The Structure of the Human Heart Explained

Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
The human heart is maybe the most vital organ in the human body due to the simple fact of pumping blood through the entire body. This knowledge regarding the structure of the human heart shows even more about its final role in maintaining health and wellness. This discussion will delve deeper into the anatomical details of the heart, how it functions, and the remarkable facts that would explain how this organ is a wonder of biological engineering.
Anatomy of the Heart
The human heart can be divided into four major chambers; on one side it contains two atrial chambers and on the other side it contains two ventricular chambers, thus making it a four-chambered heart: left atrium, right atrium, left ventricle, and right ventricle. The size of the heart is like a fist; it is placed a little on the left side of the mid-sagittal portion of the chest.
1. Chambers of the Heart
Right Atrium: This chamber receives the deoxygenated blood returning from the body through the superior and inferior vena cavae. That is, the right atrium has been considered a 'way-station' for deoxygenated blood coming back from systemic circulation.
Right Ventricle: The right ventricle then pumps the deoxygenated blood from the right atrium to the lungs through pulmonary arteries. This is where oxygenation of the blood ensues and then it comes back to the heart.
Left Atrium: The chamber receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via pulmonary veins. It acts as a holding reservoir before being pumped to the left ventricle.
Left Ventricle: This is the most muscular, and hence the strongest, chamber, as it has to pump blood into the aorta for distribution to the entire body. Its walls are thick and muscular enough for this purpose.
The anatomical structure of human heart allows this controlled blood movement by providing oxygen-rich blood.
2. Heart Valves
Four vital valves inside the heart control the movement of blood and ensure it does not move back to their initial chambers:
Mitral Valve: This mitral valve is placed between the left atrium and the left ventricle; it allows the one-way movement of blood to occur smoothly and closes up when it flows back toward the atrium.
Tricuspid Valve: This lies in between the right atrium and the right ventricle; it functions similarly to the mitral valve. It ensures that the blood flows correctly.
Aortic Valve: This valve is the one between the left ventricle and the aorta. This is the point where the valve opens so that oxygen-rich blood flows into the aorta, while closing off to prevent the blood from flowing back into the heart.
Pulmonary Valve It is located between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery, directing blood toward the lungs for oxygenation.
Understanding the heart includes having general knowledge about how valves function because it greatly influences smooth circulation and, consequently, the overall condition of the body's cardiovascular system.
Blood Flow Pathway
1. Systemic Circulation Blood to the right atrium comes from the body, which carries carbon dioxide along with other waste products. Through the tricuspid valve, blood moves from the right atrium to the right ventricle. As the right ventricle contracts, it sends the blood to the lungs in pulmonary arteries.
2. Pulmonary Circulation Carbon dioxide is exchanged for oxygen in the lungs. Oxygenated blood flows back to the heart through pulmonary veins into the left atrium. Then, this oxygen-rich blood continues through the mitral valve into the left ventricle.
3. Relapse of Systemic Circulation During the contraction of the left ventricle, it forces blood into the aorta to be distributed through the rest of the body. This is a cycle that never ceases from dispensing oxygen and removing carbon dioxide .
Heart Wall Structure
Heart walls do not consist of chambers and valves only; each is composed of three layers well designed to carry out the work it is meant to do. There are three layers found within the heart wall, each with a particular function:
1.Epicardium: The outer layer of the heart, the epicardium, protects the heart like a cloak. It is quite thin but also contains blood vessels and nerves to feed the heart muscle.
2. Heart Myocardium Myocardium refers to the middle layer of the heart, composed entirely of cardiac muscle tissue. The middle layer is responsible for heart contractions that help it pump its blood efficiently. The structure of the myocardium allows it to contract and rhythmically relax, thus ensuring a constant heartbeat.
3. Endocardium: This is the innermost layer of the heart and forms a lining of the chambers and valves of the heart. It is a smooth layer, thereby preventing much turbulence in flow of blood and wearing off frictional forces as blood circulates through the heart.
To understand the heart wall, it requires knowing all about how the layers form part of the heart and its health. Damage to any of these layers may affect its functioning.
Coronary Circulation
The heart itself needs a continuous supply of oxygenated blood, supplied to it by way of coronary circulation. The coronary arteries arise from the aorta and form a right circle around the heart muscle, which provides all the required nutrients and oxygen.
