Your Guide to Biopsy for Diagnostic Purposes
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
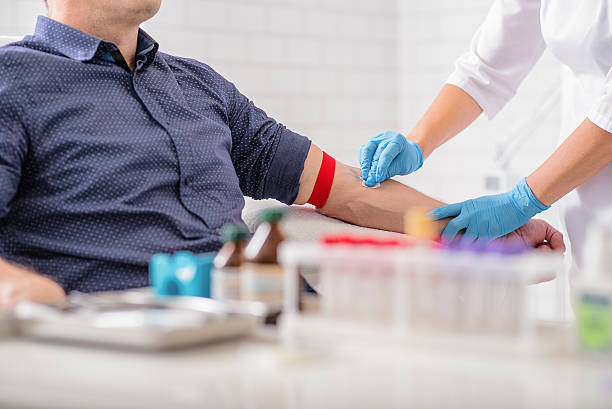
A biopsy is a crucial medical procedure used to diagnose various health conditions, including infections, inflammatory diseases, and cancers. It involves the removal of a small tissue sample from the body, which is then examined under a microscope or tested in a laboratory. Biopsy for diagnostic purposes(خزعة لأغراض التشخيص) helps healthcare providers determine the nature of abnormalities and plan appropriate treatments.
Importance of a Biopsy in Medical Diagnosis
Accurate disease detection – Biopsies provide precise information about the presence or absence of diseases.
Early diagnosis for better treatment – Detecting conditions early allows for more effective treatment strategies.
Essential for cancer detection – A biopsy is often the only way to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
Types of Biopsies and Their Uses
Needle Biopsy
A needle biopsy is a minimally invasive procedure used to extract a tissue sample using a thin or hollow needle. It is commonly used for diagnosing lumps or abnormalities in organs such as the liver, thyroid, or breast.
Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) – Uses a thin needle to extract fluid or small tissue samples.
Core needle biopsy – Utilizes a larger needle to collect a bigger tissue sample for better analysis.
Minimally invasive and quick – Often performed under local anesthesia with minimal discomfort.
Surgical Biopsy
When a larger tissue sample is needed, a surgical biopsy is performed through a minor surgical procedure.
Excisional biopsy – The entire lump or abnormal tissue is removed for examination.
Incisional biopsy – Only a portion of the abnormal tissue is extracted for testing.
Used when needle biopsy is inconclusive – Helps provide a more comprehensive analysis.
Skin Biopsy
Skin biopsies help diagnose skin conditions such as infections, rashes, and skin cancer. The procedure involves removing a small sample of skin tissue.
Punch biopsy – A circular tool is used to extract a deep skin sample.
Shave biopsy – The top layers of skin are shaved off for analysis.
Quick recovery and minimal scarring – Performed under local anesthesia with minimal side effects.
Bone Marrow Biopsy
A bone marrow biopsy is used to diagnose blood disorders, leukemia, and other bone marrow-related conditions.
Extracts bone marrow tissue – Usually taken from the hip bone.
Assesses blood cell production – Helps in diagnosing anemia, infections, and cancers.
Performed under local anesthesia – Mild discomfort, but essential for evaluating bone marrow health.
Endoscopic Biopsy
An endoscopic biopsy uses a flexible tube with a camera (endoscope) to examine internal organs and collect tissue samples.
Used for gastrointestinal, respiratory, and urinary tract issues – Helps diagnose conditions affecting the stomach, intestines, lungs, and bladder.
Minimally invasive – Inserted through natural body openings or small incisions.
Provides real-time imaging and precision – Ensures targeted tissue sampling.
Why a Biopsy is Performed
Detecting Cancer and Other Diseases
A biopsy is the most reliable method for confirming or ruling out cancer. It can also diagnose infections, autoimmune diseases, and other chronic conditions.
Essential for cancer staging – Helps determine how far cancer has spread.
Guides treatment decisions – Provides critical information for personalized treatment plans.
Assesses tumor type and aggressiveness – Helps predict disease progression.
Evaluating Abnormal Growths or Lumps
When abnormal growths are found through imaging tests like ultrasounds or MRIs, a biopsy helps determine if they are benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous).
Prevents unnecessary surgeries – Confirms if a lump is harmless before proceeding with invasive procedures.
Identifies infections and inflammatory conditions – Helps diagnose chronic diseases affecting organs.
The Biopsy Procedure: What to Expect
Preparing for a Biopsy
Preparation depends on the type of biopsy being performed. Some biopsies require fasting or stopping certain medications beforehand.
Medical history review – A complete health assessment ensures safety during the procedure.
Fasting and medication adjustments – Some biopsies require dietary restrictions or stopping blood thinners.
Discussing anesthesia options – Local or general anesthesia may be used based on the biopsy type.
Most biopsy procedures are quick and performed on an outpatient basis. The process varies depending on the method used.
Needle biopsies are fast and painless – Typically completed in under 30 minutes with minimal discomfort.
Surgical biopsies may require stitches – Longer recovery time but provides larger tissue samples.
Endoscopic biopsies involve mild sedation – Patients may experience slight discomfort but recover quickly.
Post-Biopsy Recovery and Care
After the procedure, patients need to follow specific aftercare instructions to ensure proper healing and avoid complications.
Mild soreness and swelling are common – Pain relievers and rest help in recovery.
Follow wound care instructions – Keeping the biopsy site clean prevents infections.
Wait for lab results – Biopsy results usually take a few days to a week.
Understanding Biopsy Results
Possible Outcomes
Biopsy results help determine the next steps in treatment. The three main types of results include:
Normal (benign) – No signs of disease; no further treatment needed.
Abnormal but non-cancerous – Conditions like infections or benign tumors may require treatment.
Cancerous (malignant) – Further testing and treatment plans will be discussed based on findings.
Next Steps After a Biopsy
Based on the biopsy results, a treatment plan is developed.
If results are normal, no further action is needed – Routine monitoring may be advised.
For infections or inflammatory diseases, medications may be prescribed – Treatment depends on the underlying cause.
If cancer is detected, further tests are done – Staging and treatment options like surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy are considered.
Risks and Complications of a Biopsy
While biopsies are generally safe, minor risks can occur, including:
Bleeding or bruising at the biopsy site – Usually resolves within a few days.
Infection risk – Proper wound care minimizes the chances of infection.
Mild pain or swelling – Temporary discomfort managed with over-the-counter pain relievers.
Choosing the Right Biopsy Method
Factors to Consider
Different biopsy techniques are used based on the suspected condition, location of the tissue, and patient health.
Minimally invasive options are preferred – Needle and endoscopic biopsies reduce recovery time.
Surgical biopsies are used for larger tissue samples – Needed when less invasive methods don’t provide enough information.
Advanced imaging guides precision biopsies – Ultrasound or CT-guided biopsies improve accuracy.
How Biopsies Improve Diagnosis and Treatment
Biopsy for diagnostic purposes plays a vital role in identifying diseases at an early stage, leading to more effective treatments.
Accurate diagnosis leads to targeted treatment – Helps in avoiding unnecessary procedures.
Essential for personalized medicine – Ensures the most effective treatment plan for each patient.
Increases chances of early disease detection – Improves prognosis for many conditions.
Conclusion
Biopsy for diagnostic purposes is an essential medical tool that helps detect diseases, confirm diagnoses, and guide treatment plans. Whether it’s a needle biopsy, surgical biopsy, or endoscopic biopsy, the procedure provides critical insights into a patient’s health. Understanding the process, results, and recovery helps reduce anxiety and ensures a smooth experience. If a biopsy is recommended, following professional advice and proper aftercare will contribute to better health outcomes.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.