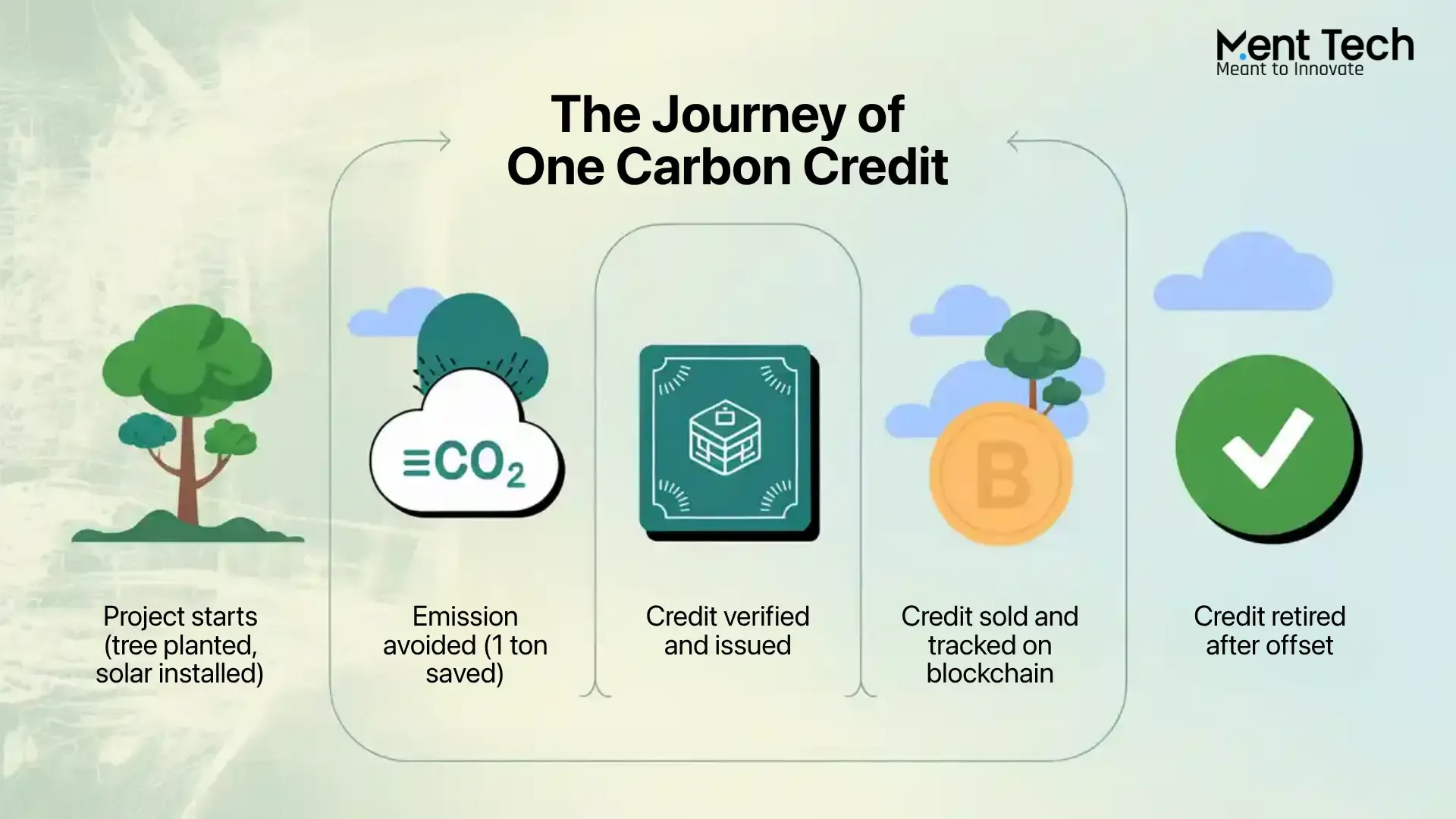
"The Beginner’s Guide to Understanding Blockchain and Its Real-World Applications"

Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
Blockchain: The Revolutionary Technology Transforming Industries
✍️ The rise of DeFi is one of blockchain’s biggest success stories. Read our article on blockchain in decentralized finance to discover how traditional banking is being disrupted.
Blockchain technology has garnered immense attention for its potential to revolutionize various industries, offering transparency, security, and decentralization. From cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin to applications in supply chain management and healthcare, blockchain is creating new opportunities for innovation and efficiency. This article explores the fundamentals of blockchain technology, its benefits, and how it is transforming different sectors.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers in a way that ensures the data cannot be altered or tampered with. It works by storing information in blocks, which are linked together in a chain. Each block contains a set of transactions, and once a block is completed, it is added to the chain. The technology is designed to be secure, transparent, and decentralized.
Key Features of Blockchain
Decentralization: Unlike traditional databases that are controlled by a central authority, blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network, where all participants (also known as nodes) have equal control.
Transparency: Transactions on a blockchain are visible to all participants, ensuring that data is auditable and traceable.
