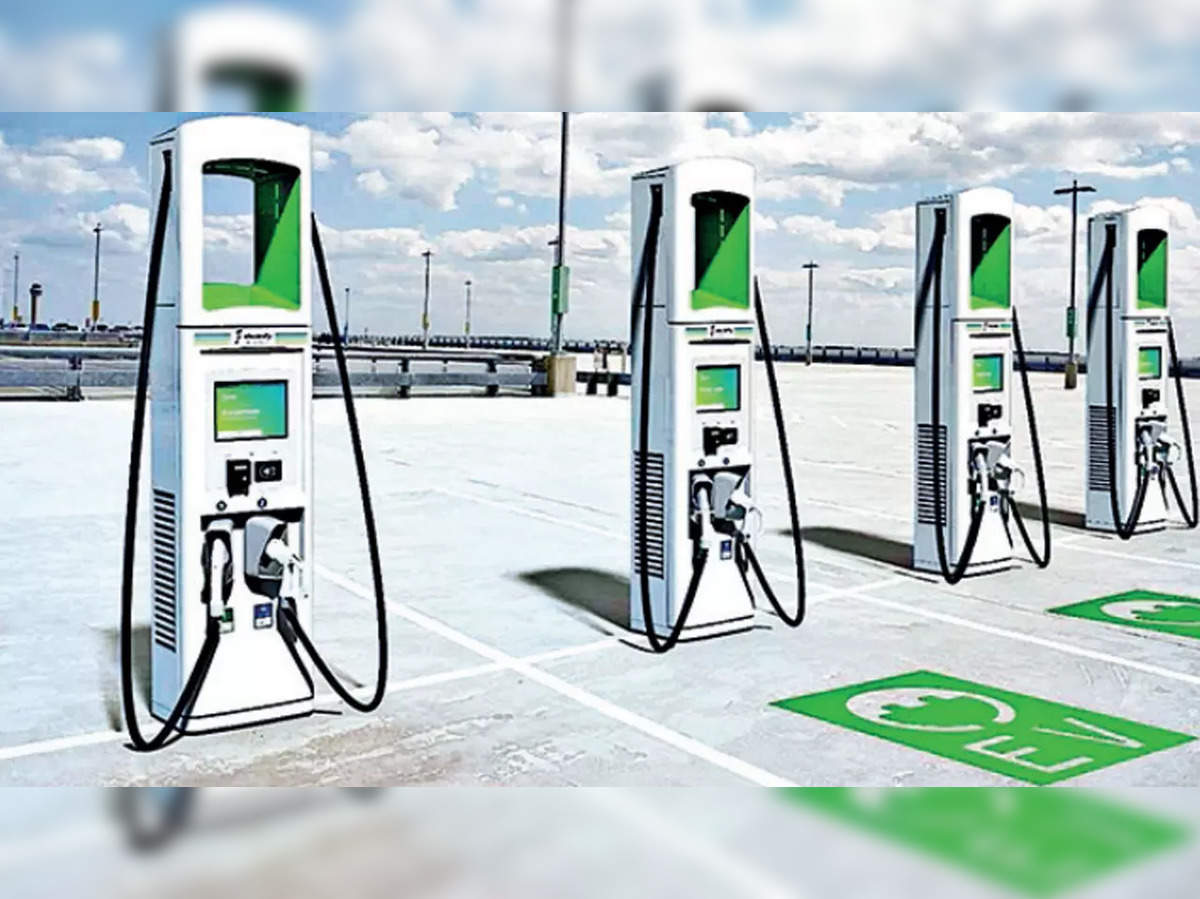
Evaluating Japan 30,000+ Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Stations Based on Various Parameters

Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
Introduction:
Japan is leading the charge in the transition to electric vehicles (EVs) with a comprehensive infrastructure network of over 30,000 charging stations. This impressive network, which is projected to expand even further by 2030, plays a crucial role in Japan's green energy efforts, offering a seamless transition for consumers adopting electric mobility. In this article, we will evaluate the parameters driving the expansion of Japan’s EV charging stations, with a specific focus on how Japan is future-proofing its EV infrastructure by integrating smart grid technology.
The Growth of EV Charging Stations in Japan
The rapid rise in the number of EV Charging stations in Japan is a direct result of government initiatives, private-sector investment, and consumer demand for greener mobility options. With ambitious environmental goals in place, such as achieving carbon neutrality by 2050, Japan has committed to significantly reducing its reliance on fossil fuels by promoting electric vehicle adoption. The country aims to have over 30,000 charging stations installed by 2030, making it one of the most robust EV infrastructure networks globally.
The government has incentivized this transition with financial incentives for EV buyers and manufacturers, and more recently, the push for infrastructure expansion has been emphasized. Local governments and businesses are increasingly contributing to the growth of EV charging stations, placing a high priority on both fast and public-accessible charging solutions. But with such rapid expansion, it’s essential to understand how Japan’s charging infrastructure is evolving to meet the long-term needs of EV owners and the larger grid.
