Difference Between TCP and UDP in Computer Networks Explained
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
When we talk about data transmission in computer networks, TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol) are two of the most vital transport layer protocols. Whether you're doing Azure fundamentals training or exploring checkpoint courses, learning the difference between TCP and UDP is quite important for anyone in networking, cybersecurity, or cloud computing.
In this UniNets blog, we will discuss the major differences between TCP and UDP, examine real-life scenarios, and demonstrate how this information intersects with transmission media in computer networks, cloud environments such as Microsoft Azure, and security protocols learned in checkpoint training.
What is TCP?
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is an association-oriented protocol created to provide guaranteed data transfer between a pair of devices. TCP initiates a connection prior to sending data, confirms that data is delivered in the correct order, and retransmits missing packets.
Important characteristics:
Guaranteed delivery
Association-oriented communication
Packet ordering
Error detection and correction
Slower because of overhead
TCP is widely implemented in scenarios where data integrity is significant, including web surfing (HTTP/HTTPS), email sending (SMTP), and file transfer (FTP). In Microsoft Azure Fundamentals, knowing TCP aids in setting up secure, consistent connections for virtual machines and services.
What is UDP?
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is a connectionless protocol that transmits data without creating a connection. It does not ensure delivery, order, or error checking, which makes it quicker and more efficient in certain applications.
Key features:
Unreliable delivery
Connectionless communication
No sequencing
No error correction
Lightweight and fast
UDP is well suited for real-time applications such as video streaming, VoIP, DNS queries, and gaming, where speed is more desirable than reliability.
TCP vs UDP: A Comparison Table
Feature TCP UDP
Connection Connection-oriented Connectionless
Reliability Reliable Unreliable
Speed Slower Faster
Data Ordering Guaranteed Not guaranteed
Overhead High Low
Use Cases
HTTP, FTP, Email
DNS, VoIP, Streaming
Knowing this TCP and UDP difference is a fundamental part of checkpoint training and Azure fundamentals training at UniNets. These protocols are crucial in designing high-performance and secure networks.
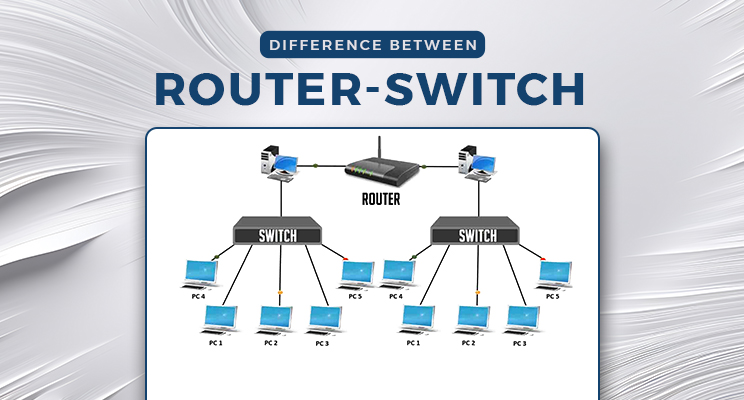
How Transmission Media Affects TCP and UDP
The behavior of TCP and UDP can differ depending upon the transmission media in computer networks. For instance, TCP performs optimally in stable and high-speed environments, like fiber optic transmission media, where packet loss is low. However, UDP could be better in less stable environments (like Wi-Fi or cellular networks), with a penalty of packet loss.
Types of Transmission Media that Affect Performance:
Twisted Pair Cable: Popular in LANs, can support both TCP and UDP but does not have much bandwidth.
Coaxial Cable: Provides better shielding and is suitable for reliable TCP connections.
Fiber Optic Cable: Suitable for high-speed TCP communications in data center and cloud environments.
Wireless Media (Radio, Microwave): More likely to lose packets; affects TCP more than UDP.
In checkpoint courses, students examine how transmission media types affect the TCP and UDP behavior when implementing firewalls and intrusion detection.
TCP and UDP in Microsoft Azure
When learning Microsoft Azure basics, you'll come across various services and settings where choosing TCP or UDP is required. For example:
Azure Load Balancer: Configurable for both TCP and UDP-traffic-based configurations.
Azure VPN Gateway: Generally employs UDP for tunneling.
Azure Virtual Network (VNet): Uses TCP for secure connectivity among services.
A course on Azure fundamentals at UniNets teaches students when to use TCP vs UDP based on the performance, security, and reliability requirements of the cloud setup.
Why This Knowledge is Important in Checkpoint Training
In checkpoint training, an understanding of the distinction between TCP and UDP is critical in firewall rules configuration, traffic inspection, and VPN or security policy setup. Firewalls would have to allow or block traffic on the basis of protocol types, ports, and services quite often—hence it becomes important to distinguish between TCP's handshake mechanism and UDP's quick, open behavior.
At UniNets, we implement TCP/UDP analysis in our checkpoint courses by using real-time lab environments. Students replicate actual attacks, set filters, and analyze packet behavior on various transmission media.
Real-World Use Cases
1. TCP Use Case: File Upload on Azure Storage
The file upload using Microsoft Azure Blob Storage employs TCP to receive the file accurately.
2. UDP Use Case: VoIP in Enterprise Networks
VoIP operations, including those with Microsoft Teams or third-party applications, use UDP for low-latency transmission even on wireless transmission media.
Conclusion
Knowing the distinction between TCP and UDP is essential for anyone who is about to venture into networking, cloud computing, or cybersecurity. The two protocols, along with the appropriate forms of transmission media, condition the manner in which data moves between networks.
At UniNets, we get you industry-ready with instructor-led training in Azure essentials, checkpoint courses, and end-to-end network infrastructure. You'll have hands-on practice with network configuration, traffic analysis, and protocol decision-making based on use cases.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.