Blockchain Technology Market: A New Dawn for Secure Digital Payments
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
Introduction
✍️ The rise of DeFi is one of blockchain’s biggest success stories. Read our article on blockchain in decentralized finance to discover how traditional banking is being disrupted.
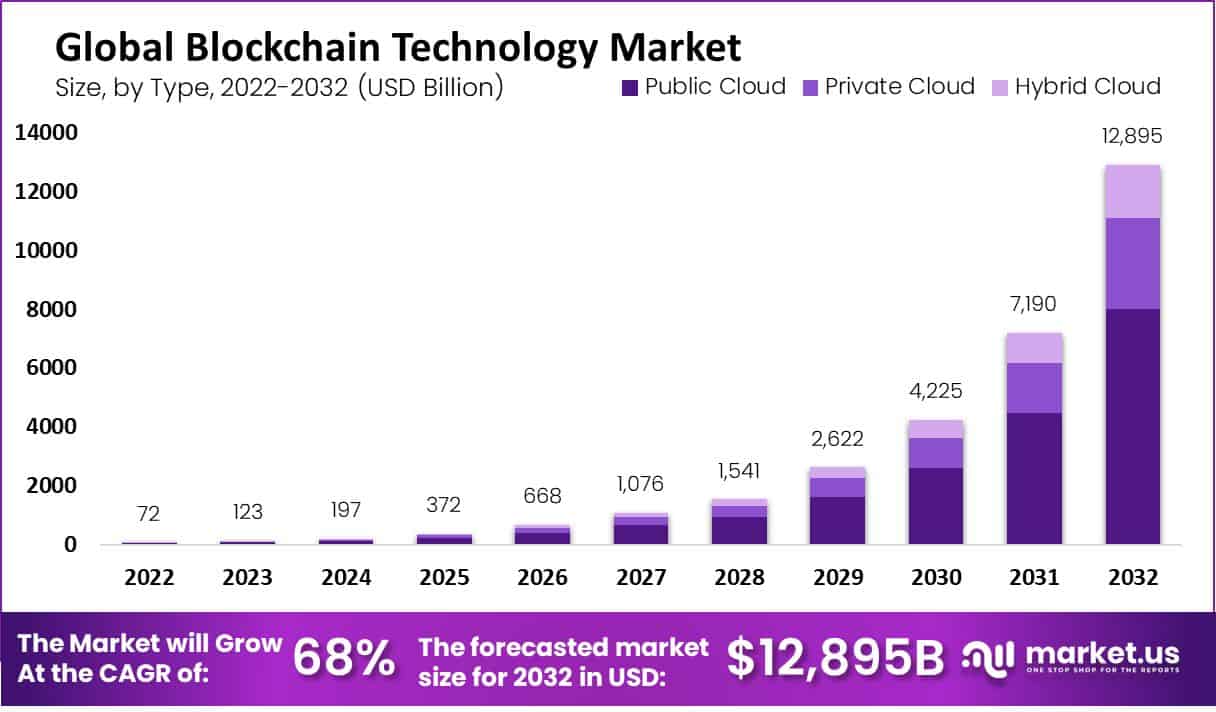
Blockchain technology is transforming industries with its ability to provide secure, decentralized data management. It is rapidly gaining traction due to its potential to enhance transparency and efficiency in transactions.
Read More - https://market.us/report/blockchain-technology-market/
Key growth factors include the rising adoption of blockchain in financial services, increasing interest from businesses in blockchain's potential to streamline processes, and the integration of blockchain with emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT). However, the market faces several challenges, such as regulatory uncertainties, scalability issues, and the need for a more skilled workforce. Despite these hurdles, there are substantial opportunities for new entrants to innovate and offer unique solutions, especially in the areas of blockchain-as-a-service (BaaS) and enterprise applications.
Emerging Trends
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): DeFi leverages blockchain to provide financial services without intermediaries, offering lending, borrowing, and trading platforms that are open to anyone with internet access.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): NFTs have revolutionized digital ownership by providing a way to represent unique digital assets on the blockchain, impacting art, music, and gaming industries.
Blockchain Interoperability: Solutions are being developed to allow different blockchain networks to communicate and exchange information, fostering a more integrated blockchain ecosystem.
Sustainability: There is a growing focus on creating eco-friendly blockchain technologies to reduce the carbon footprint associated with energy-intensive processes like mining.
Government Initiatives: Increasingly, governments are exploring blockchain for applications in identity verification, land registries, and transparent governance practices.
Top Use Cases
Cryptocurrency Transactions: The most prominent use of blockchain, providing a secure and transparent method for conducting transactions with digital currencies.
Supply Chain Management: Blockchain helps in tracking the provenance and movement of goods, ensuring authenticity and reducing fraud in the supply chain.
Smart Contracts: These are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code, enabling automated and trustless agreements.
Digital Identity Management: Blockchain-based digital identities provide secure and verifiable identification, reducing fraud and streamlining access to services.
Healthcare: Blockchain can securely store and share patient records, improving data privacy and interoperability across healthcare providers.
Major Challenges
Regulatory Uncertainty: The absence of clear and consistent regulations worldwide poses a significant obstacle to the widespread adoption of blockchain technology.
Scalability: Blockchain networks, especially public ones, often struggle with processing large volumes of transactions quickly and cost-effectively.
Security Risks: While blockchain itself is secure, the associated applications and platforms can be vulnerable to hacks and cyberattacks.
High Energy Consumption: Certain blockchain processes, particularly mining, consume large amounts of energy, raising concerns about environmental sustainability.
Interoperability Issues: The lack of standards and protocols for different blockchains to work together seamlessly remains a technical challenge.
Market Opportunity
Enterprise Blockchain Solutions: Companies are increasingly seeking blockchain solutions to improve transparency, traceability, and efficiency in various business processes.
Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS): This model allows businesses to adopt blockchain technology without needing to develop in-house expertise, offering a scalable solution for various applications.
Tokenization of Assets: Blockchain can tokenize physical and digital assets, simplifying their transfer and trading while reducing costs and increasing liquidity.
Decentralized Applications (DApps): These applications operate on blockchain networks and offer a range of services from gaming to finance, providing new ways for users to interact and transact.
Cross-Border Payments: Blockchain facilitates faster, cheaper, and more secure cross-border transactions, making it a valuable tool for international trade and remittances.
Conclusion
The blockchain technology market is poised for substantial growth, driven by its potential to revolutionize various sectors with enhanced security, efficiency, and transparency.
While challenges like regulatory uncertainty and scalability issues remain, the opportunities for innovation are immense. New entrants can capitalize on emerging trends and develop solutions that address existing gaps in the market. As blockchain continues to evolve, it holds the promise of creating a more secure, transparent, and connected global economy.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.