Security: Blockchain uses cryptographic techniques to secure transactions, making it highly resistant to hacking or unauthorized access.
Immutability: Once data is added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring a permanent and unchangeable record of transactions.
How Blockchain Works
Blockchain works by grouping transactions into blocks, which are then added to the existing chain of blocks in a linear, chronological order. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
Transaction Initiation: A transaction is requested, such as sending cryptocurrency from one person to another.
Verification: The network of computers (nodes) validates the transaction using consensus algorithms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake.
Block Creation: Once verified, the transaction is bundled with other transactions into a block.
Block Addition: The new block is added to the existing blockchain, creating a permanent, unchangeable record of the transaction.
Confirmation: The transaction is completed, and all nodes on the network update their copies of the blockchain.
Types of Blockchain
1. Public Blockchain
A public blockchain is open to anyone and is fully decentralized. Bitcoin and Ethereum are examples of public blockchains. They allow anyone to participate in the network, either by verifying transactions (mining) or by creating decentralized applications (dApps).
2. Private Blockchain
Private blockchains are controlled by a single organization, offering more privacy and faster transaction times. They are often used for internal processes within a company. Only selected individuals or institutions have access to the network.
3. Consortium Blockchain
This type of blockchain is managed by a group of organizations rather than a single entity. It is partially decentralized and is commonly used in sectors like finance, where multiple institutions need to share and verify data securely.
4. Hybrid Blockchain
A hybrid blockchain combines elements of both public and private blockchains. It allows some data to be public while keeping other data confidential, offering greater flexibility for enterprises that need both transparency and privacy.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain’s unique features make it applicable across a wide range of industries, beyond just cryptocurrencies.
1. Cryptocurrencies
Blockchain is the underlying technology behind cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and many others. It enables secure, decentralized transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks.
2. Supply Chain Management
Blockchain provides transparency in supply chains by tracking the journey of goods from the point of origin to the consumer. This allows companies to verify the authenticity of products, reduce fraud, and ensure the integrity of goods.
3. Healthcare
In healthcare, blockchain is used to secure patient records, ensuring that data is accurate and cannot be tampered with. It also facilitates easier sharing of medical information across institutions, improving collaboration and patient care.
4. Finance and Banking
Blockchain has the potential to transform the financial sector by enabling faster, cheaper, and more secure transactions. It also eliminates the need for intermediaries in cross-border payments, reducing transaction costs and improving efficiency.
5. Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automatically enforce and execute the terms once predefined conditions are met. These contracts are used in decentralized applications (dApps) and decentralized finance (DeFi).
6. Voting Systems
Blockchain can be used to create secure and transparent voting systems. It ensures that each vote is accurately recorded and cannot be tampered with, reducing the risk of electoral fraud.
7. Real Estate
In the real estate sector, blockchain can streamline the process of buying, selling, and transferring property by providing a transparent and secure ledger of property ownership. This reduces the need for intermediaries like lawyers and agents.
Benefits of Blockchain
Increased Security: Blockchain’s decentralized nature and cryptographic techniques make it highly secure, reducing the risk of fraud and data breaches.
Transparency: All transactions are recorded on a public ledger, making it easy to track and verify information.
Cost Efficiency: Blockchain eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing transaction costs in industries like finance and real estate.
Speed: Blockchain can process transactions much faster than traditional systems, especially in cross-border payments.
Trust: Blockchain creates a tamper-proof, verifiable record of transactions, building trust among participants.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its potential, blockchain technology faces several challenges:
Scalability: As the size of the blockchain grows, the network can become slower, affecting transaction speed and efficiency.
Energy Consumption: Consensus algorithms like Proof of Work (used by Bitcoin) require significant computational power, leading to high energy consumption.
Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments around the world are still figuring out how to regulate blockchain and cryptocurrencies, leading to legal challenges.
Complexity: Blockchain is still a relatively new and complex technology, making widespread adoption slower, particularly in industries that are traditionally resistant to change.
The Future of Blockchain
Blockchain technology is rapidly evolving, and its potential uses continue to expand. From decentralized finance (DeFi) to non-fungible tokens (NFTs), blockchain is paving the way for new innovations that could transform the way we interact with technology, finance, and data.
Potential Developments:
Integration with IoT: Blockchain can enhance the security and functionality of IoT devices by providing a decentralized network for communication and data storage.
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): Many governments are exploring the idea of issuing digital currencies using blockchain, which could reshape the financial system.
Enhanced Privacy Solutions: New consensus mechanisms and privacy-focused blockchains are being developed to address concerns about data privacy and security.
Conclusion
Blockchain is more than just the technology behind cryptocurrencies. Its potential to transform industries through decentralization, transparency, and security is immense. While there are challenges to overcome, blockchain is poised to become an integral part of the digital future, impacting everything from finance and healthcare to supply chains and beyond.
This revolutionary technology is still in its early stages, but as it matures, its influence is expected to grow, making blockchain an essential tool for innovation in the years to come.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.