Fragment-based Drug Discovery Market Outlook 2035: Innovations in Structural Biology Driving Growth
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
The fragment-based drug discovery (FBDD) market has emerged as one of the most dynamic segments within the global biopharmaceutical research ecosystem. Valued at US$ 1.1 billion in 2024, the market is projected to expand at a CAGR of 10.6% between 2025 and 2035, surpassing US$ 3.2 billion by the end of 2035. The growth of this market reflects a broader paradigm shift in drug discovery, where efficiency, precision, and innovation are becoming critical to addressing rising therapeutic challenges.
The Role of FBDD in Modern Drug Discovery
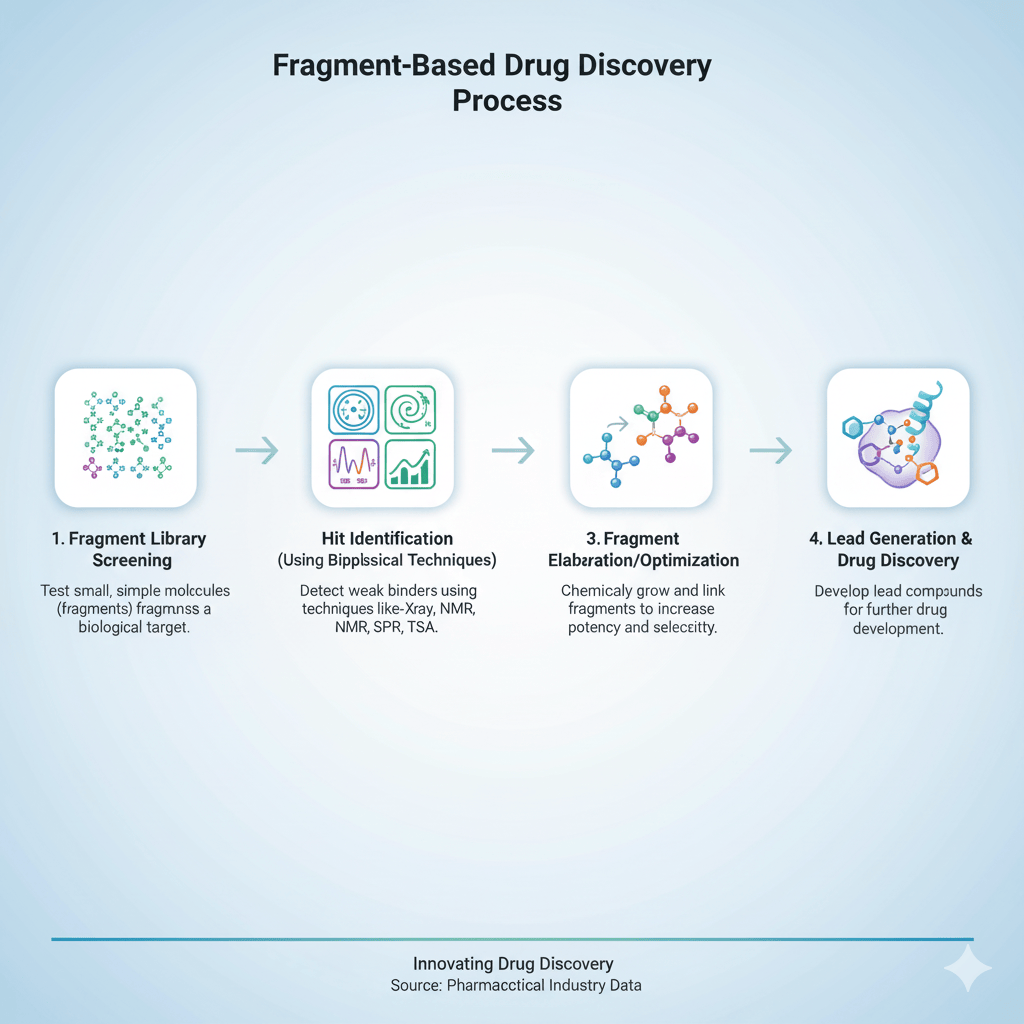
Fragment-based drug discovery is a cutting-edge strategy that identifies and develops low-molecular-weight chemical fragments as starting points for new drugs. Unlike traditional high-throughput screening, which involves testing large molecules from vast libraries, FBDD employs small chemical fragments that can bind to protein targets with high efficiency, even when binding affinity is weak.
