"How Turbine Pumps Revolutionize High-Pressure Fluid Transfer in Industrial Operations"
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
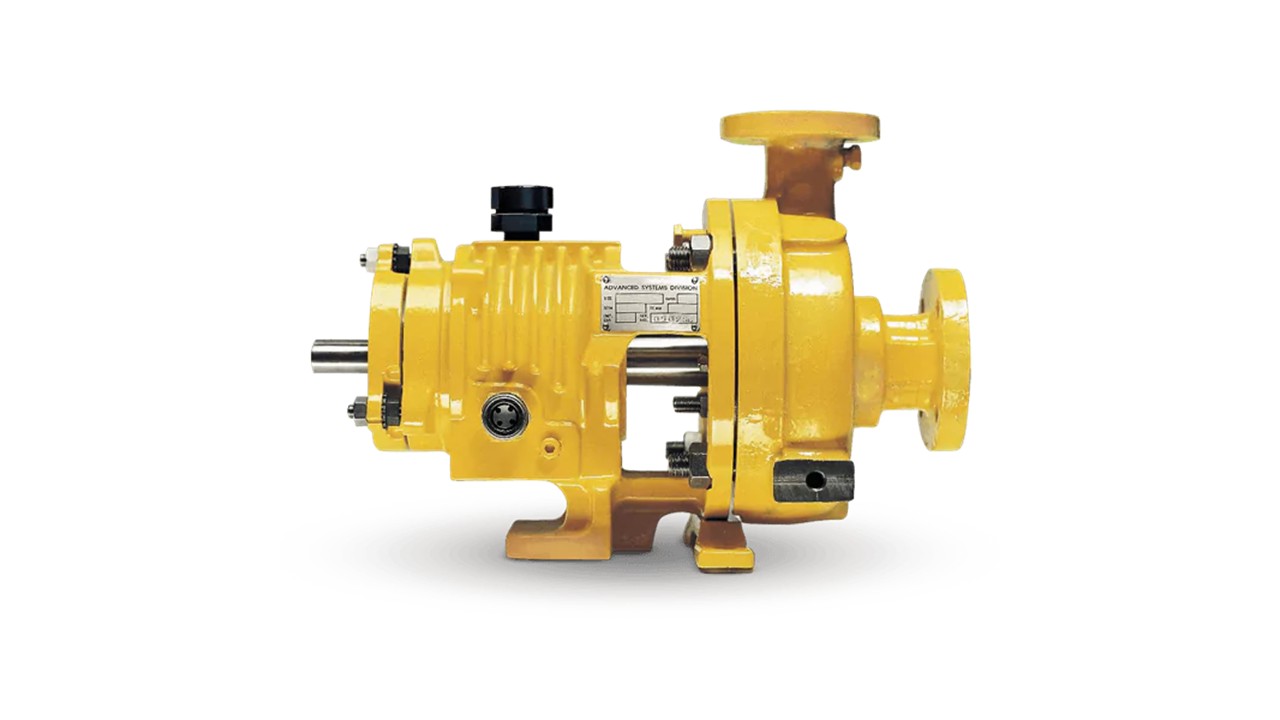
"A turbine pump is a rotodynamic pump particularly employed for fluid transfer owing to the kinetic energy developed by a revolving impeller." The pumps are particularly of choice for applications in various processes with a medium flow rate and relatively high head."
Principles of Operation
The functioning of a turbine pump is based on the conversion of the moving impeller's energy of rotation to the fluid. Impellers consist of curved vanes as an array of vanes which are moving in a casing. When the fluid is fed to the pump, motion energy is imparted to the fluid by the revolving vanes on the impeller which increases fluid velocity. The fluid is then forced into a volute or diffuser where motion energy converts to pressure energy. The conversion of energy results in greater pressure at the pump's discharge than at its inlet.
Key Components
The main parts of a turbine pump are:
Impeller: The turning part with curved vanes which gives the fluid its kinetic energy.
Casing: The Outer casing is above the impeller and regulates the flow of the fluid.
Diffuser or Volute: A device converting the energy of motion of the fluid into pressure energy.
Shaft: The rotating component joining the impeller to the motor or drive.
Bearings: Support the shaft and allow it to turn without any resistance.
Seals: Keep the fluid from leaking out of the pump.
Types of Turbine Pumps
There are dissimilar types of turbine pumps, and every type is appropriate for specific applications. Some of the most common are:
Vertical Turbine Pumps: They are vertical shafts and are usually employed to pump the fluid from underground sources such as wells or sumps.
