Peptides and Inflammatory Response: Advancing Innovative Research
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
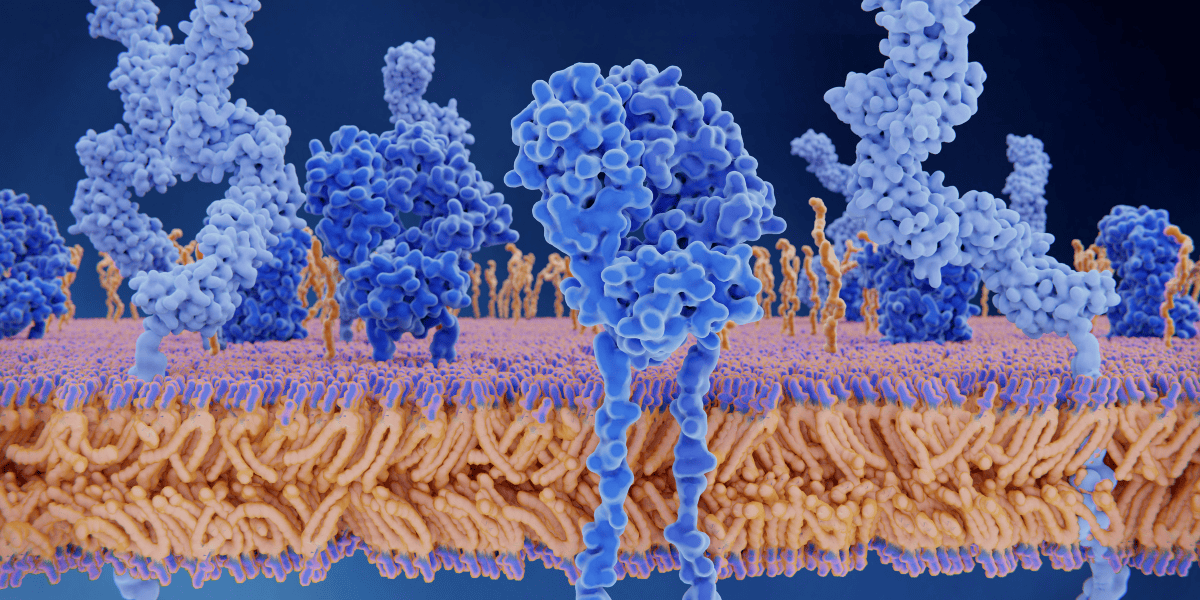
Inflammation is an essential biological process that helps the body defend against injury, pathogens, and toxins. It initiates repair mechanisms vital for restoring homeostasis. However, when inflammation becomes chronic or uncontrolled, it can drive numerous health conditions, including autoimmune disorders, cardiovascular issues, metabolic dysfunction, and neurodegenerative diseases. This is why scientists and clinicians are now prioritizing research into ways to regulate inflammatory pathways effectively and safely.
In recent years, research peptides short chains of amino acids with targeted biological functions have gained attention for their ability to influence inflammatory responses at the cellular level. These peptides can help regulate cytokine activity, modulate immune signaling, and promote tissue recovery without the adverse effects often seen with conventional anti-inflammatory drugs. For individuals and researchers interested in exploring their therapeutic potential, buy peptides has become a growing area of interest, offering access to cutting-edge compounds that support experimental studies in inflammation and regeneration.
Ultimately, peptides are redefining how modern medicine approaches inflammation. By enabling more precise control of biological processes, they open new doors in immunology, neuroscience, and metabolic research. As science continues to uncover their mechanisms and potential benefits, peptides could become central to the next generation of treatments focused on balance, repair, and long-term wellness.
Peptides as Tools in Inflammation Research
Peptides are of particular interest to scientists because they can interact with specific cellular receptors, either mimicking endogenous molecules or antagonizing pathological signals. This specificity allows researchers to study inflammation at multiple levels, from the initiation of immune responses to the resolution phase.
The availability of best peptides online now has facilitated broader experimental studies, enabling laboratories to examine their effects in controlled research environments. With this access, scientists are uncovering how peptides may modulate cytokines, chemokines, transcription factors, and other molecular mediators involved in inflammatory processes.
Mechanisms of Peptide Interaction with Inflammatory Pathways
Research suggests that peptides can influence inflammation through several key mechanisms:
- Cytokine Regulation: Certain peptides appear to modulate pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α). By influencing these signaling molecules, peptides may help restore balance in overactive inflammatory pathways.
- Transcription Factor Modulation: Peptides are believed to interact with transcription factors like NF-κB, which regulates the expression of many pro-inflammatory genes. Dampening NF-κB activity could reduce excessive inflammation and promote resolution.
