Synthetic Camphor Powder Manufacturing Plant Project Report 2025: Process, Cost and Consideration

Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
Introduction
Synthetic camphor is an essential compound used in a wide variety of industries, including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, food, and as an industrial chemical. It is primarily used for its medicinal properties, such as in cough and cold medicines, as well as in the production of plasticizers, pesticides, and fragrances. The growing demand for synthetic camphor across these sectors has created a profitable market opportunity for setting up a manufacturing plant. This Synthetic Camphor Powder Manufacturing Plant Project Report provides a detailed analysis of the various factors involved in establishing a camphor powder manufacturing plant. From market dynamics and production processes to infrastructure requirements and financial projections, this report covers all aspects of setting up a successful facility.
Market Overview
The global synthetic camphor market has experienced consistent growth due to the increased use of camphor in the pharmaceutical, personal care, and automotive industries. The rising demand for synthetic camphor is driven by its broad applications, including its use as a key ingredient in many over-the-counter medicinal products like balms, ointments, and inhalers, as well as in plasticizers for the plastic industry.
Key Market Drivers:
Increased Pharmaceutical Use: Synthetic camphor is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry for cough remedies, pain relief ointments, and as a rubefacient.
Cosmetic and Personal Care Products: Camphor is a popular ingredient in lotions, creams, deodorants, and hair care products due to its soothing and anti-inflammatory properties.
Rising Demand from the Plastic Industry: Camphor is used in the production of plasticizers that improve the flexibility of plastics.
Growing Need in Industrial Applications: Camphor is used in the manufacturing of explosives, paints, and coatings, where its stabilizing properties are valuable.
Increased Usage in Aromatherapy: Synthetic camphor is used in incense sticks and oils due to its calming properties, increasing its demand in the wellness sector.
Product Overview: Synthetic Camphor Powder
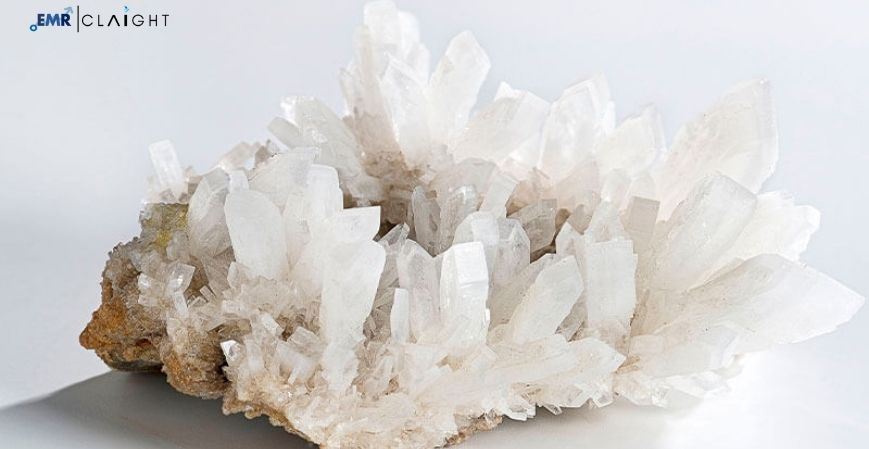
Synthetic camphor is produced through the hydrogenation of turpentine oil or through the dehydrogenation of camphene. The product is then processed into a fine powder that is used in various applications. Synthetic camphor powder has a distinctive aroma and is white, crystalline, and odorless when pure.
The primary uses of synthetic camphor powder include:
Pharmaceuticals: Used as a decongestant, cough suppressant, and analgesic.
Cosmetics: Incorporated into creams, lotions, and hair oils.
Industrial: Used as a plasticizer and stabilizer in the plastic and automotive industries.
Aromatherapy: Incorporated in incense sticks, essential oils, and air fresheners.
Manufacturing Process
The process of manufacturing synthetic camphor powder involves several key steps, from raw material sourcing to final packaging. Here's an overview of the typical production process:
1. Raw Material Procurement
Turpentine Oil: The main raw material for producing camphor powder, derived from pine resin or distillation of turpentine.
Camphene: Obtained from natural camphor or synthesized from turpentine.
2. Hydrogenation of Turpentine Oil
The first stage in camphor production is the hydrogenation of turpentine oil to produce camphene, a precursor for camphor.
Camphene is then processed under specific conditions of temperature and pressure to facilitate the conversion to synthetic camphor.
3. Dehydrogenation
The camphene undergoes dehydrogenation, a process that involves removing hydrogen molecules to produce camphor.
This reaction takes place under controlled conditions, with catalysts used to enhance efficiency.
4. Purification
The crude camphor is purified by sublimation or recrystallization to remove impurities and obtain high-quality camphor powder.
5. Grinding
The purified camphor is ground into a fine powder, which can then be packaged for distribution.
6. Quality Control
Rigorous quality control measures are taken throughout the production process to ensure that the camphor powder meets industry standards for purity, aroma, and effectiveness.
Infrastructure Requirements
Setting up a synthetic camphor manufacturing plant requires specific infrastructure and equipment to ensure efficient and high-quality production. The following infrastructure elements are essential:
1. Location
The plant should be located in an industrial zone that complies with environmental and zoning regulations. Proximity to raw material suppliers, such as turpentine oil, will reduce logistics costs.
The location should also have access to transportation networks for easy distribution of finished products.
2. Plant Layout
Raw Material Storage: An area for storing turpentine oil and other chemicals.
Processing Area: A clean and well-ventilated space for hydrogenation, dehydrogenation, and purification processes.
Grinding and Packaging: A dedicated area for grinding the camphor and packaging the final product into consumer-ready containers.
Quality Control Lab: A laboratory for testing the purity and effectiveness of camphor during production and before shipment.
3. Equipment
Hydrogenation Reactors: For converting turpentine oil into camphene.
Dehydrogenation Units: To process camphene into synthetic camphor.
Sublimation Equipment: To purify the camphor.
Grinding Mills: For producing powdered camphor.
Packaging Machines: For efficient packaging of camphor powder into containers or bags.
Quality Control Instruments: For testing purity, aroma, and other specifications.
4. Utilities
Energy: A reliable source of electricity or fuel to power the equipment.
Water: For cooling, cleaning, and other essential plant operations.
Waste Management: A proper system to handle waste materials, including any by-products from hydrogenation or dehydrogenation processes.
Financial Projections
1. Initial Investment
Setting up a synthetic camphor manufacturing plant involves significant capital investment. The cost will vary based on factors such as location, production scale, and equipment quality.
2. Operating Costs
Major operating costs include:
Raw Material Costs: The purchase of turpentine oil and other chemicals.
Labor Costs: Salaries for production staff, quality control analysts, and plant management.
Utilities: Energy and water consumption for production processes.
Maintenance: Regular maintenance and servicing of equipment.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Sustainability is an important aspect of modern manufacturing practices. A synthetic camphor manufacturing plant should consider adopting the following green practices:
Energy Efficiency: Use of energy-efficient equipment and renewable energy sources to reduce operational carbon footprint.
Waste Recycling: Efficient recycling of waste by-products and packaging materials.
Water Management: Reduction in water usage and reusing water in manufacturing processes where possible.
Media Contact:
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: [email protected]
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.