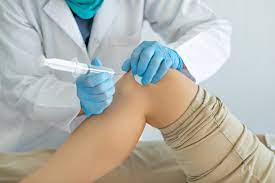
A Closer Look at Stem Cell Therapy for Chronic Pain
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
Stem cell therapy for chronic pain is emerging as a revolutionary treatment option, offering potential relief for those suffering from long-term pain conditions that traditional therapies often fail to address. Chronic pain, whether resulting from arthritis, injury, or degenerative diseases, can severely impact quality of life. While pain medications and physical therapies provide temporary relief, stem cell therapy offers a regenerative approach that targets the root causes of pain, such as damaged tissues and inflamed joints. As the field of regenerative medicine advances, Stem Cell Therapy(العلاج بالخلايا الجذعية) are gaining traction as a promising alternative for managing chronic pain.
What Is Chronic Pain and How Does It Affect the Body?
Chronic pain is defined as pain that persists for more than three months, often outlasting the expected healing time of an injury or illness. It can stem from a variety of conditions, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, back pain, fibromyalgia, and nerve damage. Unlike acute pain, which is a natural response to injury, chronic pain continues even after the original cause has healed, often due to nerve damage or ongoing inflammation. Chronic pain can affect every aspect of a person’s life, leading to mobility issues, reduced functionality, and mental health challenges such as depression and anxiety. Traditional treatments, including pain medications, physical therapy, and surgery, often offer only temporary relief and come with side effects or complications.
The Role of Stem Cells in Treating Chronic Pain:
Stem cells offer a novel approach to managing chronic pain by addressing its root causes, such as inflammation, tissue degeneration, and nerve damage. Stem cells can regenerate damaged tissues, promote healing, and reduce inflammation, which is often the underlying cause of chronic pain. When injected into the affected area, stem cells can differentiate into specialized cells, such as cartilage, bone, or muscle cells, and help repair damaged tissues. This regenerative effect not only alleviates pain but also promotes long-term healing by restoring normal tissue function and improving mobility.
Types of Stem Cells Used in Chronic Pain Treatment:
Several types of stem cells are used in the treatment of chronic pain, each offering unique benefits and challenges. The most common stem cells used in pain management include:
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs): These adult stem cells, typically harvested from sources like bone marrow or adipose tissue, have the ability to differentiate into a variety of cell types, including cartilage, bone, and muscle cells. MSCs have shown promising results in treating joint pain, back pain, and conditions like osteoarthritis by promoting tissue regeneration and reducing inflammation.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs): iPSCs are adult cells that have been reprogrammed to become pluripotent, meaning they can differentiate into any type of cell in the body. While iPSCs are still in the experimental stage for chronic pain treatment, they hold great potential due to their versatility and the ability to be generated from a patient’s own cells, minimizing the risk of immune rejection.
Stem Cell Therapy for Joint and Back Pain:
One of the most common uses of stem cell therapy for chronic pain is in treating joint and back pain, particularly for conditions like osteoarthritis and degenerative disc disease. In osteoarthritis, the cartilage in the joints deteriorates over time, leading to pain, swelling, and stiffness. Stem cells can be injected into the affected joint, where they differentiate into cartilage cells and promote tissue regeneration. Similarly, in cases of chronic back pain caused by degenerative disc disease, stem cells can be injected into the damaged spinal discs to regenerate healthy tissue, alleviate pain, and improve mobility. Early studies and clinical trials have shown promising results, with patients reporting significant pain relief and improved function after stem cell injections.
Stem Cells for Nerve Pain:
Chronic nerve pain, or neuropathy, can result from conditions like diabetes, nerve injury, or autoimmune disorders. Traditional treatments for nerve pain, such as medications and nerve blocks, often provide limited relief. Stem cell therapy is showing potential in repairing nerve damage by promoting nerve regeneration. By injecting neural stem cells (NSCs) or MSCs into the affected area, researchers hope to stimulate the regrowth of healthy nerve cells, alleviate pain, and improve nerve function. Although more research is needed, early results suggest that stem cells may be able to repair damaged nerves and offer long-term relief from chronic neuropathic pain.
Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy for Chronic Pain:
Stem cell therapy offers several advantages over traditional pain management treatments. One of the primary benefits is its ability to regenerate damaged tissues and promote healing, providing a long-term solution for chronic pain rather than just masking the symptoms. Additionally, stem cell therapy is minimally invasive, often requiring only injections into the affected area, which reduces the need for major surgeries and lengthy recovery times. Stem cells also have the potential to reduce the need for pain medications, which can be addictive and come with a range of side effects. Furthermore, because stem cells can be sourced from the patient’s own body, the risk of rejection or complications is minimized.
A Natural Alternative to Pain Medications:
Stem cell therapy offers a natural alternative to pain medications, which are often prescribed for chronic pain management. While opioids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can provide short-term relief, they do not address the underlying causes of pain and can lead to dependence, side effects, and long-term health risks. Stem cells, on the other hand, promote healing from within, allowing the body to regenerate damaged tissues and reduce inflammation. This natural approach can lead to longer-lasting pain relief and a reduction in the need for medications.
Challenges and Considerations in Stem Cell Therapy for Pain:
Despite the promising potential of stem cell therapy for chronic pain, there are still several challenges to overcome. One of the primary obstacles is the need for more large-scale clinical trials to fully understand the long-term efficacy and safety of stem cell treatments. Although early results have been encouraging, more data is needed to confirm the benefits and identify potential risks. Additionally, the cost of stem cell therapy can be prohibitive, and insurance coverage for these treatments is often limited. Standardization of treatment protocols is also necessary to ensure consistent and reliable results across different patient populations.
Future Prospects for Stem Cell Therapy in Pain Management:
As stem cell technology advances, the future of chronic pain treatment looks promising. Ongoing research into stem cell-based therapies, along with advances in gene editing and tissue engineering, may further enhance the effectiveness of these treatments. With continued clinical trials and improvements in stem cell science, stem cell therapy could become a mainstream treatment for chronic pain, offering patients a safer, more sustainable alternative to traditional pain management methods.
In conclusion, Stem Cell Therapy(العلاج بالخلايا الجذعية) is a transformative approach to treating chronic pain, providing long-term relief by addressing the underlying causes of tissue damage and inflammation. While still in its early stages, stem cell therapy has shown great potential in treating conditions like joint pain, back pain, and nerve pain, offering a regenerative solution that can improve quality of life. As research continues and clinical trials progress, stem cell therapy may become a key tool in managing chronic pain, providing patients with a more effective, natural alternative to traditional pain medications and surgeries.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.