Maximizing Efficiency: Understanding OEE Manufacturing
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
Manufacturers are continuously looking for ways to raise output, cut waste, and raise the caliber of their operations in the fast-paced industrial environment of today. OEE, or overall equipment effectiveness, is one of the most effective instruments available for reaching these objectives. Lean manufacturing is based on this measure, which also is crucial for companies trying to improve performance. In this post, we will explore what OEE in manufacturing is, why it is significant, how it is computed, and how operational success could be driven by it.
OEE Manufacturing: What is it?
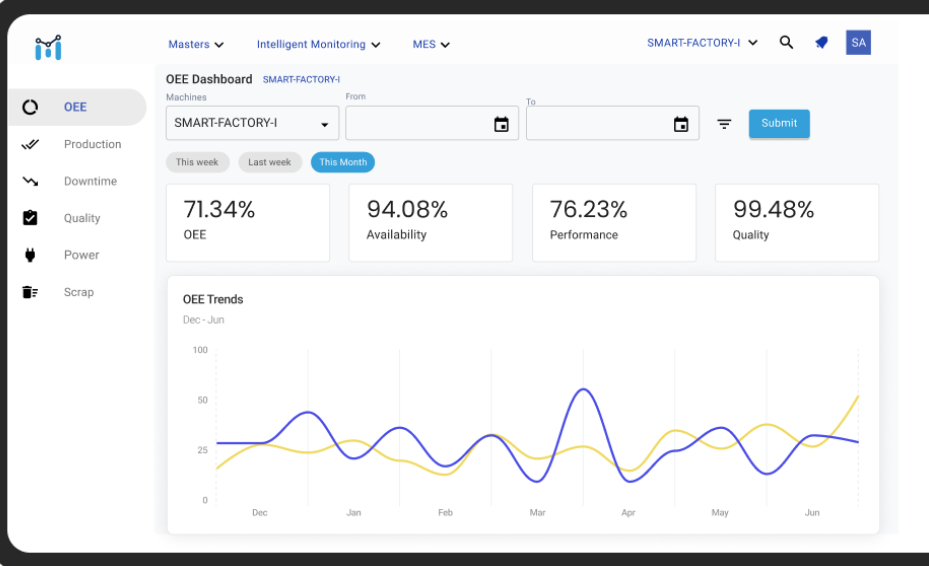
Measuring the efficiency and effectiveness of a manufacturing process, OEE—Overall Equipment Effectiveness—is a key performance indicator (KPI). It specifically shows how effectively a machine or manufacturing line is performing relative to its full capability during planned running hours. Said another way, OEE in manufacturing clarifies how much of your production time is really effective.
OEE seeks to identify and eradicate losses in a manufacturing process. It dissectes efficiency into three main elements:
Availability — Counts both scheduled and unscheduled downtime.
Performance counts minor stoppages and slow cycles.
Quality: Count rework and faulty items.
A 100% OEE indicates that you are manufacturing just good parts, fast as feasible, without downtime.
Why is OEE so important?
Several causes depend on an awareness of and tracking of OEE in production:
Finds Hidden Losses: OEE brings out areas of lost efficiency—be they delayed manufacturing, downtime, or product flaws.
Increases Equipment Use: It enables producers to maximize current tools before making new equipment investments.
Highlights inefficiencies to let teams take focused actions resulting in more throughput.
Foundational in lean manufacturing, Six Sigma, and other continuous improvement systems, OEE is also fundamental in
Benchmarking offers a consistent approach for evaluating performance among lines, machines, even buildings.
OEE Calculation Methodology
Manufacturing OEE computation calls for three steps:
One is availability.
Availability= Operating Time Planned Production Time Availability= Planned Production Time Operating Time
Planned production time less downtime is the operating time.
2. Ideal Performance Cycle Time x Total Pieces
Ideal Cycle Time × Total Pieces = Operating Time Performance
3. Quality Good pieces =
Quality of Total Pieces:
Excellent Compositions
4. OEE Index
OEE = Availability times performance times quality.
OEE=Availability×Performance×Quality
Every element is stated as a percentage; the product of three these numbers determines the final OEE in production.
- Define a good OEE score.
- Here's a broad guide on reading your OEE result:
- 85% and more — World-class production
- 60% to 85% room for development.
- Below 60% - Important losses to deal with
You need not panic if your present OEE falls short of industry averages. It is a strong basis for development.
Typical Losses Affecting OEE Manufacturing
Increasing efficiency requires an awareness of what pulls down your OEE. Usually in manufacturing, these losses fit one of the Six Big Losses:
Equipment failures—unplanned downtime brought on by breakdowns.
Time lost in machine setup or changeovers is setup and adjustment related.
Idling and minor stops cause little delays that slow down output.
Running machines below ideal speed results in a slowed down output.
Process flaws—products falling short of accepted norms for quality.
Lower yield - losses during ramp-up or startup.
Improving OEE in manufacturing and keeping competitive depend on addressing these six issues.
Methods to Boost OEE in Manufacturing
Although it takes time to improve your OEE, with the correct techniques significant increases are possible:
1. Collect data automatically.
Get real-time data with manufacturing execution systems (MES) and smart sensors. Slow and prone to mistakes is manual data entry.
2. Analyze Root Cause Problems
Using techniques like fishbone diagrams or the 5 Whys, probe the underlying cause of downtime or quality problems.
3. Apply preventive maintenance.
With planned maintenance, keep machines in excellent condition to prevent unplanned breakdowns.
4. Standardize Processes
Especially in setups and operator changes, consistency lowers variation and mistakes.
5. Instruct Staff Members
Give operators and technicians the tools to discover and fix inefficiencies on demand.
6. Visual Administration
KPI boards and dashboards make OEE in production clear and support responsibility.
OEE Tools & Software
Modern software solutions abound that enable businesses to monitor, analyze, and raise OEE. These systems might provide dashboards, real-time tracking, alarms, and even predictive analytics. Purchasing such instruments can help you to speed up your path of ongoing development.
Conclusion Notes
OEE in manufacturing is a perspective rather than only a statistic. Understanding and using OEE can help firms to increase profitability, lower latent potential in their operations, and raise product quality. Whether you manage a worldwide manufacturing line or a small business, emphasizing OEE in production will clearly show results.
First figure your present OEE, then find areas of loss and start a constant improvement program. With time, effort, and the correct tools, you will be well on your path to world-class effectiveness.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.