1. Coronary Arteries Coronary artery on the left supplies blood to the left side of the heart, while the right coronary artery supplies blood to the right side of the heart. Two big arteries act as main nourishment providers for the heart. Blockage or damage to these arteries leads to critical situations like heart attacks.
2. CORONARY VEINS After the heart muscle has utilized the oxygen and nutrients, deoxygenated blood is drained from the coronary veins into the right atrium. Such a system is quite efficient in ensuring the heart is nourished and waste products are expelled.
Keeping coronary circulation healthy is very important for the proper functioning of the heart. Regular exercises, a proper diet, and no smoking are some steps toward helping the coronary advance in health.
Electrical Conduction System
This electrical conduction system controls the heart's pumping efficiency for blood. This regulation by the electrical conduction system helps in a coordinated and rhythmic heartbeat to ensure the effective carrying out of blood circulation.
1. Sinoatrial (SA) Node Commonly known as the heart's natural pacemaker, the sinoatrial node is located in the right atrium. It produces electrical impulses that start each heartbeat. This results in the contraction of the atria and forcing blood into the ventricles.
2. Atrioventricular (AV) Node It then goes to the AV node, which is in between the atria and ventricle. The AV node acts like a gate; they retard the signal before it gets into the ventricles in order that they have had a chance to fill up with blood before contraction occurs.
3. Bundle of Purkinje Fibers After the AV node, the electrical impulse travels down the Bundle and distributes itself into the Purkinje fibers, which distribute themselves throughout the ventricles in order to make them contract and pump blood through to the lungs and body.
Understanding of this electrical system brings out how the heart operates and what goes wrong when the problems like arrhythmias arise.
Heart Health and Disease
For a human heart to be healthy, it must always have its structure. Heart disease has featured as one of the primary causes of morbidity and death all over the world hence the reason for knowing what drives heart health.
1. General Heart Conditions
Coronary Artery Disease: It is caused by the plaque that collects in the arteries of the heart. This leads to the reduced blood supply to the heart muscle.
Heart Attack: This is the blockage of part of the heart due to blood flow and might damage the heart muscle.
Arrhythmias: This is a form of irregular heartbeat that, if unchecked, leads to other problems.
Healthy lifestyle behaviors can also be tapped for a healthy heart by adopting a wholesome diet full of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, and not smoking are all essential factors in the prevention of heart disease.
Routine Check-ups: Because regular follow-ups can be scheduled with a healthcare provider to screen for heart-related problems, potential problems can be detected early. Keeping a close check on blood pressure, cholesterol, and the entire functioning of the heart leads to the long-term sustainability of the human heart.
Role of the Heart in the Cardiovascular System
The heart serves as the central unit of the cardiovascular system in association with blood vessels to distribute blood to other regions of the body.
1. Association with blood vessels
The heart pumps the blood into the arteries, which carry it away from the heart, but veins carry the deoxygenated blood back to the heart. In this process, all tissues in the body receive the oxygen and nutrients they require to carry out their tasks.
2. Homeostasis
The heart is the primary organ for maintaining homeostasis. Normalizing blood pressure, and supplying blood supply to those parts of the body with a higher concentration of demand. To receive more oxygen for working muscles during exercise, the heart will pump faster.
Understanding how the heart functions with the cardiovascular system provides a far better sense of its importance in general health and well-being.
Visualizing the Heart
Visualizations provide an accessible way to learn about the heart and understand its complexities. For a human heart to be healthy, it must always have its structure. Heart disease has featured as one of the primary causes of morbidity and death all over the world hence the reason for knowing what drives heart health.
1. Diagrams and Models Detailed sketches of the heart's chambers and valves and patterns of blood flow outline its structure and functions. Models allow the exploration of the heart's anatomy by hand.