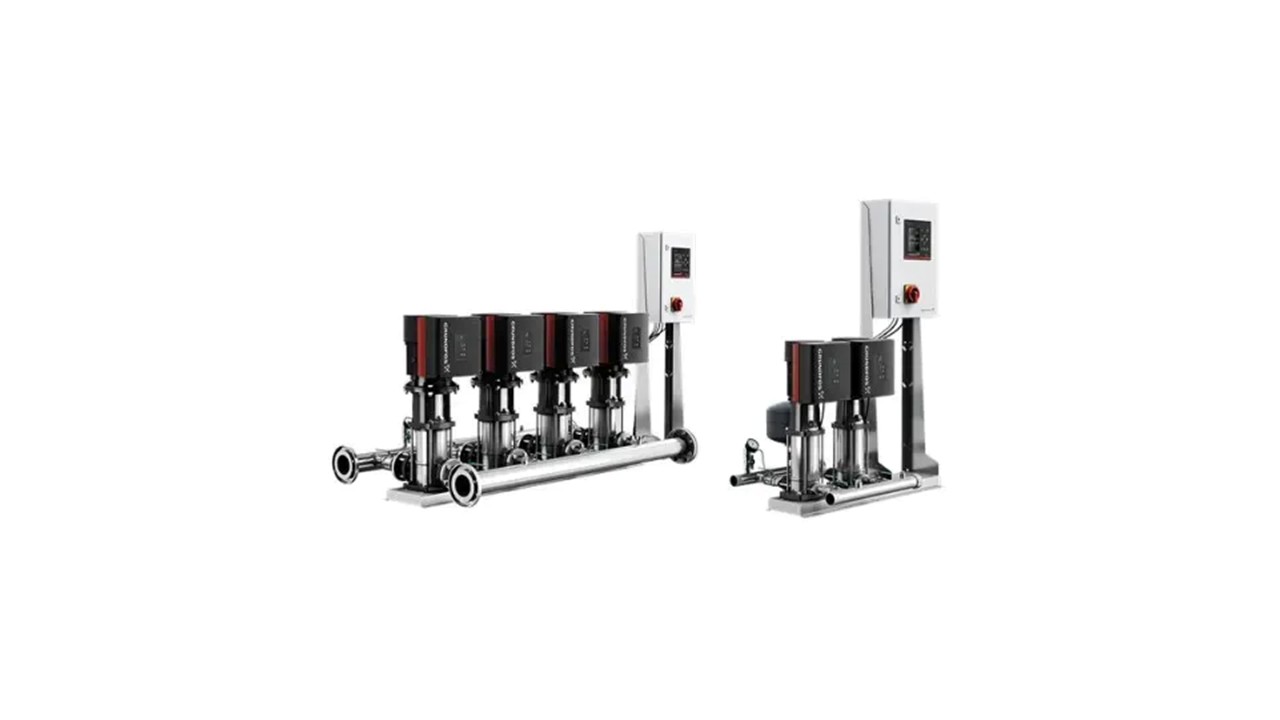
Horizontal Turbine Pumps: They are horizontal shafts and are used in most industrial operations.
Regenerative Turbine Pumps: They are also known as peripheral turbine pumps and are used to create high head at low flow rates.
Applications of Turbine Pumps
Turbine pumps are widely used in most civil industries since they can produce high pressure. Some of the typical applications are:
Water Supply: Turbine pumps are utilized for water movement from reservoirs or wells to distribution systems in municipal water supply systems.
Irrigation: They are used in farm applications to pump irrigation water.
Boiler Feed: They are commonly found to feed water to power plant boilers and industrial plants.
Chemical Processing: They are put to use to transport dissimilar chemicals and liquids.
Oil and Gas: They are also utilized to transport crude oil and other petroleum products.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- High head capability
- Small size relatively
- Smooth, unbroken flow
- Ideal for handling clear liquids
Disadvantages
- Not suited for handling high-viscosity liquids or solids
- Noisy compared to other pump types
- Moderately low efficiency when compared to centrifugal pumps
Conclusion
Turbine pumps are an efficient and flexible choice for many different applications where there is a requirement for high head and moderate flow. Their power and capability of developing high pressure make them most suitable for use in water supply, irrigation, chemical processing, and oil and gas. They have their downsides, nonetheless, including an inability to operate with fluids with high viscosity or solids. Nevertheless, turbine pumps remain a critical technology for fluid transfer in most industries.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.