Once identified, these fragments can be grown or linked into larger molecules with improved pharmacological properties, offering unique opportunities to design drugs against challenging targets, including protein-protein interactions, allosteric binding pockets, and RNA targets. The method has already contributed to the development of several FDA-approved drugs and multiple clinical-stage candidates, reinforcing its significance as a mainstream discovery platform.
Key Market Drivers
High Efficiency and Versatility of FBDD
FBDD enables the exploration of chemical space more effectively than conventional approaches. With smaller, manageable fragment libraries, researchers can identify high-value starting points at lower cost and with reduced complexity. This accelerates early-stage drug discovery while reducing attrition rates, making the method highly attractive to pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies.
Additionally, the flexibility of fragments allows medicinal chemists to modify, extend, or merge them into more selective and potent drug candidates. Combined with techniques such as NMR spectroscopy, X-Ray crystallography, cryo-electron microscopy, and computational modeling, FBDD provides a robust framework for first-in-class and best-in-class discoveries.
Innovations in Fragment Libraries
The evolution of fragment libraries is a critical driver for the market. While earlier libraries were limited in diversity, modern designs focus on three-dimensional chemical diversity, new scaffolds, and drug-like properties. Specialized libraries, including covalent fragments, RNA-targeted fragments, and natural product-like scaffolds, are opening new opportunities to tackle previously “undruggable” targets.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are also being leveraged to design computationally optimized fragment libraries, improving hit rates and reducing time to clinical leads. These innovations ensure greater reproducibility and reliability in screening outcomes, thus reinforcing FBDD as a preferred discovery strategy.
Market Segmentation Insights
By Techniques
Biophysical techniques dominate the FBDD market due to their sensitivity and accuracy in detecting weak fragment interactions. NMR spectroscopy, surface plasmon resonance (SPR), isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC), and X-ray crystallography remain the backbone of fragment screening, offering detailed binding and structural insights. Emerging tools like native mass spectrometry and microscale thermophoresis (MST) are increasingly being integrated to accelerate triaging and optimization.
By Application
Oncology remains the largest application area, driven by the urgent need for targeted therapies and the ability of FBDD to address complex protein interactions in cancer biology.
CNS disorders and infectious diseases are witnessing rising adoption, as fragment libraries enable discovery of molecules with better blood-brain barrier penetration and novel mechanisms against resistant pathogens.
Expanding applications in cardiovascular diseases, metabolic disorders, autoimmune conditions, and RNA-based drug discovery further broaden the market scope.
Regional Outlook
North America
North America led the global FBDD market in 2024, supported by strong academic institutions, well-capitalized biotech firms, and contract research organizations (CROs) specializing in structural biology. Regulatory frameworks encouraging precision medicine, coupled with significant venture capital and government funding, further enhance regional leadership.
Europe and Asia Pacific
Europe continues to be a hub for structural biology and fragment library development, while Asia Pacific is expected to grow rapidly, fueled by expanding CRO networks, rising R&D investments in China and India, and increasing adoption of advanced screening platforms.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive dynamics in the FBDD market are shifting toward platform-driven strategies rather than individual drug assets. Companies are building integrated studios combining automated biophysical screening, parallel synthesis, and real-time structural analysis to accelerate the discovery cycle.
Key players in the global market include:
Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
Astex Pharmaceuticals
Domainex
Beactica Therapeutics AB
Charles River Laboratories
Evotec International GmbH
WuXi AppTec
Schrödinger, Inc.
ZOBIO BV, among others.
These players are actively pursuing strategic partnerships, IP development, and risk-sharing collaborations to strengthen their pipelines. Investments in cryo-EM, high-field NMR, microfluidics, and AI-enabled fragment design are key differentiators in the competitive landscape.
Recent Developments
In April 2025, Enamine and Pohang Accelerator Laboratory (PAL) signed an MoU to accelerate fragment-to-lead drug discovery, integrating advanced screening with rapid chemical development systems.
The growing adoption of covalent and electrophile-tuned fragments, as well as physics-informed scoring methods such as water thermodynamics and free-energy perturbation, is reshaping the field.
Expanding focus on RNA targets, molecular glues, and degrader strategies reflects FBDD’s growing role in next-generation drug discovery.
Conclusion
The fragment-based drug discovery market is poised for sustained growth, driven by technological advancements, expanding fragment libraries, and increasing adoption across multiple therapeutic areas. As biopharma companies navigate patent expiries, cost pressures, and the need for novel first-in-class drugs, FBDD is emerging as a core engine for innovation.
With its ability to accelerate discovery timelines, reduce attrition, and unlock previously inaccessible targets, FBDD is expected to remain a central strategy for the global pharmaceutical industry through 2035.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.


