Leakage Current Testing Methods: Complete Guide 2025

Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
Electrical safety cannot be ignored today due to the advances in electronics and linked systems. One important requirement for ensuring safety is having the correct data on and control over leakage currents. This comprehensive guide demystifies leakage current testing methods for 2025, explains their significance, details the main standards, and explores how earth leakage current testing methods protect people and equipment. We’ll also clarify the types of leakage current tests, the role of standards, and the importance of earth bonding in the context of leakage current measurement.
Understanding Leakage Current and Its Risks
A live circuit can send current by mistake to the ground or to touchable conductive objects, a process called leakage current. Insulation sometimes looks complete, but small leaks can happen, resulting in a shock, equipment problems, or fires. Proper handling of leakage current is important for all three: compliance, safety, and dependability in systems used in medical, industrial, and consumer areas.
What Are Leakage Current Testing Methods?
Testing leakage current is a planned practice used to detect and quantify unwanted electric current in electronic devices. These methods ensure that leakage remains within safe limits as defined by international and national standards. Earth leakage current testing methods complete guide 2025 emphasizes that these tests are vital for both new products and ongoing maintenance.
Key goals of leakage current testing include:
- Verifying insulation integrity
- Detecting faults before they become hazards
- Ensuring compliance with safety regulations
- Protecting users and sensitive equipment
Types of Leakage Current Tests
There are several types of leakage current tests, each tailored to specific equipment and risk scenarios. The main types include:
- Earth Leakage Current Test: Measures current flowing from the protective earth to ground, crucial for devices with metal enclosures (Class I equipment).
- Enclosure Leakage Current Test: Assesses current escaping to accessible conductive parts of the device.
- Patient Leakage Current Test: Used in medical equipment to ensure patient safety by measuring the current that could flow through a patient.
- Touch Current Test: Simulates what a person would experience if touching the device, using a human body resistance model.
Each test type is designed to address different risks and is performed under both normal and single-fault conditions.
Leakage Current Test Standards
To ensure consistency and safety, leakage current testing methods must follow recognized standards. Some of the most widely referenced leakage current test standards include:
- IEC 60990: For measuring touch current and protective conductor current.
- For medical electrical equipment, IEC 60601-1 sets strict requirements for leakage current and explains what tests to use.
- For household and similar appliances, IEC 60335 is applied.
- UL and EN Standards: For North American and European compliance, respectively.
These standards define the maximum allowable leakage current, the test circuits to use, and the conditions under which tests must be performed. For example, typical limits for earth leakage current are 0.75mA for handheld Class I devices and 3.5mA for other Class I devices.
Earth Leakage Current Testing Methods: Complete Guide 2025
Earth leakage current testing methods complete guide 2025 highlights best practices and evolving techniques for accurate measurement:
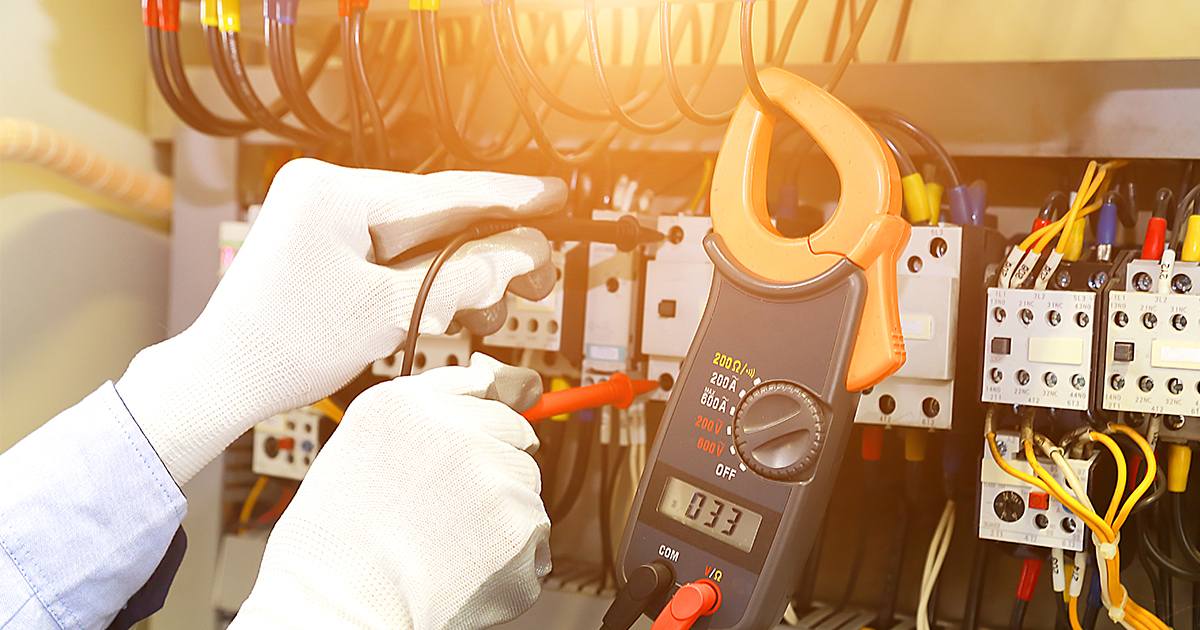
- Clamp Meter Method: The most popular and non-intrusive approach, using a sensitive clamp ammeter to measure current flowing in earth or protective conductors.
- Direct Measurement: Involves connecting a meter in series with the grounding connection to directly measure current flow.
- Differential Method: Measures the imbalance between phase and neutral conductors, indicating leakage to ground.
