Understanding Hearing Loss: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
Hearing plays a vital role in how we communicate, learn, and connect with the world. Yet, hearing loss is a condition that often goes unnoticed or untreated, especially in its early stages. It can affect people of all ages—from newborns to the elderly—and if not managed properly, it can impact quality of life, emotional well-being, and even safety.
In this article, we’ll explore the common causes of hearing loss, the signs you shouldn’t ignore, and the various treatment options available today.
What Is Hearing Loss?
Hearing loss refers to a partial or complete inability to hear sounds in one or both ears. It can occur suddenly or gradually and may be temporary or permanent. Depending on the underlying cause, hearing loss is typically classified into three main types:
- Conductive Hearing Loss – Caused by problems in the outer or middle ear, such as wax buildup or ear infections.
- Sensorineural Hearing Loss – Due to damage in the inner ear (cochlea) or the auditory nerve, often permanent.
- Mixed Hearing Loss – A combination of both conductive and sensorineural hearing loss.
Common Causes of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can result from a wide range of medical, environmental, or genetic factors. Some of the most common causes include:
1. Age-Related Hearing Loss (Presbycusis)
As we age, the tiny hair cells in the inner ear begin to degenerate, making it harder to hear high-pitched or soft sounds. This is a natural part of aging but can be managed with the right interventions.
2. Exposure to Loud Noise
Prolonged exposure to loud sounds—like music through headphones, traffic, or machinery—can damage inner ear structures. This type of hearing loss is often permanent but preventable.
3. Ear Infections or Blockages
Repeated ear infections, fluid buildup, or impacted earwax can obstruct sound from reaching the inner ear and cause temporary hearing problems.
4. Injuries and Medical Conditions
Head injuries, diabetes, heart disease, and conditions like Meniere’s disease can also affect hearing. Ototoxic medications (certain antibiotics and chemotherapy drugs) may also cause hearing loss.
5. Genetic Factors
Some people are born with hearing problems due to inherited conditions or complications during birth. Early diagnosis in such cases is crucial for timely intervention.
Signs and Symptoms of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can be subtle in the beginning, making it easy to overlook. Watch out for the following signs in yourself or loved ones:
- Asking people to repeat themselves frequently
- Difficulty understanding speech in noisy environments
- Turning up the volume on the TV or phone too loud
- Ringing or buzzing in the ears (tinnitus)
- Withdrawal from conversations or social settings
- Trouble hearing high-pitched sounds like birds chirping or doorbells
