Predictive Maintenance Market: The Role of Advanced Sensors in Preventative Care
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
Introduction
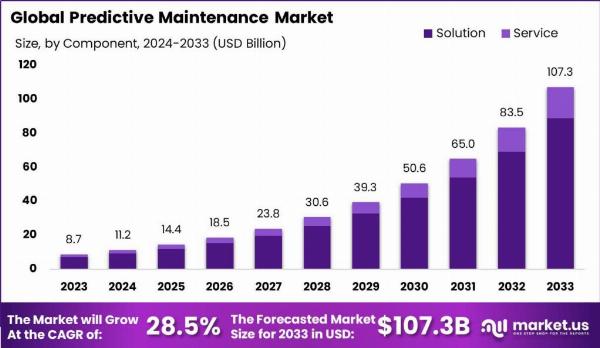
Predictive maintenance is a rapidly growing market, driven by the increasing need to minimize downtime, enhance operational efficiency, and extend equipment lifespan.
Read More - https://market.us/report/predictive-maintenance-market/
By utilizing advanced technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), machine learning, and data analytics, businesses can predict equipment failures before they happen. This proactive approach saves costs and boosts productivity. However, challenges such as high initial costs and the requirement for skilled personnel can pose significant barriers. Nevertheless, the market presents numerous opportunities, especially for new entrants offering innovative and cost-effective solutions.
Emerging Trends
AI and Machine Learning Integration: Companies are increasingly using AI and machine learning to analyze sensor data and predict potential equipment failures more accurately. These technologies enhance the precision of maintenance schedules and reduce unexpected downtime.
IoT Expansion: The widespread adoption of IoT devices provides more data points, enabling more precise predictions and better maintenance scheduling. IoT sensors continuously collect data, which is crucial for effective predictive maintenance.
Cloud Computing: Cloud platforms are used to store and process vast amounts of data, making predictive maintenance solutions more scalable and accessible. The cloud allows for real-time data analysis and remote monitoring, which is essential for predictive maintenance.
Digital Twins: The use of digital twins, virtual replicas of physical assets, allows for real-time monitoring and simulation, improving maintenance strategies. Digital twins help in identifying potential issues before they become critical.
Mobile and Remote Solutions: The development of mobile apps and remote monitoring tools makes it easier for technicians to access data and perform maintenance tasks from anywhere. This trend enhances flexibility and response times in maintenance operations.
Top Use Cases
Manufacturing: Predictive maintenance is crucial for reducing downtime and optimizing production lines. By predicting equipment failures, manufacturers can schedule maintenance during non-productive hours.
Energy Sector: Utilities use predictive maintenance to monitor infrastructure, prevent outages, and ensure efficient energy distribution. This approach helps in maintaining a stable and reliable power supply.
Transportation: Airlines and railway companies use these technologies to maintain vehicles and infrastructure, ensuring safety and reliability. Predictive maintenance in transportation can prevent accidents and delays.
Healthcare: Hospitals use predictive maintenance to manage medical equipment, ensuring functionality and safety for patient care. This is essential for avoiding equipment failures during critical procedures.
Oil and Gas: In this sector, predictive maintenance helps monitor and maintain critical equipment, preventing costly downtime and accidents. This ensures continuous and safe operations in oil and gas facilities.
Major Challenges
High Initial Costs: Implementing predictive maintenance systems can be expensive, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises. The cost of sensors, software, and skilled personnel can be a significant barrier.
Data Security and Privacy: With the increase in data collection, concerns over data breaches and privacy are growing. Ensuring data security is crucial for the adoption of predictive maintenance technologies.
Skill Gap: There is a shortage of skilled professionals who can manage and interpret predictive maintenance systems. This gap needs to be addressed through training and education.
Integration with Legacy Systems: Integrating new predictive maintenance technologies with existing legacy systems can be complex and costly. Compatibility issues can hinder the seamless implementation of predictive maintenance solutions.
Data Quality and Availability: The effectiveness of predictive maintenance heavily depends on the quality and availability of data, which can vary. Inaccurate or insufficient data can lead to incorrect predictions and maintenance schedules.
Market Opportunity
The predictive maintenance market is ripe with opportunities, particularly for new entrants who can offer innovative and cost-effective solutions. The growing emphasis on digital transformation across industries presents a vast market. Companies that can provide scalable, cloud-based solutions or specialize in niche areas such as cybersecurity within predictive maintenance stand to gain a significant market share. The increasing adoption of IoT and AI further expands the scope for new technologies and applications.
Conclusion
Predictive maintenance is transforming how industries manage and maintain their assets. While the market faces challenges such as high costs and a lack of skilled professionals, the benefits of reduced downtime, cost savings, and improved efficiency are undeniable. As technology continues to advance, the potential for growth in this market is substantial. Companies that can navigate the challenges and leverage emerging technologies will find significant opportunities for innovation and market entry.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.