- Test Under Operating and Fault Conditions: Tests are performed at nominal voltage (+10%) and under simulated single-fault scenarios to ensure comprehensive safety.
Step-by-step process for earth leakage current testing:
- Identify the circuit or equipment to be tested.
- For single-phase circuits, clamp both phase and neutral conductors together. The measured value is the leakage to ground.
- For three-phase circuits, clamp all phase conductors (and neutral if present) together with a similar reading.
- To trace the source of leakage, start at the main panel and progressively move to sub-circuits, identifying where the leakage increases.
- For direct measurement, connect the meter in series with the earth conductor and operate the device at its rated voltage.
Practical Tips for Effective Leakage Current Testing
- Use the Right Instrument: Leakage current clamp meters are more sensitive than standard load clamp meters and can detect currents below 5 mA.
- Simulate Real Conditions: Always test with the device operating at nominal voltage, and include both normal and single-fault scenarios.
- Follow Standards: Adhere strictly to the relevant leakage current test standard for your product type and market.
- Document Results: Record all readings, test conditions, and equipment details for compliance and traceability.
- Repeat Regularly: Periodic testing is essential, especially for mission-critical or medical equipment.
What Is Earth Bonding and Why Is It Important?
What is Earth bonding? Earth bonding is the intentional connection of all exposed metal parts and conductive objects in a building or system to the main earth terminal. Thanks to this practice, if insulation fails, everything made from metal stays at the same electrical potential, making the chance of electric shock very low.
Key benefits of earth bonding:
- Prevents dangerous voltage differences between metal objects
- Minimizes the risk of electric shock in fault conditions
- Ensures compliance with safety codes and standards
- Essential for environments with water or high humidity (bathrooms, pools, etc.)
Earth bonding works hand-in-hand with leakage current testing methods by providing a reliable path for fault currents to flow safely to ground, triggering protective devices and minimizing hazards.
Advanced Leakage Current Testing Methods
Modern leakage current testing methods have evolved to meet the demands of increasingly complex electrical systems:
- Automated Testers: Programmable instruments can run multiple test cycles, record data, and flag failures automatically.
- High-Resolution Clamp Meters: Detect even microamp-level leakage for sensitive applications.
- Networked Monitoring: IoT-enabled sensors allow for continuous, remote monitoring of leakage current in critical installations.
- Hipot (Dielectric Withstand) Testing: Applies high voltage to test insulation integrity and monitor excessive leakage current, especially in manufacturing and QA environments.
Common Sources and Causes of Leakage Current
Knowing where leakage current arises makes it easier to fix and improve the system:
- As insulation ages, becomes damaged from cracks, moisture or chemicals, it functions less effectively and allows electricity to leave the lines.
- With good insulation, AC systems may still show some small amount of leakage current caused by capacitance.
- When Earth bonding is not done well, potential differences and risks of leakage may increase.
- Unintentional Paths: Water pipes, metal ducts, or structural steel inadvertently bonded to the electrical system can provide alternate paths for leakage current.
Interpreting Test Results and Troubleshooting
- Compare to Standards: Always interpret readings in the context of the relevant leakage current test standard. Exceeding limits requires immediate investigation and corrective action.
- Trace the Source: Use the clamp meter method to isolate circuits with high leakage. Disconnect loads sequentially to pinpoint faulty devices or wiring.
- Check Bonding Integrity: Inspect all earth bonding connections for corrosion, looseness, or damage. Reinforce or repair as necessary to maintain safety.
- Repeat After Repairs: Always retest after any corrective work to confirm that leakage current is within permissible limits.
The Role of Leakage Current Testing in Compliance and Maintenance
Routine application of leakage current testing methods is essential for:
- Market access and legal operation require devices to satisfy the IEC, UL, EN, and a range of other standards.
- If insulation or bonding problems can be spotted, the result is less downtime and fewer big expenses.
- Program for Safe Electrical Equipment: Guards users, people who look after equipment, and sensitive equipment from being involved in electric shock or fire incidents.
- Before putting new or fixed equipment into service, it is checked against its design and safety standards by Quality Control.
Best Practices for 2025 and Beyond
With increasing complexity in electrical systems, it is now more important than ever to have strong leakage current testing. Here are the best practices for the coming year:
- Integrate Testing into Routine Maintenance: Make leakage current testing a standard part of preventive maintenance schedules.
- Train Personnel: Ensure technicians are trained in the latest earth leakage current testing methods, complete guide 2025.
- Leverage Technology: Use advanced, networked testing tools for continuous monitoring in critical environments.
- Check new updates to standards and make sure your testing methods are updated often.
- Document all activities and data, and use analysis to project and address more issues.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can you measure leakage current?
You apply a voltage and a leakage tester to measure the current moving from the equipment to the ground through available conductive parts.
Out of the three, which are the leakage current types?
Earth leakage, touch (enclosure) leakage, and patient leakage (for medical devices).
What sets the standards for leakage current testing?
Some common standards are IEC 60990, IEC 60601 (medical), and UL 61010 for electric equipment.
What does the principle of leakage current mean?
It describes how a current accidentally moves from a live part to ground or another conductive part as a result of an imperfect covering.
Conclusion
Making sure electrical devices and systems are safe and meet world standards heavily depends on leakage current testing methods. Organisations should understand the different heavy current tests, obey the newest standards for leakage current tests and apply effective testing methods for earth leakage current to keep people, buildings and tools from hidden electric dangers. When used with sound bonding techniques, these solutions ensure the safety and reliability of our electricity into the future.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.