What Causes Joint Inflammation and How to Manage It?
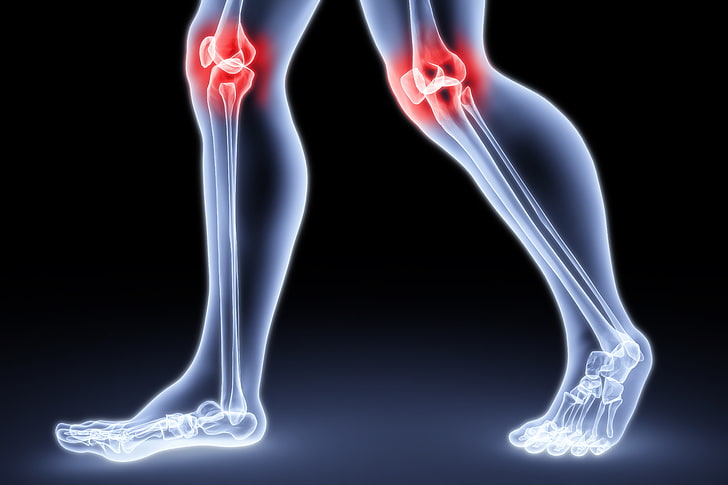
Joint inflammation, a common complaining factor among people of all walks of life, is redness, swelling, heat, and soreness in the joints. An awareness of why it happens and how it might best be treated can make a difference to one's lifestyle.
Causes of Joint Inflammation
Joint inflammation most commonly is the body's defensive reaction to injury, infection, or chronic disease. The following are the most common causes:
- Arthritis: The two most frequent forms are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis occurs as a result of degeneration of cartilage, while rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease where the immune system of the body attacks the joint tissues.
- Infections: Septic arthritis is an infection, typically bacterial, that enters directly into the joint space and produces acute inflammation.
- Injuries: Trauma, such as sprains or breaks, can lead to inflammation as the body tries to repair damaged tissue.
- Gout: Deposition of uric acid crystals in joints leads to sudden and often severe inflammation.
- Lifestyle Factors: Excess weight, inactivity, and nutritional factors may increase the risk of inflammation and joint symptoms.
Certain weather changes or prolonged inactivity may also worsen underlying joint conditions. In cases of severe pain or inflammation, medications such as zerodol p tablets may be recommended by healthcare providers for short-term relief. These medications help reduce the discomfort, making it easier for patients to carry out daily activities.
Symptoms to Watch For
Recognizing the early symptoms of joint inflammation is crucial for timely management. Common manifestations of joint inflammation are:
- Swelling and redness over the joint area
- Warmth to the touch
- Pain and tenderness
- Stiffness, especially after resting or waking up
- Limited movement of the joint
Some individuals may also experience fatigue or a low-grade fever, especially in autoimmune-related inflammation. These symptoms can significantly reduce quality of life if not addressed early.
Management of Joint Inflammation
Joint inflammation management is a combination of medicinal and lifestyle adjustments. Some of the most recommended methods are as follows:
1. Medications
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Medications such as ibuprofen or prescription medications such as Zerodol P tablet (combination of aceclofenac and paracetamol) are normally prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Other Prescribed Medications: Doctors may also prescribe medications like Acemiz Plus, which contains aceclofenac along with serratiopeptidase, for the treatment of chronic inflammation or chronic pain. These drugs inhibit the formation of chemicals in the body that cause inflammation.
- Disease-Modifying Medications: In autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) or biologics are used to control immune activity. These medicines may help prevent long-term joint damage if started early.
Always follow the dosage and timing recommended by your healthcare provider to avoid possible side effects or interactions.
2. Lifestyle Changes
- Exercise: Low-impact activities such as cycling or swimming maintain joint mobility without placing an excessive load on the joints. Yoga, stretching, and guided movement therapy can also be beneficial.
- Weight Management: Weight reduction lightens weight on weight-bearing joints, especially the hips and knees. Even a small weight loss can reduce the load on the joints and improve symptoms.
- Healthy Diet: An anti-inflammatory diet containing foods such as omega-3 fatty acids (found in fish), fruits, vegetables, turmeric, and nuts can alleviate symptoms. Reducing processed foods, sugar, and saturated fats is also advised.
Hydration plays a crucial role as well—drinking enough water helps maintain joint lubrication and reduce stiffness.
3. Other Therapies
- Physical Therapy: Specific exercise and stretch can enhance functioning of the joints and alleviate stiffness. A physiotherapist can tailor exercises based on the severity and location of inflammation.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Application of heat or cold packs may be helpful in reducing pain and swelling. Heat helps relax muscles and improve circulation, while cold therapy can numb the area and reduce acute inflammation.
- Assistive Devices: In some cases, braces, orthotics, or canes may be recommended to reduce strain on joints during movement.
When to See a Doctor
Medical attention is recommended in the following cases:
- The swelling of the joint is extremely severe or sudden.
- Recurring episodes of inflammation or stiffness.
- Associated symptoms like fever, fatigue, or unexplained weight loss.
- Pain that interferes with daily activities or sleep.
Prompt diagnosis and treatment are likely to prevent long-term damage. Blood tests, imaging (X-rays or MRI), or fluid analysis may be done to confirm the underlying cause.
Disclaimer:
This article is for general information only and not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult your doctor before beginning any new treatment for inflammation or joint pain.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.