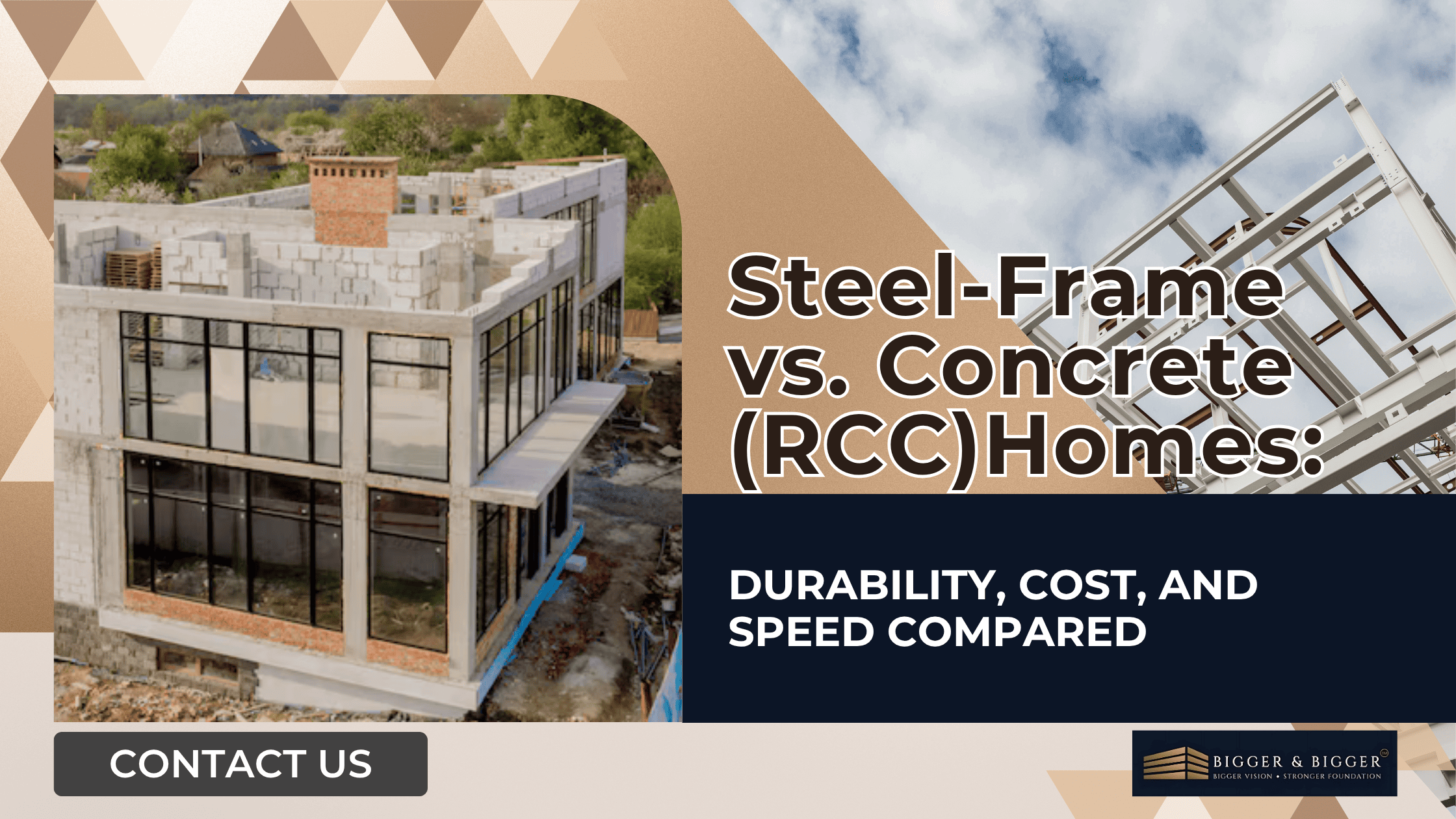
Steel-Frame vs. Concrete (RCC) Homes: Durability, Cost, and Speed Compared
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
When building a home, one of the first decisions you’ll face is choosing the construction method. In India, reinforced cement concrete (RCC) has been the traditional choice for decades. But today, steel-frame construction is gaining attention for its speed, flexibility, and sustainability. If you're considering your options, here’s a side-by-side look at how these two systems compare in key areas like strength, speed, cost, and maintenance.
Understanding the Basics
A steel-frame home uses prefabricated steel beams and columns as its primary structural support. These components are manufactured off-site and then assembled on location. On the other hand, RCC structures are made by pouring concrete over steel reinforcement bars directly at the construction site. RCC offers strong compression strength, while steel excels in tensile strength.
Both systems are capable of producing long-lasting, stable homes. The right choice depends on your priorities and site conditions.
Durability and Strength
Steel frames are known for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio. Despite being lightweight, steel is strong and flexible, which is especially beneficial in areas prone to earthquakes. It can bend under stress without breaking, offering resilience against structural shifts during seismic activity. Steel also resists pests, does not warp or crack, and remains dimensionally stable over time.
