Understanding the Difference Between OMR and OCR: A Comprehensive Guide
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
In the realm of document processing and data extraction, two technologies frequently come into play: Optical Mark Recognition (OMR) and Optical Character Recognition (OCR). While both are used to automate data capture from physical documents, they serve distinct purposes and are suited for different types of data. In this blog, we will delve into the key differences between OMR and OCR, their applications, and how they can benefit various industries.
What is Optical Mark Recognition (OMR)?
Optical Mark Recognition (OMR) is a technology used to read and interpret marks on a document, such as checkboxes or bubbles. OMR systems are designed to detect the presence or absence of these marks, making it a highly efficient tool for processing forms and surveys where responses are captured using predefined mark patterns.
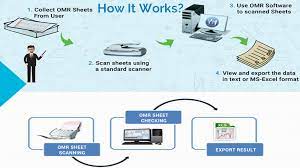
How OMR Works:
• Predefined Forms: OMR requires pre-designed forms with clearly defined areas for marking, such as bubbles or checkboxes.
• Scanning: The forms are scanned using OMR software or devices that capture the marks on the paper.
• Data Extraction: The software detects the presence or absence of marks within specified areas and translates this information into digital data.
Applications of OMR:
• Examinations and Tests: OMR is widely used in educational institutions for grading multiple-choice tests and exams.
• Surveys and Feedback Forms: OMR streamlines the processing of paper-based surveys and feedback forms, allowing for quick and accurate data collection.
• Attendance Tracking: OMR sheets are often used to record attendance in large-scale events or classrooms.
Advantages of OMR:
• Speed and Accuracy: OMR can process large volumes of forms quickly and accurately, minimizing human errors associated with manual data entry.
• Cost-Effective: OMR systems are relatively inexpensive to implement and maintain, making them ideal for organizations with high-volume form processing needs.
What is Optical Character Recognition (OCR)?
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) is a technology that converts printed or handwritten text on scanned documents into machine-readable text. OCR is used to digitize text-based information, allowing for easy searching, editing, and storage of documents.
How OCR Works:
• Scanning: Documents are scanned using OCR software that captures the text on the paper.
• Character Recognition: The software analyzes the scanned images, recognizing and converting individual characters into digital text.
• Output: The converted text can be stored in various formats, such as PDF, Word, or plain text, making it searchable and editable.
Applications of OCR:
• Document Digitization: OCR is commonly used to digitize paper documents, such as contracts, invoices, and historical records, for easy access and archiving.
• Data Entry Automation: OCR automates the data entry process by extracting text from forms and documents, reducing the need for manual input.
• Text Recognition in Images: OCR is used to extract text from images, such as scanned books, magazines, and photographs.
Advantages of OCR:
• Enhanced Accessibility: OCR makes text-based information easily accessible and searchable, improving productivity and efficiency.
• Time Savings: OCR significantly reduces the time required for data entry and document processing.
• Data Preservation: OCR helps preserve important historical documents by converting them into digital formats for long-term storage and retrieval.
Key Differences Between OMR and OCR
Aspect OMR OCR
Purpose Detects marks on predefined forms Recognizes and converts text from scanned images
Input Marks (checkboxes, bubbles) Printed or handwritten text
Applications Exams, surveys, attendance tracking Document digitization, data entry automation
Technology Requires specific form design Analyzes text patterns in images
Output Digital data indicating mark presence/absence Machine-readable text
Flexibility Limited to predefined mark areas Flexible with various text layouts and fonts
Error Handling Susceptible to errors if marks are not clear Advanced algorithms improve accuracy with text
Choosing Between OMR and OCR
When deciding whether to use OMR or OCR, consider the nature of your documents and the type of data you need to extract:
• Use OMR if:
o You need to process forms with predefined marks, such as multiple-choice tests or surveys.
o Speed and accuracy in detecting mark presence are critical.
• Use OCR if:
o You need to digitize text-based documents for searching, editing, or archiving.
o You have a variety of document types and formats, including handwritten text.
Conclusion
OMR and OCR are powerful technologies that streamline data extraction from physical documents. While OMR excels in processing forms with predefined marks, OCR is the go-to solution for digitizing text-based documents. By understanding the key differences and applications of these technologies, businesses and organizations can make informed decisions to enhance their document processing workflows and improve overall efficiency. Whether you're grading exams or digitizing archives, the right technology can make all the difference in managing your data effectively in the digital age.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.


