Unlocking the Power of PBR in Cisco Networks
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
Policy-based routing (PBR) stands as a transformative force within the realm of Cisco Networks, presenting a unique approach to routing that goes beyond traditional methods. If you're eager to optimize your network's performance and exert precise control over traffic flow, a comprehensive understanding and implementation of PBR is essential. In this article, we'll delve into the intricacies of PBR, exploring its benefits, guiding you through Cisco router configuration, and shedding light on real-world applications and best practices.
Understanding Policy-Based Routing (PBR)
Policy-based routing introduces a paradigm shift by allowing administrators to make routing decisions based on predefined policies rather than relying solely on conventional routing protocols. This means that, unlike traditional routing methods, PBR provides a more nuanced and flexible control over how data is directed through the network.
How PBR differs from traditional routing becomes clearer when we consider its dynamic nature. Unlike the static routes established by traditional protocols, PBR enables administrators to customize routing decisions based on specific criteria. This flexibility is a game-changer, especially in dynamic network environments where conditions can change rapidly.
Benefits of Implementing PBR in Cisco Networks
The advantages of implementing PBR in Cisco Networks are manifold. One of the key benefits is enhanced traffic control. PBR allows administrators to prioritize or redirect traffic based on a variety of factors, providing a level of control that traditional routing methods struggle to achieve.
Improved network performance is another significant advantage. By directing traffic along optimized paths, PBR contributes to reduced latency and enhanced overall network responsiveness. This results in a smoother and more efficient data flow throughout the network.
The increased flexibility in routing decisions is perhaps one of the most compelling reasons to embrace PBR. Organizations can tailor routing decisions to align with their unique needs, adapting dynamically to changing network conditions. This adaptability is crucial in modern networks where agility and responsiveness are paramount.
Key Components of Policy-Based Routing
To grasp the essence of policy-based routing, it's essential to understand its key components. The first component is match criteria, which involves defining the conditions under which PBR should be applied. This can include factors such as source/destination IP, protocol type, or input interface.
Set actions constitute the second component. Once match criteria are met, set actions specify what should happen to the matched traffic. This could involve changing the next-hop, setting IP precedence, or forwarding the traffic to a specific interface.
The third and final component is route maps. Route maps organize match criteria and set actions into logical sequences, providing a structured framework for efficient policy application. Understanding these components is crucial for effective PBR implementation.
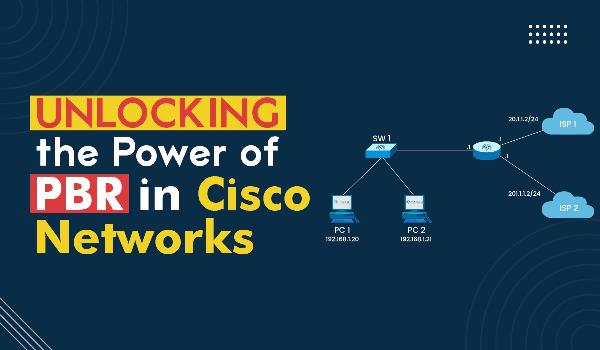
Cisco Router Configuration for PBR
Implementing PBR in Cisco Networks involves navigating the router interface and configuring specific settings. Accessing the router interface is the first step, requiring administrators to log in and access the configuration settings.
Creating route maps is the next critical step in Cisco router configuration for PBR. Route maps define the criteria and actions for policy-based routing. This involves specifying the match criteria and the corresponding set actions that should be applied to the matched traffic.
Once route maps are configured, the next step is applying PBR to specific traffic. This ensures that the policies defined in the route maps influence the routing decisions for the designated traffic flows. The configuration process demands careful attention to detail to ensure the desired outcomes.
Real-world Applications of PBR
PBR isn't just a theoretical concept; its real-world applications make it a valuable tool for network administrators. One prominent application is load balancing. PBR enables intelligent load balancing by distributing traffic across multiple paths, optimizing resource utilization and preventing network congestion.
Traffic redirection for optimization is another practical application. Administrators can redirect specific types of traffic through optimized routes, ensuring efficient utilization of network resources. This targeted approach enhances overall network efficiency and performance.
Quality of Service (QoS) implementation is yet another compelling use case for PBR. By prioritizing certain types of traffic, PBR ensures a consistent quality of service for critical applications, contributing to a seamless user experience.
Best Practices for PBR Implementation
Effective implementation of PBR requires adherence to best practices. Understanding the network topology is crucial. Administrators should have a clear understanding of the network's structure and flow to design PBR rules that align with the natural flow of traffic.
Monitoring and troubleshooting PBR is an ongoing process. Regular monitoring helps identify any deviations from expected performance, and troubleshooting measures should be in place to address issues promptly. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and ensures a stable network environment.
Considering security implications is paramount. While PBR itself doesn't inherently pose security risks, administrators must configure policies in a way that doesn't compromise network security. This involves careful consideration of access controls and policy definitions.
Challenges and Solutions in PBR Implementation
Implementing PBR may come with its set of challenges. Identifying potential issues, such as misconfigurations or conflicts with existing routing protocols, is crucial. A proactive approach to troubleshooting and quick resolution of issues ensures the smooth functioning of PBR within the network.
Troubleshooting tips are valuable tools for network administrators dealing with PBR issues. Whether it's monitoring performance metrics, identifying misconfigurations, or addressing conflicts, having a well-defined troubleshooting strategy is essential. This helps maintain the integrity and performance of the network.
- Case Studies
Examining real-world case studies provides insights into the practical impact of PBR. Success stories of PBR implementation highlight organizations that have unlocked the power of PBR to achieve significant improvements in network performance.
Lessons learned from these case studies offer valuable takeaways. Understanding the challenges faced and the strategies employed by other organizations can guide administrators in making informed decisions during their own PBR implementation.
Future Trends in Policy-Based Routing
As technology evolves, so does PBR. Staying informed about the evolution of PBR technology is crucial for network administrators. This includes understanding how PBR integrates with emerging networking solutions and adapts to the changing landscape of networking technologies.
Integration with emerging networking technologies, such as Software-Defined Wide Area Networking (SD-WAN) and the Internet of Things (IoT), represents the future trends in policy-based routing. PBR is adapting to work seamlessly with these technologies, providing enhanced capabilities for network administrators.
FAQs - frequently asked questions
What is policy-based routing?
Policy-based routing is a network management technique that allows administrators to make routing decisions based on predefined policies rather than relying solely on routing protocols.
How does PBR enhance network performance?
PBR enhances network performance by providing granular control over traffic, allowing administrators to prioritize or redirect data based on specific criteria.
Can PBR be applied selectively to certain traffic?
Yes, PBR can be applied selectively to certain traffic by defining match criteria and specifying actions for the desired traffic flows.
Are there security concerns with PBR implementation?
While PBR itself doesn't inherently pose security risks, administrators should be cautious and ensure that policies are configured in a way that doesn't compromise network security.
How can I troubleshoot PBR issues?
Troubleshooting PBR involves monitoring performance, identifying potential misconfigurations, and applying troubleshooting tips to address issues promptly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, unlocking the power of policy-based routing in Cisco Networks is a strategic move for any organization seeking to optimize its network performance. From enhanced traffic control to improved flexibility in routing decisions, PBR offers a myriad of benefits. As you explore the world of PBR, remember to tailor its implementation to your specific network needs and stay abreast of future trends shaping the networking landscape.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.