In children, delayed speech, inattentiveness, or difficulty in school could be warning signs of hearing problems.
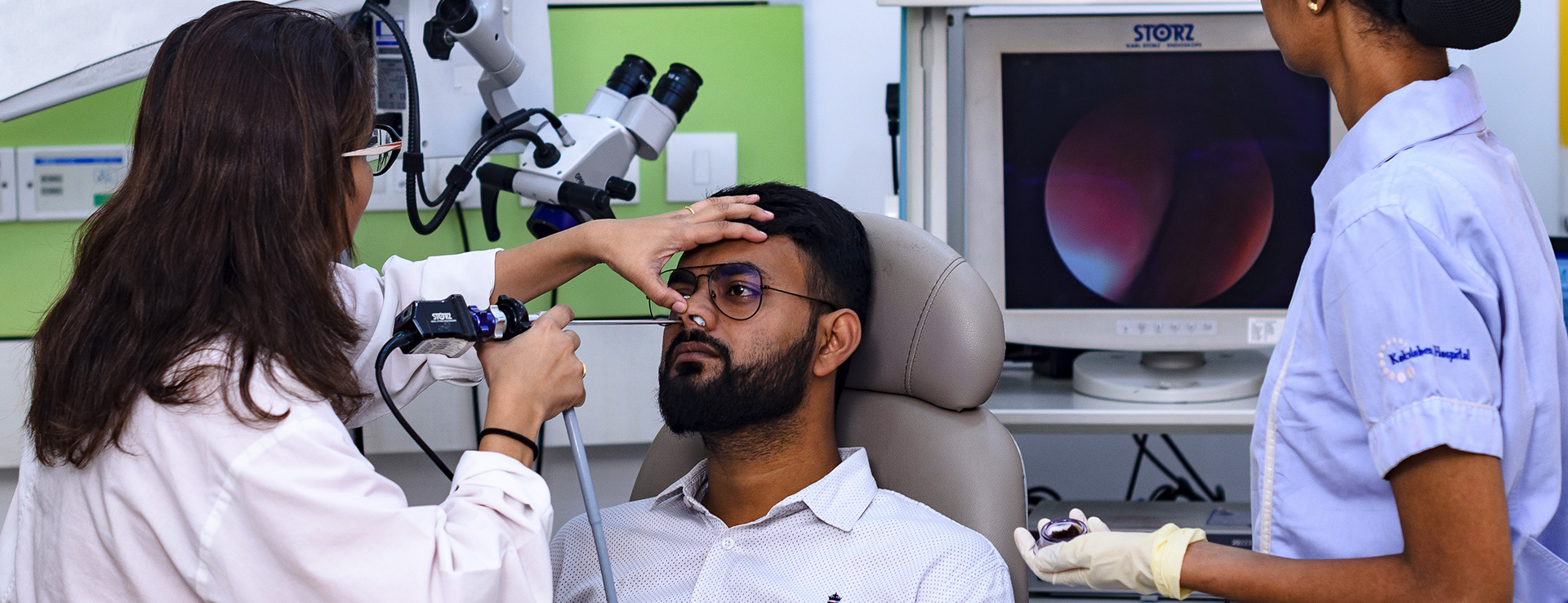
Diagnosis and Testing
If you suspect hearing loss, it’s important to seek medical evaluation from an ENT specialist or audiologist. A thorough assessment usually includes:
- Physical examination of the ear
- Hearing tests such as audiometry, tympanometry, and otoacoustic emissions (OAE)
- Imaging tests like CT or MRI in complex cases
Early diagnosis not only helps in planning treatment but also prevents further complications.
Treatment Options for Hearing Loss
Treatment depends on the cause and severity of the hearing loss. At Kokilaben Hospital, a wide range of medical, surgical, and rehabilitative options are available to help patients regain or manage their hearing.
1. Medical Treatment
Infections and wax blockages can often be treated with medications or minor procedures. Antibiotics, antifungal drops, or ear cleaning can restore hearing in many such cases.
2. Hearing Aids
These are small electronic devices that amplify sound and are suitable for people with sensorineural hearing loss. Modern hearing aids are discreet, comfortable, and come with features like Bluetooth connectivity and background noise cancellation.
3. Cochlear Implants
For individuals with severe or profound hearing loss who don’t benefit from hearing aids, cochlear implants are a viable option. These devices bypass damaged parts of the ear and directly stimulate the auditory nerve.
4. Surgical Options
Surgery may be recommended for conditions like chronic ear infections, tumors, or malformations. Procedures such as tympanoplasty, stapedectomy, or implantable devices can restore hearing in select cases.
5. Speech and Auditory Therapy
Especially in children, speech therapy and auditory training play an important role in helping them develop communication skills. Our team of audiologists and therapists work closely with families to ensure optimal outcomes.
Living with Hearing Loss
While hearing loss can be challenging, it doesn't have to define your life. With proper diagnosis, timely treatment, and supportive care, most individuals can continue to lead full and active lives. Staying connected, using hearing devices consistently, and participating in rehabilitation programs can make a big difference.
Family members and caregivers also play a crucial role by being supportive, patient, and proactive in seeking help for their loved ones.
Conclusion
If you or someone you care about is experiencing signs of hearing loss, don’t delay seeking help. Early diagnosis can prevent complications and greatly improve quality of life. The ENT Department at Kokilaben Hospital, Navi Mumbai offers expert evaluation and personalized treatment plans using advanced technology and compassionate care. Let us help you rediscover the joy of hearing.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.