- Receptor Targeting: Some peptides are theorized to interact with Toll-like receptors (TLRs), critical components of the innate immune system. By modulating TLR activity, peptides may fine-tune immune responses to pathogens while preventing chronic inflammatory damage.
- Oxidative Stress Reduction: Inflammation and oxidative stress are closely linked. Peptides may influence reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and enhance antioxidant defense mechanisms, helping to mitigate tissue damage associated with chronic inflammation.
Peptides in Specialized Research Areas
Immunology
In immunology, research peptides provide a powerful tool for understanding immune regulation. Some peptides are believed to enhance the activity of regulatory T cells (Tregs), which maintain immune tolerance and prevent autoimmune reactions. Modulating Treg activity could offer insights into chronic inflammatory diseases and potential therapeutic strategies.
Additionally, certain peptides may polarize macrophages toward an anti-inflammatory (M2) phenotype. This shift supports tissue repair and resolution of inflammation, providing valuable models for wound healing and regenerative medicine.
Neuroscience
Neuroinflammation is a critical factor in neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Peptides can serve as probes for studying microglial activation the resident immune cells of the central nervous system and their role in neuronal survival and synaptic plasticity.
Research also suggests that some peptides may reduce overactivation of microglia without compromising their protective functions, offering a way to study the delicate balance between neuroprotection and inflammatory damage in the brain.
Metabolic Research
Chronic low-grade inflammation is a key contributor to metabolic disorders, including obesity and type 2 diabetes. Peptides may provide a means to explore the intersection of metabolic stress and inflammatory signaling.
For instance, certain research peptides may target inflammasomes, intracellular protein complexes that trigger inflammatory cascades. By modulating inflammasome activity, peptides help researchers understand how inflammation contributes to insulin resistance and dysregulated glucose metabolism.
Some peptides also interact with adipokines bioactive molecules released by adipose tissue which are involved in both metabolism and inflammation. Investigating these pathways could reveal new insights into how chronic inflammation exacerbates metabolic disease. Interestingly, compounds like Mots C peptide for sale are being studied for their potential to influence both energy balance and inflammatory pathways, highlighting the overlap between metabolic and immune research.
Tissue Repair and Regeneration
Beyond inflammation modulation, peptides play a significant role in tissue repair and regenerative processes. Acute inflammation is necessary for wound healing, but unresolved inflammation can impair tissue regeneration.
Certain peptides may accelerate the transition from inflammatory to reparative phases by stimulating growth factor activity, angiogenesis, and extracellular matrix remodeling. Peptides that mimic endogenous molecules such as transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) can support scar formation and tissue restoration, while others enhance cellular proliferation and differentiation. These regenerative properties have made peptides indispensable tools in modern biological research, and interest continues to grow alongside other compounds commonly explored in laboratories where researchers also buy melanotan and similar peptides to investigate diverse cellular pathways.
Antimicrobial and Immunomodulatory Functions
Some research peptides exhibit dual functionality: regulating inflammation and exhibiting antimicrobial activity. Peptides like defensins and cathelicidins naturally provide both immunomodulatory and pathogen-fighting properties. Modified or synthetic versions allow researchers to explore their ability to support pathogen clearance while minimizing collateral inflammatory damage. This dual action highlights the versatility of peptides as tools bridging immunology, microbiology, and inflammation research.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite their promise, research peptides present challenges that require ongoing investigation. These include:
- Stability: Peptides can degrade quickly in biological environments, necessitating structural modifications for experimental reliability.
- Specificity: Off-target effects may complicate interpretation of research results.
- Delivery: Efficient delivery systems are needed to target specific tissues or cell types.
Advances in computational biology, molecular modeling, and machine learning are helping predict peptide interactions and optimize their design. These tools accelerate discovery, allowing scientists to identify novel peptides that target inflammation with precision.
Additionally, access to specialized compounds such as buy retatrutide peptide has enabled laboratories to conduct advanced metabolic and inflammatory studies, further expanding the understanding of peptide function across diverse biological systems.
Conclusion
Research peptides represent a groundbreaking frontier in the study of inflammation. Their ability to interact with precise molecular targets, regulate immune responses, and influence tissue repair positions them as essential tools for modern scientific exploration.
By leveraging these small but powerful molecules, researchers can gain insights into complex biological processes ranging from immune regulation to metabolic control and neuroprotection. The growing availability of tb 500 peptide ensures that labs worldwide can continue to explore these pathways with rigor and reliability, contributing to the development of innovative solutions for inflammation-related disorders.
The future of peptide research promises transformative discoveries, with applications that span immunology, neuroscience, metabolic health, and regenerative medicine, offering a new lens through which to understand and potentially modulate inflammation at the molecular level.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.







