Unveiling the Microscopic Marvel: The Promises of Nanoscience
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
In an era where science continually pushes the boundaries of what is possible, nanoscience stands out as one of the most fascinating and transformative fields. At the nanoscale—one billionth of a meter—materials exhibit unique properties that differ significantly from their macroscopic counterparts. This microscopic realm can lead to revolutionary advancements across various disciplines, including medicine, electronics, materials science, and energy.
Understanding Nanoscience
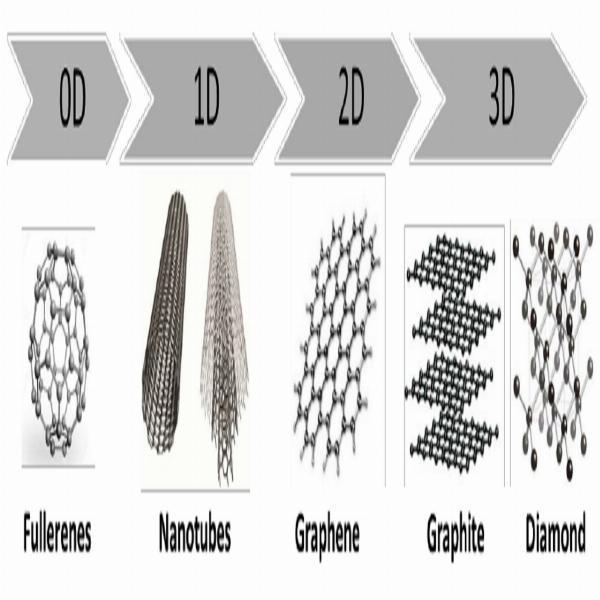
Nanoscience is the study of structures and devices on the nanoscale, typically between 1 to 100 nanometers. To put this scale into perspective, a nanometer is roughly 100,000 times smaller than the width of a human hair. At this minuscule scale, atoms and molecules interact in ways that give rise to new physical and chemical properties. For instance, gold nanoparticles appear red or purple rather than the traditional metallic color due to quantum effects that become pronounced at this size.
The significance of nanoscience lies in its interdisciplinary nature, integrating physics, chemistry, biology, and engineering. Researchers across these fields collaborate to explore how manipulating materials at the nanoscale can lead to groundbreaking applications.
Applications of Nanoscience
1. Medicine: One of the most promising applications of nanoscience is in the medical field. Nanoparticles can be engineered to target specific cells, such as cancerous cells, allowing for targeted drug delivery that minimizes side effects and maximizes treatment efficiency. This type of therapy utilizes nanocarriers, which can encapsulate drugs and release them in a controlled manner, enhancing therapeutic outcomes.
Furthermore, nanotechnology is paving the way for advanced imaging techniques. Quantum dots, semiconductor particles that emit light when excited, can be used for high-resolution imaging of biological processes in real time, improving diagnostics and disease monitoring.
2. Electronics: As electronic devices become smaller and more powerful, nanoscience plays a vital role in the development of the next generation of technology. Nanoscale transistors, made from materials like graphene or carbon nanotubes, promise to enhance computing speed and efficiency. This miniaturization not only improves device performance but also reduces energy consumption, addressing the growing need for sustainable technology.
3. Energy: The energy sector is also experiencing a revolution due to nanoscience. Nanomaterials are being used to create more efficient solar cells, capable of converting sunlight into electricity at higher rates. Nanotechnology enhances the light absorption capacity of solar panels, while also enabling the development of lightweight and flexible designs. Additionally, nanomaterials are improving battery technology, leading to faster charging times, increased storage capacities, and longer lifespans.
4. Environmental Remediation: Nanotechnology has the potential to significantly impact environmental science by providing innovative solutions for pollution control. Nanoparticles can be employed to clean up contaminated water and soil by breaking down toxic substances into less harmful compounds. Moreover, nanomaterials can absorb heavy metals and other pollutants, thus improving water quality and promoting a healthier ecosystem.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the immense potential of nanoscience, it is not without its challenges and considerations. One of the most pressing issues is the potential toxicity of nanoparticles. As materials are reduced in size, their interactions with biological systems can lead to unforeseen consequences. Understanding the safety and environmental impact of nanomaterials is crucial to ensuring their responsible development and deployment.
Furthermore, as research progresses, ethical considerations surrounding the use of nanotechnology must be carefully navigated. Issues ranging from privacy concerns related to nanoscale surveillance technology to the implications of creating new materials require a thoughtful and inclusive dialogue among scientists, policymakers, and society.
Conclusion
nanoscience is an emerging frontier with the potential to change the world in ways we are only beginning to understand. From revolutionary advances in medicine to groundbreaking innovations in electronics and energy, the implications of manipulating materials at the nanoscale are profound. As researchers continue to unveil the mysteries of this microscopic domain, the future promises countless opportunities to improve and enrich human life. Embracing this science not only straightens the bridge to innovation but also requires a commitment to ensuring ethical and environmental responsibility as we forge ahead into the nanoscopic age.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.







