Rare Disease Diagnostic Development to Small Molecule Drug Development
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
Rare diseases, also known as orphan diseases, affect a small percentage of the population, making them particularly challenging to diagnose and treat. However, thanks to advancements in medical research and technology, significant progress has been made in the field of rare disease drug development, from developing accurate diagnostic tools to making effective small-molecule drugs.
Rare diseases R&D
In 2019, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first gene therapy, Zolgensma, for the treatment of SMA. This breakthrough has shown promising results in improving the health and prolonging the lives of infants with this rare genetic disorder. So far, some promising areas of research and technological advancements could further lead to significant progress in rare disease research in the coming years, including but not limited to:
1. Stem cell therapies: Stem cell research is likely to make significant progress in the coming years. By harnessing the potential of stem cells, scientists hope to develop innovative therapies for rare diseases by replacing damaged tissue or regenerating organs.
2. Biomarker discovery: Another breakthrough expected is the identification of biomarkers that can aid in early diagnosis or monitoring of rare diseases. Biomarkers are specific indicators found in blood, tissues, or other biological fluids that can provide information about the presence or progression of a disease. They have the potential to revolutionize healthcare by enabling early intervention and personalized treatment plans for patients with rare diseases.
One of the biggest hurdles in treating rare diseases is accurately diagnosing them. Many of these conditions have nonspecific symptoms that overlap with more common illnesses, leading to misdiagnosis and delayed treatment. Therefore, diagnostic development for rare diseases is needed, aiming to provide fast and reliable strategies for disease identification and detection. To improve the diagnostic efficiency and accuracy of rare diseases, a variety of cutting-edge technologies led by high throughput next-generation sequencing technology have been introduced into the diagnosis of rare diseases, which not only deeply explore the genetic pathogenesis, but also provide new ideas and directions for treatment and research.
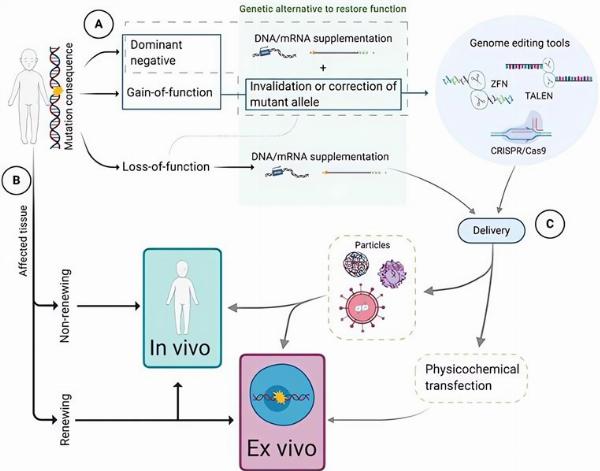
Following with the early detection and diagnosis of rare diseases, the next step is developing effective treatments. Excitingly, recent advancements in gene engineering and drug R&D have led to the development of rare disease gene therapy and small-molecule drugs. Commonly, gene engineering technologies used in gene therapy include CRISPR/Cas9, zinc finger nucleases (ZFNs), transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALEN), and meganucleases. These technologies offer hope to accelerate the research and development of rare disease therapies.
Developing rare disease drugs is a complex and challenging process that often requires collaboration between researchers, pharmaceutical companies, and regulatory agencies. Usually, the drug development process of small molecule drugs includes identification and validation of initial targets, screening of lead compounds, method development and modeling, pharmacokinetic characterization, preclinical safety assessment, selection of preclinical drug candidates, and clinical studies. However, due to the small number of rare disease patients, traditional drug development approaches may not be economically viable.
To address this issue, researchers have turned to innovative strategies, such as repurposing existing drugs, using artificial intelligence to screen potential compounds, and partnering with CRO companies working on rare disease research. By leveraging these approaches, the drug development process for rare diseases can be expedited, bringing more much-needed information for pharmaceutical firms to transform preclinical endeavors into clinical use. Despite the obstacles, the collective efforts of the medical and scientific communities continue to make strides in providing hope and relief for individuals suffering from rare diseases.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.


