IoT in Healthcare: Driving Efficiency, Innovation, and Better Patient Outcomes
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
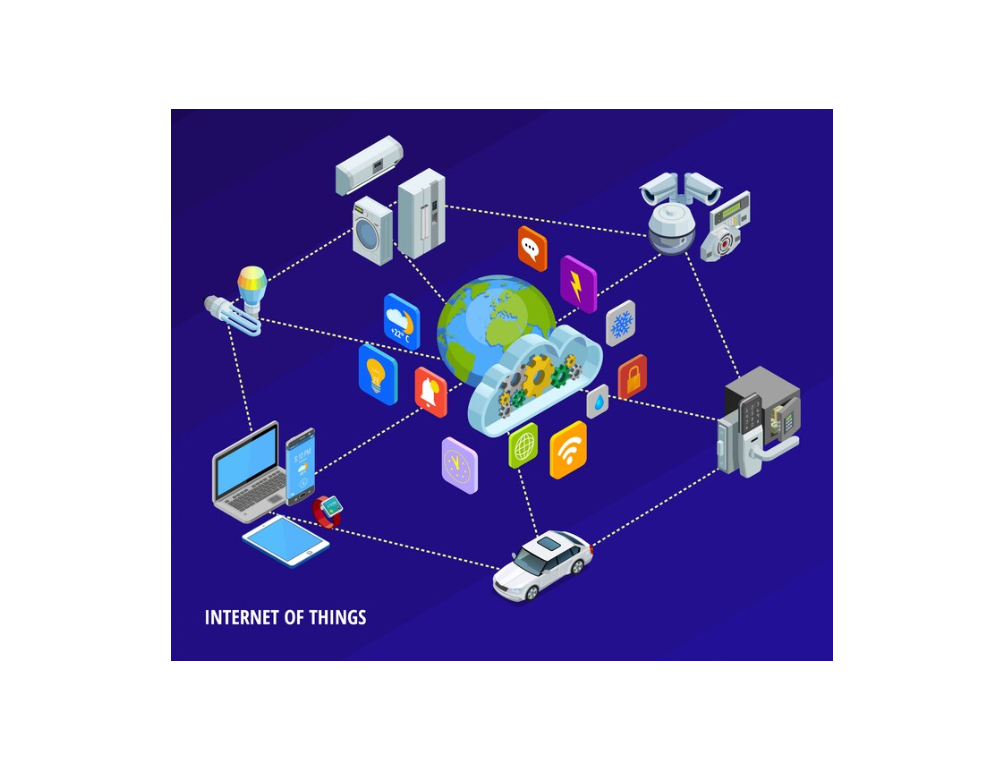
The healthcare sector is witnessing a transformative wave, propelled by technological advances that aim to streamline patient care, boost medical research, and optimize operational processes. Among the most impactful trends is the application of IoT in Healthcare—a network of connected devices, sensors, and software platforms that share data in real time. By leveraging these interconnected technologies, healthcare providers can track patient health, manage critical inventories, reduce human error, and deliver more personalized care.
An often-overlooked element in this transformation is the critical support offered by healthcare IT professional services. These specialized consultancies not only tailor IoT solutions to the unique needs of different healthcare settings but also ensure robust security, seamless integrations, and long-term scalability. The combination of IoT technologies and expert IT services is reshaping the modern medical landscape, making care more accessible, precise, and patient-centric.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the fundamentals of IoT in healthcare, delve into its key applications, discuss challenges, and highlight the indispensable role of healthcare IT professional services in driving effective and sustainable IoT implementations.
Understanding IoT in Healthcare
At its core, the Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of internet-connected devices that gather and share data. In the healthcare arena, IoT solutions often involve medical devices, wearables, and environmental sensors continuously transmitting information to central data repositories. Care teams can then analyze these data points to gain insights into patient health, equipment status, and facility operations.
Key Characteristics of IoT in Healthcare
- Real-Time Data: Information is captured and transmitted around the clock, enabling immediate interventions and informed clinical decisions.
- Remote Monitoring: Patients can be monitored in their homes or any non-clinical environment, reducing hospital admissions and easing the burden on healthcare infrastructures.
- Interoperability: Effective IoT solutions seamlessly integrate with existing Electronic Health Records (EHR) and third-party applications, promoting a unified healthcare ecosystem.
- Automation: With machine learning and analytics, certain decisions—like adjusting medication doses or flagging anomalies in patient vitals—can be automated, saving time for clinicians.