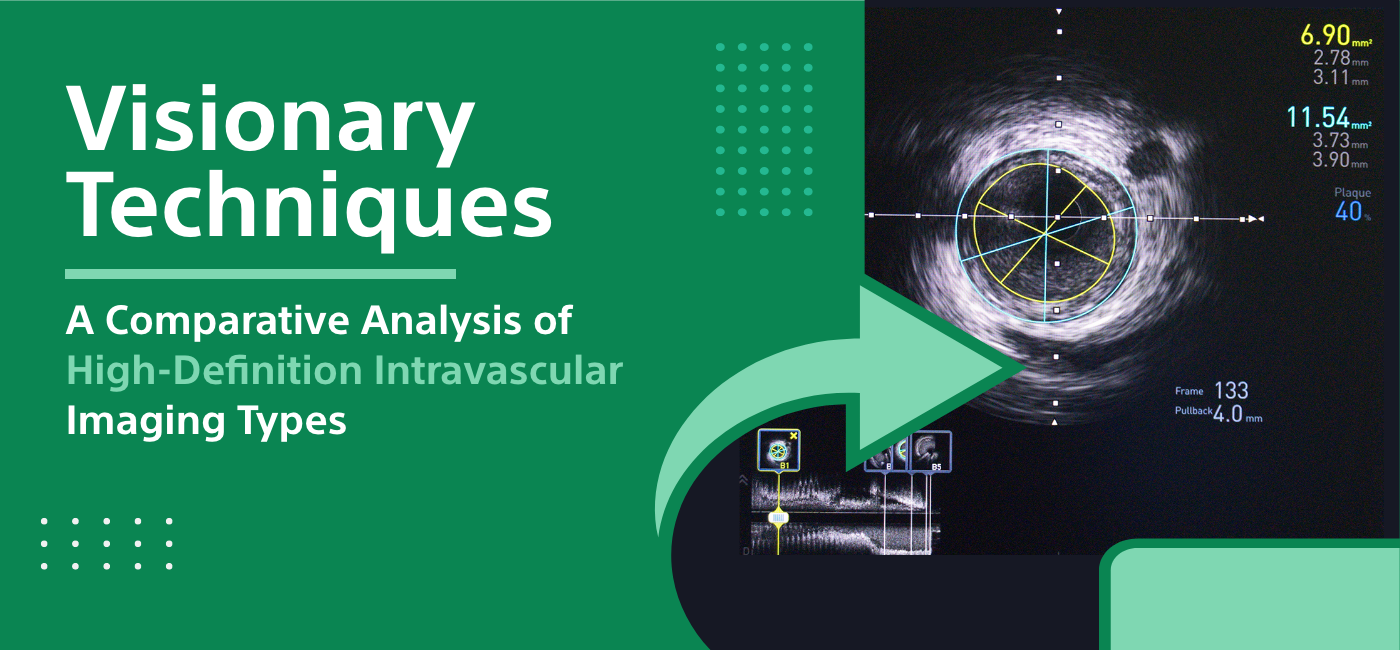
2. Modern Imaging Technologies Thanks to modern imaging technologies, such as echocardiograms, MRI, and CT scans, doctors are now able to see the structure of the heart in real-time. Through these diagnostic tools, medical professionals diagnose conditions relating to the heart and can also analyze heart health.
Visualizations have made learning about the heart as well as even its complexities user-friendly.
Interesting Facts About the Heart
There are just too many astounding facts about the human heart that show what makes it one of a kind
1. Heart Rate Approximately 100,000 times daily, a heart pumps 2,000 gallons of blood throughout the body.
2. Size Variations Though the heart is generally fist-sized, enormous variations can be witnessed based on the health and fitness of an individual.
3. Independent Functioning It is quite amazing that the heart of a dead person continues to beat if it has been provided with a good supply of oxygen. This, in a very big way, is testimonial of the very high flexibility exhibited by this organ of life.
These interesting facts explain why the heart has become so fascinating and also explains why its anatomy and functions are very significant
Future of Cardiac Research
An extensive research of the heart is highly pushed by developments in science. The hope that it can be better in health and treatment regarding the heart never fades.
1. New Technologies: Advancements in medical equipment, especially from implantable defibrillators and pacemakers, have come to advance the treatment and management of the heart. Gene therapy and stem cell research are the upcoming treatments of heart disease.
2. Prevention With the increased awareness of the need to keep the heart healthy, prevention measures and education programs for a heart-healthy lifestyle are established.
3. Regenerative Medicine The outlook is bright with hope in the field of regenerative medicine that perhaps one day will be able to prevent or reverse heart disease by repairing or replacing damaged heart tissue.
To keep the interests of individuals abreast of the best research available and trends, staying current and up to date in the knowledge of a healthy human heart is of fundamental importance. This all-embracing overview helps any enthusiastic individual learn about this fantastic organ through its structure, its functions, and all types of factors that impact heart health.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.