DA 70+ Guest Post Placements – Elite Authority at Your Fingertips!
DA 70+ Guest Post Placements – Elite Authority at Your Fingertips!
How Do Doctors Diagnose the Causes of Chronic Stomach Pain
Written by Dinesh » Updated on: June 17th, 2025

INTRODUCTION
Chronic stomach pain is a persistent and uncomfortable issue that many people face. It can range from mild to severe and often lasts for several weeks or months. As Dr. Dinesh Reddy, the best gastroenterologist in Hyderabad, I often encounter patients who are struggling to understand why they are experiencing chronic stomach pain. Diagnosing the cause of this pain is essential for finding the right treatment.
In this article, I will walk you through the various ways doctors diagnose the causes of chronic stomach pain. By understanding the steps involved, you can better appreciate the process and feel more confident in managing your health.
Understanding Chronic Stomach Pain
Before diving into the diagnostic process, it’s important to understand what chronic stomach pain is. Chronic stomach pain refers to ongoing discomfort in the abdominal region, lasting for more than three months. The pain can be intermittent or constant, sharp or dull, and it can be caused by many factors, ranging from digestive issues to more serious conditions.
For doctors, diagnosing the root cause of chronic stomach pain is challenging because there are numerous potential sources, including digestive disorders, infections, food intolerances, or even stress.
Patient History and Symptoms
The first step any gastroenterologist will take in diagnosing chronic stomach pain is gathering a detailed patient history. This is crucial because it provides valuable clues about what could be causing the pain.
Duration of Pain: The doctor will ask how long the pain has lasted. Is it a recent problem, or has it been present for several months? Chronic pain usually lasts for more than three months.
Location of Pain: The location of the pain is another key indicator. Is the pain in the upper, middle, or lower abdomen? Is it focused on one area or spread across the entire stomach? For example, pain in the upper right quadrant may suggest gallbladder issues, while lower abdominal pain might indicate a problem with the intestines.
Nature of the Pain: Understanding the nature of the pain is important. Is it sharp, dull, cramping, or burning? Does the pain come and go, or is it constant? These details help doctors narrow down possible causes.
Associated Symptoms: Doctors will also ask about any additional symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, bloating, weight loss, or changes in bowel movements. These symptoms help identify whether the issue may be related to the digestive system.
Physical Examination
Once the doctor has collected information from the patient, the next step is a physical examination. During this exam, the gastroenterologist will check the abdomen for any signs of tenderness, swelling, or masses.
Abdominal Tenderness: By pressing on different areas of the abdomen, the doctor can identify regions of tenderness, which may point to specific organs or issues.
Bloating or Distension: Swelling in the abdomen can indicate the presence of gas, fluid, or an enlarged organ.
Signs of Inflammation: Redness or warmth on the skin over the abdomen might suggest underlying inflammation, which could be a sign of conditions such as appendicitis or an infection.
Diagnostic Tests
After the initial assessment, the doctor may recommend a series of diagnostic tests to further investigate the cause of the chronic stomach pain. Some of the most common tests used by gastroenterologists include:
1. Blood Tests
Blood tests are often one of the first diagnostic tools used. They help doctors identify infections, inflammation, or abnormalities in organ function. Common blood tests include:
Complete Blood Count (CBC): A CBC checks for signs of infection or anemia, which could indicate conditions like ulcers or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Liver Function Tests: These tests check the health of the liver and can help identify liver diseases such as hepatitis.
Pancreatic Enzymes: High levels of certain enzymes can indicate issues with the pancreas, such as pancreatitis.
2. Stool Tests
Stool tests are used to check for infections, parasites, or blood in the stool. These tests are particularly useful if the patient is experiencing changes in bowel movements, such as diarrhea or constipation. Conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), Crohn's disease, and infections can often be diagnosed through stool analysis.
3. Imaging Studies
Imaging studies are crucial for visualizing the internal organs and identifying structural problems that could be causing chronic stomach pain.
Ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of the organs inside the abdomen. It is commonly used to examine the gallbladder, liver, and pancreas for signs of inflammation, stones, or other abnormalities.
CT Scan (Computed Tomography): A CT scan provides detailed images of the abdomen, allowing doctors to see any potential problems with the intestines, kidneys, or liver. It is especially helpful in diagnosing conditions like appendicitis, diverticulitis, or tumors.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): MRI uses magnetic fields to produce detailed images of the abdomen. It is often used when doctors need to assess the soft tissues of the digestive system, such as in cases of Crohn's disease or tumors.
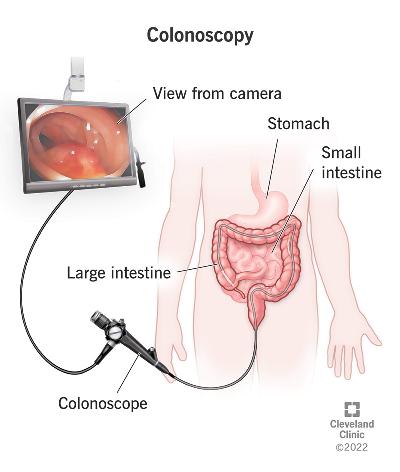
4. Endoscopy and Colonoscopy
Endoscopic procedures allow doctors to directly view the inside of the digestive tract. These tests are highly effective in diagnosing gastrointestinal conditions that cause chronic stomach pain.
Upper Endoscopy: During an upper endoscopy, a flexible tube with a camera is inserted through the mouth to examine the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine. This procedure helps diagnose issues like ulcers, gastritis, and acid reflux.
Colonoscopy: A colonoscopy involves inserting a camera through the rectum to examine the colon and large intestine. It is used to detect conditions such as colon cancer, polyps, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Specialized Tests
In some cases, doctors may need to perform more specialized tests to diagnose the cause of chronic stomach pain. These tests include:
Lactose Intolerance Test: This test checks whether the patient can properly digest lactose, a sugar found in dairy products. Lactose intolerance can cause bloating, gas, and stomach pain.
H. pylori Test: H. pylori is a type of bacteria that can cause stomach ulcers and inflammation. Doctors can test for H. pylori through a breath test, stool test, or biopsy during an endoscopy.
Capsule Endoscopy: In cases where traditional endoscopy does not provide enough information, doctors may use capsule endoscopy. The patient swallows a small camera in the form of a capsule, which captures images of the digestive tract as it moves through the body.
Diagnosing Specific Conditions
Once the diagnostic tests are complete, the doctor can begin narrowing down potential causes of chronic stomach pain. Some common conditions that cause chronic stomach pain include:
Gastritis: Inflammation of the stomach lining, often caused by infections, medications, or excessive alcohol consumption.
Peptic Ulcers: Open sores in the stomach or small intestine, often caused by H. pylori infection or the overuse of NSAID pain relievers.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): A functional disorder that affects the large intestine, causing symptoms like cramping, bloating, and changes in bowel habits.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): A group of conditions, including Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, that cause chronic inflammation of the digestive tract.
Gallstones: Hard deposits in the gallbladder that can cause severe abdominal pain, particularly after eating fatty foods.
Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas, which can cause sharp, severe pain in the upper abdomen.
Conclusion
Diagnosing the cause of chronic stomach pain is a detailed process that involves gathering a thorough medical history, conducting a physical examination, and using a variety of diagnostic tests. As a gastroenterologist, my goal is to accurately identify the underlying issue and provide the best possible treatment for my patients.
If you are experiencing chronic stomach pain, it’s important to seek medical attention early. Proper diagnosis is the key to managing the condition effectively and improving your quality of life.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.
Copyright © 2019-2025 IndiBlogHub.com. All rights reserved. Hosted on DigitalOcean for fast, reliable performance.