RCC structures, however, offer outstanding compressive strength. When built properly, RCC homes can last for over 50 years. Concrete also provides excellent thermal insulation and fire resistance. Since concrete doesn’t burn, it can maintain structural integrity longer during a fire, an important consideration in hot or fire-prone regions.
That said, RCC can be more brittle than steel. It is prone to cracking due to tension or environmental conditions like temperature shifts. These cracks might not compromise the structure immediately but could lead to long-term maintenance issues if not addressed.
Construction Time
One of the key advantages of steel-frame construction is speed. Because steel components are prefabricated in a factory, they arrive at the site ready to install. This minimizes delays and eliminates the need for curing time. The assembly process is straightforward, and a well-coordinated team can erect the structure in a fraction of the time it takes to build with concrete.
RCC construction, in contrast, is labor-intensive and sequential. Each step, setting up formwork, pouring concrete, waiting for curing, takes time. Concrete generally needs about 28 days to achieve full strength, which stretches out the project timeline. Weather conditions can also impact progress, especially during monsoon season.
For homeowners or home builders working with tight timelines, steel offers a clear edge by reducing construction time significantly.
Cost Comparison
While RCC might appear more affordable at first glance due to the lower cost of materials like cement, sand, and aggregate, it’s essential to look beyond just raw material prices. The real cost difference often lies in labor, timeline, and efficiency.
RCC projects tend to involve more labor, longer durations, and potentially higher costs if delays occur. Additionally, costs related to curing, finishing, and scaffolding can add up. If the project experiences errors in formwork or pouring, it can lead to material waste and extra labor.
Steel structures might carry a slightly higher material cost, but they often save money through faster assembly, less labor, and fewer errors. The reduced construction timeline also means lower holding costs, reduced site overhead, and potential savings on loan interest during the build.
In many mid to large-scale projects, the total cost of steel-frame construction ends up being comparable, or even slightly lower than RCC when you factor in all variables.
Maintenance Over Time
Steel structures require minimal upkeep when properly treated. Galvanized or painted steel is resistant to rust, and since the material doesn’t absorb moisture or warp, it remains stable for decades. Occasional inspections and paint touch-ups are usually sufficient.
Concrete, although robust, can develop surface cracks over time due to environmental factors or settling. These cracks, if left unsealed, can allow moisture to reach the embedded steel reinforcement, leading to corrosion. Repairs like sealing or grouting may be needed periodically, especially in older buildings or in humid environments.
In terms of daily upkeep and long-term durability, steel tends to demand less attention, making it a preferred choice for homeowners who want a low-maintenance structure.
Environmental Impact
Sustainability is becoming a priority in modern construction. Steel is one of the most recycled materials in the world, with structural steel often containing 90% or more recycled content. It can be reused without losing strength, and steel structures can be dismantled and relocated, reducing demolition waste.
Concrete, on the other hand, has a heavier environmental footprint. Cement production is a major contributor to carbon emissions globally. While some crushed concrete can be reused as aggregate, most of it ends up in landfills. Additionally, RCC structures are heavier and bulkier, leading to more resource consumption during construction.
Steel-frame homes are often the better option for green building certifications and sustainability goals. They support a more circular construction model and produce less on-site waste.
Use Case Flexibility
Steel’s lightweight nature and modular design make it ideal for open layouts, large spans, or future extensions. It’s a common choice for high-rise buildings, industrial units, and increasingly, modern residential homes that require speed and adaptability.
RCC, by contrast, remains a practical choice for more conventional housing. It performs well in areas where fire protection is critical or where local construction teams are more familiar with traditional building methods.
In rural or semi-urban regions where steel fabrication services may be limited, RCC might still be the more accessible option.
Combining Both for the Best of Both Worlds
Many home construction projects now use a hybrid approach, leveraging RCC for foundations and basements, and steel for the superstructure or roofing. This combination maximizes the strengths of each material while minimizing weaknesses.
Using steel for upper floors can reduce total structural weight, ease load on the foundation, and speed up vertical construction. At the same time, concrete at the base ensures solid ground contact and natural insulation from heat.
Choosing What’s Right for You
The decision between steel and RCC ultimately comes down to your project’s requirements:
- If you're working with tight timelines, want design flexibility, and value low maintenance, steel could be the better choice.
- If you’re in a location with limited access to steel vendors, prefer traditional construction, or are focused on fire resistance, RCC may suit your needs better.
Each method offers advantages, and both can be engineered to meet high safety and performance standards. In many modern builds, combining them delivers the most efficient and cost-effective results.
Final Takeaway
Whether you’re building your first home, working with home constructors, expanding your business premises, or planning a long‑term investment, understanding the core differences between steel frame and RCC construction empowers you to make the right call. Think beyond just materials; consider speed, location, sustainability, and maintenance when making your decision. With a well‑informed approach, you can create a structure that lasts, fits your budget, and meets your long‑term goals.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.