What Are the Side Effects of Melasma Treatments in Islamabad?
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
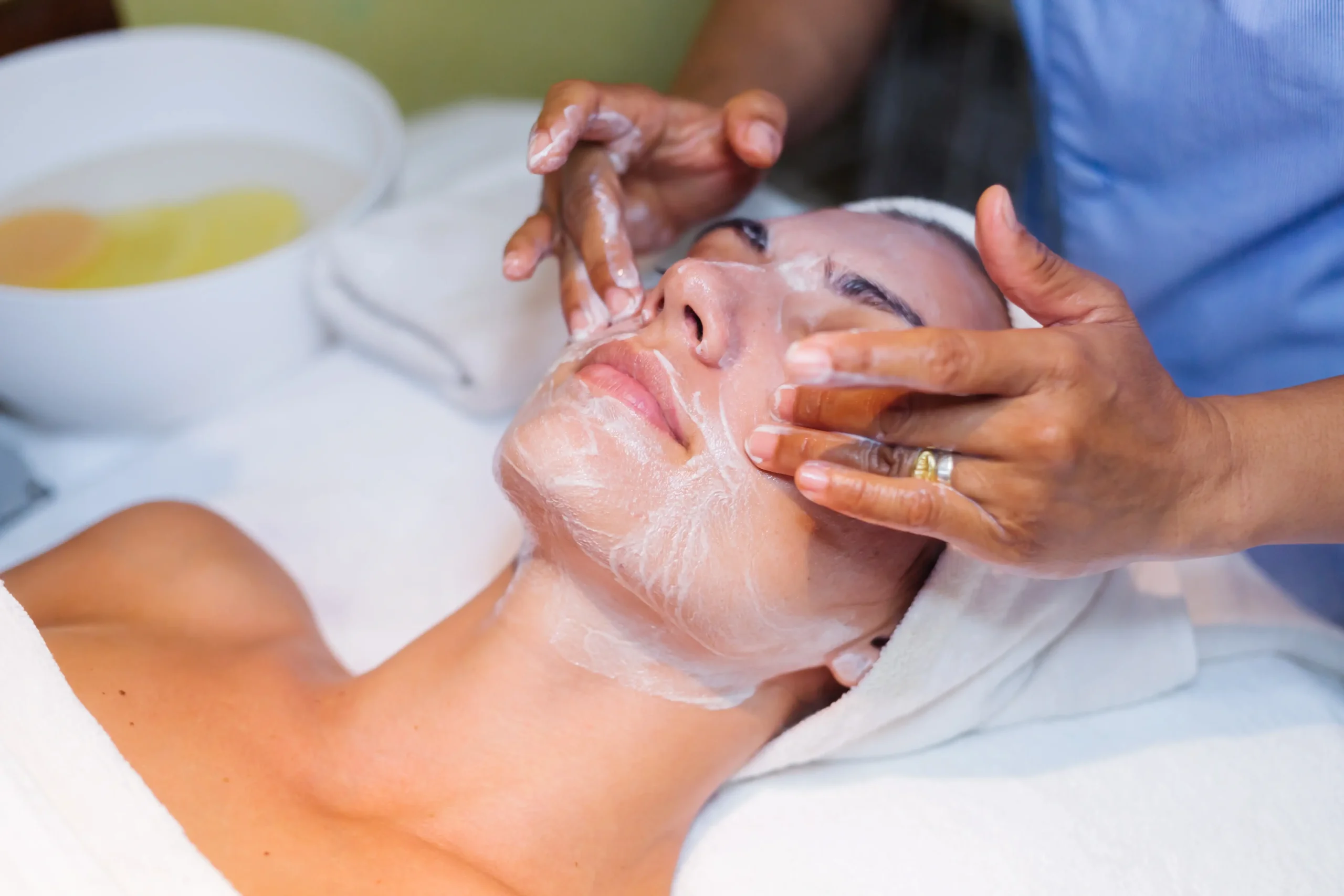
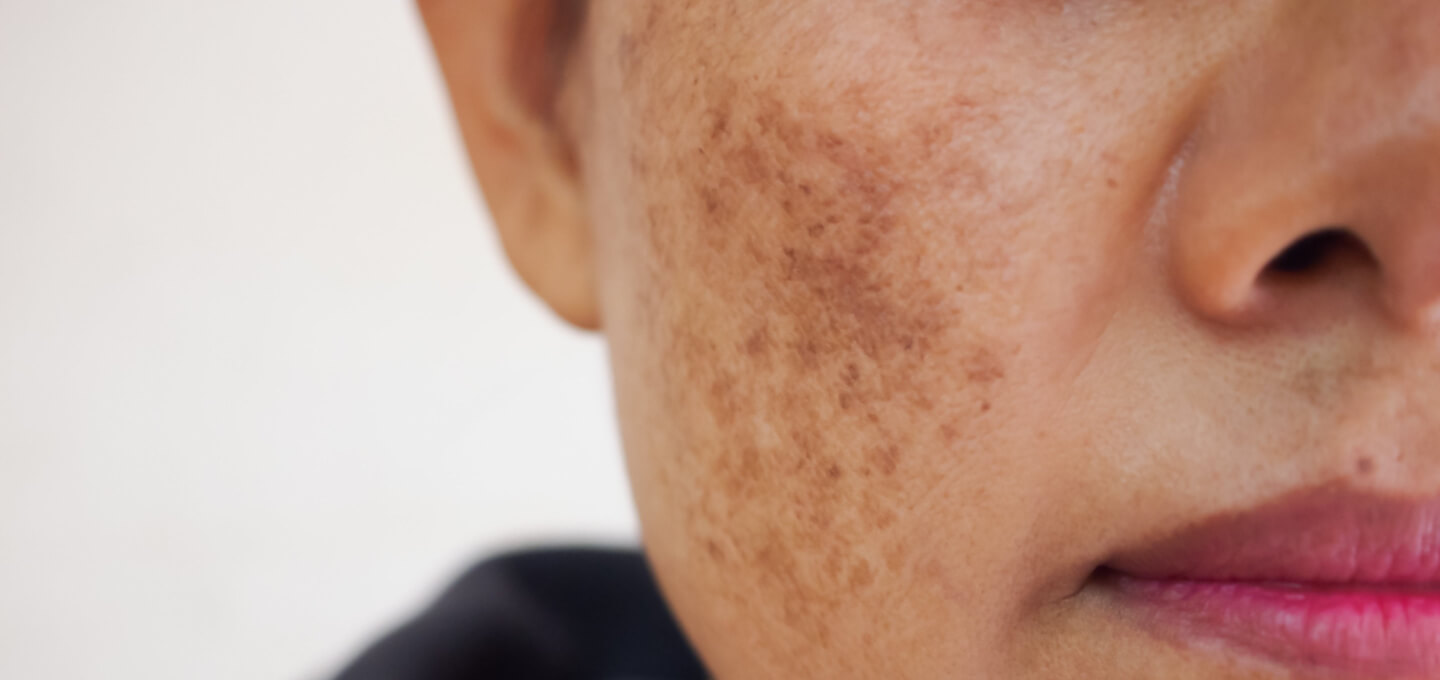
Melasma, a chronic skin pigmentation disorder, is a widespread concern among men and women in Pakistan, especially in sun-rich cities like Islamabad. Characterized by brown or grayish patches on the face—most commonly on the cheeks, forehead, nose, and upper lip—melasma is often driven by sun exposure, hormonal changes, and genetics. Given its persistent nature, many people seek advanced clinical options to treat it. However, with every treatment—whether it’s topical, procedural, or oral—there may be side effects. Understanding the potential risks and how to manage them is just as important as the treatment itself. Whether you're considering topical creams, chemical peels, or laser therapies, it's essential to be aware of the possible drawbacks associated with Melasma Treatment in Islamabad.
1. Topical Creams and Serums
Topical agents are often the first line of treatment for melasma. These typically include:
Hydroquinone
Retinoids (like tretinoin)
Corticosteroids
Azelaic acid
Kojic acid
Tranexamic acid
While effective in reducing melanin production and improving skin tone, they can come with temporary or long-term side effects, especially when used incorrectly or without supervision.
Possible Side Effects:
Skin irritation: Redness, itching, and peeling are common during the first few weeks, particularly with retinoids or hydroquinone.
Increased sensitivity to sunlight: Some agents make the skin more prone to UV damage, which can worsen melasma if sunscreen is not used diligently.
Allergic reactions: Rare but possible, especially with kojic acid or fragranced products.
Ochronosis: Prolonged or unsupervised use of hydroquinone may lead to a condition where the skin darkens instead of lightening—a risk in cases of overuse, particularly in medium to dark skin tones.
2. Chemical Peels
Chemical peels help by exfoliating the top layers of skin, promoting new cell growth and breaking down excess melanin. Common peeling agents used for melasma include glycolic acid, salicylic acid, TCA (trichloroacetic acid), lactic acid, and mandelic acid.
