Polycaprolactone (PCL) - Medical Biodegradable Material
Introduction to Polycaprolactone
PCL is a semi-crystalline polymer with a melting point of 60°C and a Tg of about -60°C. Its repeating structural unit has five non-polar methylene groups -CH2- and a polar ester group -COO-, the C-C bonds and C-O bonds in the molecular chain can rotate freely. This structure makes PCL have good flexibility and processability, such as extrusion, injection molding, wire drawing, film blowing, and so on.
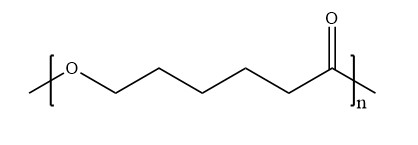
Molecular Formula of PolycaprolactoneFig. 1 Molecular Formula of Polycaprolactone
Synthesis of Polycaprolactone
Synthesis of PolycaprolactoneFig. 2 Synthesis of Polycaprolactone
Polycaprolactone is a high molecular organic polymer formed by ring-opening polymerization of ε-caprolactone (ε-CL) monomer under the catalysis of active hydrogen initiator system, cationic catalyst, anionic catalyst, coordination polymerization catalyst, etc., by controlling the polymerization conditions, different molecular weights can be obtained.
Active Hydrogen Initiation System
Compounds containing active hydrogen such as water, alcohol, and acid can trigger the ring-opening polymerization of ε-CL. The reaction rate is slow and requires a higher temperature (generally 200°C~250°C). The molecular terminals of the polymerization product contain hydroxyl groups.
Cationic Catalytic System
Cationic catalysts that catalyze the ring-opening polymerization of ε-CL include methylfluorosulfonic acid, ethylfluorosulfonic acid, methylnitrobenzenesulfonic acid, methyl methanesulfonate, etc.
Anionic Catalyst
The mechanism of anion-catalyzed lactone ring-opening polymerization is as follows: anion attacks the carbonyl carbon, and then breaks the acyloxy bond and opens the ring to further form a chain growth reaction.
Coordination Complex Catalyst
There are mainly alkyl or alkoxy metal compounds, rare earth compounds, etc. The current research focus is on rare earth compounds.
Biomedical Polycaprolactone
The application of polycaprolactone has low temperature molding, strong plasticity, certain memory function, can be reused, and excellent bonding function, biodegradable, environmentally friendly, non-toxic, good skin affinity, very good permeability for drugs, and good compatibility with biological cells in vivo, cells can grow normally on its substrate and can be degraded into CO2 and H2O. In the field of surgery and medicine, it can be used as cryogenic orthopaedic splint, radiotherapy plate, resin bandage, dental mold, fully degradable plastic surgical suture, controlled release drug carrier, cell, and tissue culture base.
Polycaprolactone (PCL) - Medical Biodegradable Material
Drug-loaded PCL
PCL Microspheres
PCL microspheres are free-flowing spherical particles with a particle size of 0.05~2.00 mm, and drugs can be embedded in them.
PCL Nanoparticles
PCL nanoparticles have unique drug release characteristics, solubility and targeted drug delivery properties, and are generally injected subcutaneously.
PCL Fiber
PCL drug-loaded fiber is generally directed and continuous release of drugs, there is no sudden release effect, which is one of the best ways to improve the solubility of insoluble drugs.
PCL Hydrogel
The cross-linked network of PCL hydrogel has high hydrophilicity and excellent biocompatibility. The porous structure can load drugs and maintain sustained release of drugs during the drug delivery process, allowing local high concentrations to be maintained for a long time. Active pharmaceutical ingredients, hydrogels are generally used externally.
Modification of Polycaprolactone
PCL has high potential application value in the field of biomedicine and is an ideal drug carrier and shape memory material. However, its high crystallinity and low mechanical strength limit its wide application as a degradable plastic. It is important to blend and modify PCL with natural polymers, synthetic polymers, and inorganic particles to improve its mechanical properties and expand its application fields.
CAS NO. Product Name
24980-41-4 Polycaprolactone, mw 150000
24980-41-4 Polycaprolactone, mw 70000
24980-41-4 Polycaprolactone, mw 100000
24980-41-4 Polycaprolactone, mw 55000
31831-53-5 Polycaprolactone-block-polytetrahydrofuran-bloc-polycaprolactone
36890-68-3 Polycaprolactone diol(167cs(55°c))
36890-68-3 Polycaprolactone diol(88cs(55°c))
36890-68-3 Polycaprolactone diol(1,550cs(55°c))
36890-68-3 Polycaprolactone diol(635cs(55°c))
37625-56-2 Polycaprolactone triol(180-230cs(55°c))
37625-56-2 Polycaprolactone triol(200-250cs(55°c))
37625-56-2 Polycaprolactone triol (technical grade)
39280-09-6 Polycaprolactone triol
9051-88-1 Polycaprolactone-b-polytetrahydrofuran-&
68084-39-9 Poly[4,4-methylenebis(phenyl isocyanate)-alt-1,4-butanediol/di(propylene glycol)/polycaprolactone]
97387-29-6 Carboxy-polycaprolactone acrylate
30174-06-2 Poly(ethylene oxide)-block-polycarprola&
54735-63-6 Poly(caprolactone)triol
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.