Smart Grid Technology and Its Role in EV Charging
As electric vehicles continue to become more popular in Japan, the demand for charging stations is rising at an unprecedented rate. A crucial factor in managing this demand, especially in a country with a high population density, is the integration of smart grid technology. Smart grids allow for the efficient distribution of electricity across various sectors, particularly during peak charging hours.
Japan is embracing smart grid technology to ensure that its EV charging infrastructure is capable of managing the increased electricity demand without compromising grid stability. Smart grids enable the dynamic management of energy distribution, providing benefits like optimized energy usage, the ability to integrate renewable energy sources, and, importantly, future-proofing the infrastructure.
How Japan’s EV Charging Stations Are Adapting to Smart Grid Technology
Enhanced Energy Efficiency and Grid Management
The integration of smart grid technology into Japan's EV charging network allows charging stations to better coordinate with the electrical grid. This coordination prevents the grid from becoming overloaded during periods of high demand, which is particularly important for balancing electricity use across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors.
With smart grids, charging stations can communicate with each other and the grid, allowing utilities to adjust the energy flow and charging speeds based on real-time demand. For instance, during off-peak hours, when electricity demand is low, charging stations can charge vehicles at higher speeds, whereas, during peak demand hours, charging can be slowed down to avoid overloading the grid. This flexibility ensures that energy consumption remains efficient and sustainable.
Seamless Integration with Renewable Energy Sources
Japan’s push toward renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, is another reason why smart grid technology is a key component of its EV infrastructure. Smart grids facilitate the integration of these renewable energy sources into the grid, making it possible to charge electric vehicles using clean energy. By utilizing energy storage solutions in combination with EV charging stations, excess energy from renewable sources can be stored and used to charge EVs when needed.
For example, many public EV charging stations are being equipped with solar panels, allowing them to generate their own electricity during the day. This electricity can then be stored in battery storage systems for use during nighttime charging or on cloudy days. By relying on renewable energy sources, smart grid technology helps Japan’s EV charging stations contribute to the country’s sustainability goals.
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Capabilities
An exciting development in Japan’s EV charging stations is the potential for vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology. V2G allows electric vehicles to not only draw energy from the grid but also feed energy back into the grid when necessary. This bi-directional energy flow can be managed through smart grid systems, which allows EV owners to sell excess electricity stored in their car batteries back to the grid during peak hours.
This capability enhances the flexibility and stability of the grid, reduces the need for additional energy generation during peak times, and provides financial incentives for EV owners. Japan is exploring the integration of V2G capabilities within its charging infrastructure, which would create an additional layer of value for EV owners while contributing to grid stability.
Real-Time Data and Charging Optimization
Smart grid technology enables real-time data collection from EV charging stations, which is used to optimize energy distribution and enhance user experience. For example, charging stations can provide EV owners with real-time information on charging availability, energy usage, and optimal times for charging based on grid demand.
This data can also be used by utility companies to predict peak charging periods, improving their ability to plan for future energy needs. Additionally, this data-sharing creates a more user-friendly experience for EV owners, as it can help them plan their charging sessions to avoid crowded stations or high-demand times.
Support for DC Fast-Charging Stations
As part of Japan’s EV infrastructure upgrade, many charging stations are being equipped with direct current (DC) fast chargers, which allow electric vehicles to recharge much faster than with traditional alternating current (AC) chargers. With the integration of smart grid technology, these fast-charging stations can be more easily managed during periods of high demand. By balancing energy distribution, smart grids ensure that EVs can continue to charge quickly without putting unnecessary strain on the grid.
The Future of EV Charging Infrastructure in Japan
The continued expansion of Japan’s EV charging infrastructure will rely heavily on the successful integration of smart grid technology. By future-proofing charging stations with grid coordination, renewable energy integration, and V2G capabilities, Japan is ensuring that its EV infrastructure will not only support the growing number of electric vehicles on the road but also contribute to the country’s environmental and energy efficiency goals.
The Japanese government’s proactive approach to EV infrastructure, combined with innovations in smart grid technology, is setting a global standard for sustainable mobility. The investment in this technology, as well as the collaboration between public and private sectors, is shaping the future of electric vehicle adoption in Japan.
Conclusion
Japan’s EV charging infrastructure is rapidly growing and adapting to meet the needs of the country’s increasing number of electric vehicles. By integrating smart grid technology, Japan is enhancing the efficiency, sustainability, and resilience of its charging stations. This smart infrastructure not only optimizes the energy distribution process but also helps create a more sustainable and future-proofed EV ecosystem.
The shift toward clean energy solutions and electric mobility is reshaping the transportation landscape in Japan, and the adoption of smart grids is a key driver of this change. As Japan continues to expand its charging network, the integration of cutting-edge technologies will ensure that it remains at the forefront of the global transition to electric vehicles.
Read the complete blog
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.