and sleep issues are commonly reported. Post-recovery care includes:
Gradual return to physical activity
Adequate sleep and nutrition
Medical follow-ups for persistent symptoms
Preventive Measures
Prevention remains the most effective way to combat the spread of the JN.1 variant. Here are key strategies to minimize the risk of infection:
1. Vaccination
Staying up to date with COVID-19 vaccinations, including booster shots tailored for new variants, provides protection against severe illness and reduces transmission.
2. Wearing Masks
In crowded or indoor public spaces, wearing a high-quality mask (such as an N95 or KN95) is recommended, especially during outbreak surges.
The Mutant’s Ascent: Nick Walker’s Training Journey for Olympia 2025
3. Hand Hygiene
Frequent handwashing with soap and water or using alcohol-based hand sanitizer helps eliminate the virus from hands and prevents its spread to the mouth or nose.
4. Social Distancing
Maintaining physical distance from others, particularly in poorly ventilated areas, lowers the chance of airborne transmission.
5. Ventilation
Improving indoor air circulation by opening windows or using air purifiers can significantly reduce viral particles in the air.
6. Avoiding Crowds
Limiting exposure in large gatherings, especially during outbreaks, is an effective precaution.
7. Testing and Isolation
Regular testing, especially after exposure or before attending gatherings, helps detect cases early. If symptoms appear or if tested positive, immediate self-isolation is necessary to prevent spreading the virus.
Mental Health During the Pandemic
The continued threat of COVID-19 variants like JN.1 can take a toll on mental health. Anxiety, stress, and feelings of isolation are common. Mental well-being should be taken seriously by:
Staying connected with friends and family through virtual platforms
Engaging in regular physical activity
Practicing mindfulness or relaxation techniques
Seeking professional help if stress or depression persists
Conclusion
The emergence of the JN.1 variant serves as a reminder that the COVID-19 pandemic is not yet over. By understanding its symptoms, following the correct treatment procedures, and implementing preventive measures, individuals can protect themselves and their communities. Staying informed, practicing good hygiene, and prioritizing health can go a long way in controlling the spread of this and future variants. While the virus continues to evolve, so must our awareness and response.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.