Possible Side Effects:
Temporary redness and peeling: This is expected after a peel and usually resolves in a few days.
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH): A significant concern for South Asian skin types, especially if strong peels are used too frequently or sun exposure follows treatment.
Infection: Rare but possible if the skin barrier is broken and not cared for properly after the peel.
Scarring: Improper application or strong peels used on sensitive skin can lead to mild scarring.
Due to Islamabad's high UV index, chemical peels must be timed carefully—usually in cooler months—and followed by rigorous sun protection.
3. Laser and Light-Based Treatments
Laser treatments such as Q-switched lasers, fractional lasers, and Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) can target melanin deposits deep within the skin. These are popular options for treating stubborn melasma, but they also carry some of the highest risks, especially in darker skin tones.
Possible Side Effects:
Temporary redness and swelling: Most patients experience mild redness and sensitivity for a few hours to a couple of days.
PIH (Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation): Perhaps the most concerning risk in Fitzpatrick skin types III-V, which are common in Pakistan. This occurs when laser energy irritates the skin, prompting more melanin production instead of less.
Hypopigmentation: Loss of pigment in treated areas, making them appear lighter than the surrounding skin.
Scabbing and crusting: In some cases, particularly with fractional lasers.
Skin texture irregularities: Rare but possible if the laser settings are too aggressive.
To minimize these risks, it's essential to have laser treatments performed by a skilled and experienced dermatologist who understands how to work with South Asian skin.
4. Microneedling with Serums
Microneedling is often used to enhance the penetration of depigmenting agents like tranexamic acid or vitamin C. It involves using fine needles to create micro-injuries on the skin, stimulating collagen production and improving absorption.
Possible Side Effects:
Redness and irritation: Usually resolves within 24–48 hours.
Swelling and sensitivity: More noticeable in the first few hours post-treatment.
Risk of infection: If needles are not sterile or aftercare is ignored.
Hyperpigmentation: Once again, a risk if sun protection is not followed strictly after treatment.
In Islamabad’s climate, the key concern after microneedling is sun exposure. Even minimal UV exposure after treatment can reverse progress and darken the skin again.
5. Oral and Injectable Treatments (e.g., Glutathione, Tranexamic Acid)
These treatments are often used as adjuncts to topical or procedural therapies. They work internally by reducing melanin production or addressing inflammation and oxidative stress.
Possible Side Effects:
Tranexamic Acid (oral or injectable):
Gastrointestinal discomfort
Headache
Rare but serious risks include blood clot formation, so it is contraindicated in people with a history of thrombosis.
Glutathione (injectable):
Mild discomfort at the injection site
Allergic reaction (rare)
Long-term effects of high-dose injections are still under investigation globally
Both treatments must be carefully supervised by medical professionals, especially in patients with underlying health conditions.
How Islamabad’s Climate Affects Side Effects
Islamabad has a relatively dry climate with high sun exposure throughout the year. This poses specific challenges for melasma patients:
High UV index: Can worsen PIH and interfere with post-treatment healing
Dry weather: Can increase irritation and slow recovery from procedures like peels and lasers
Pollution: Airborne pollutants can irritate freshly treated skin, especially after invasive treatments
To minimize side effects, dermatologists in Islamabad recommend scheduling treatments in the cooler months (October to March), using SPF 50+ daily, wearing physical barriers like hats or scarves, and using hydrating and calming skincare post-procedure.
How to Reduce the Risk of Side Effects
Here are a few ways to minimize complications from melasma treatments:
Choose a qualified dermatologist: Ensure they have experience treating melasma in Fitzpatrick skin types III–V.
Follow post-treatment instructions religiously: Especially sun protection and avoiding harsh skincare.
Avoid DIY treatments and unverified products: Many whitening creams available over the counter contain harmful ingredients like steroids or mercury.
Stick with a consistent routine: Switching between treatments or overusing strong agents can worsen pigmentation.
Hydrate and nourish your skin: A healthy skin barrier reduces inflammation and improves recovery.
Conclusion
Melasma treatments, while effective, come with potential side effects, especially when not carefully administered or followed by proper aftercare. Whether it's a mild irritation from a cream or the risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation from a laser, understanding these possibilities is essential for achieving long-lasting and safe results. In Islamabad’s sunny and dry climate, protecting your skin before, during, and after treatment becomes even more critical.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.