Major Applications of IoT in Healthcare
1. Wearable Health Devices
From smartwatches that measure heart rate and physical activity to specialized glucose monitors for diabetics, wearables are the most recognizable face of IoT in healthcare. These devices track crucial data—like heart rate variability, step counts, or blood sugar levels—and transmit readings to healthcare portals. Physicians gain a continuous view of patient health, enabling proactive interventions rather than reactive treatments. Key Benefits:
- Early Detection of Anomalies: Subtle changes in vital signs can alert healthcare providers to potential complications.
- Patient Engagement: Wearable dashboards empower patients to understand their metrics and be more active in their care.
- Chronic Disease Management: Conditions like diabetes, hypertension, or congestive heart failure benefit significantly from continuous monitoring.
2. Smart Hospital Infrastructure
IoT goes beyond patient monitoring. Hospitals deploy connected sensors and devices to improve facility management. These can include temperature controls for sensitive medical supplies, RFID tags to track medical assets, and environmental sensors that ensure infection control. Data from these devices feed into integrated dashboards, helping administrators make real-time decisions regarding inventory, equipment maintenance, and staff deployment. Example Use Cases
- Inventory Management: Automated alerts when medication or surgical supplies are running low, avoiding shortages and last-minute scrambling.
- Equipment Tracking: Locating wheelchairs, IV pumps, or specialized devices in real time, reducing the time clinicians spend searching for resources.
- Energy Efficiency: Smart lighting and HVAC systems can reduce operational costs while maintaining patient comfort and safety.
3. Telemedicine and Remote Consultations
Telemedicine platforms increasingly incorporate IoT devices to facilitate remote patient assessments. Physicians can observe patients’ real-time vitals, view medical images, and even receive diagnostic data from digital stethoscopes or otoscopes. By eliminating geographical barriers, these solutions expand healthcare access to remote or underserved areas. Advantages:
- Reduced Hospital Visits: Routine follow-ups and non-urgent consultations can occur virtually, freeing hospital resources for acute patients. Improved Chronic Care Management: Regular check-ins for conditions like COPD or cardiac illnesses can happen conveniently at home, alleviating patient travel burdens. Emergency Support: IoT-enabled devices can send emergency alerts to telehealth teams, who can guide immediate first-aid steps before the patient reaches a hospital.
- Reduced Hospital Visits: Routine follow-ups and non-urgent consultations can occur virtually, freeing hospital resources for acute patients.
- Improved Chronic Care Management: Regular check-ins for conditions like COPD or cardiac illnesses can happen conveniently at home, alleviating patient travel burdens.
- Emergency Support: IoT-enabled devices can send emergency alerts to telehealth teams, who can guide immediate first-aid steps before the patient reaches a hospital.
4. Medication Management
Medication adherence is a long-standing challenge, especially among patients with complex regimens. IoT-enabled pill dispensers and smart medication containers can provide reminders and track when doses are taken. If a patient misses a dose, automated alerts can notify healthcare providers or family members, preventing potential health complications. Impact:
- Enhanced Patient Safety: Real-time visibility into medication intake helps quickly spot adherence issues.
- Fewer Hospital Readmissions: Proper medication management significantly lowers the risk of preventable readmissions and emergency visits.
- Data-Driven Adjustments: Patterns of missed doses can prompt care teams to adjust the regimen for better compliance.
5. Robotics and Automated Systems
From robotic-assisted surgeries to automated nurse assistants that move supplies, IoT-based robotics are gaining traction in healthcare. These systems often rely on sensor data to navigate hospital floors, dispense medication, or assist in rehabilitation exercises. Notable Developments:
- Surgical Precision: Robot-assisted surgeries in orthopedics or urology yield faster recovery times and reduced complications.
- Enhanced Rehab Programs: IoT-driven exoskeletons or robotic arms can support stroke patients in regaining muscle function.
- Labor Optimization: Automated devices free up human staff for more complex tasks, easing workforce shortages and cutting labor costs.
Benefits of IoT in Healthcare
- Improved Patient Outcomes: Constant monitoring and data analytics enable early detection of complications and personalized treatment plans, leading to fewer hospital visits and better long-term health.
- Operational Efficiency: Automated tasks, real-time asset tracking, and smarter resource allocation reduce unnecessary costs and delays. Hospitals can reallocate saved resources to improve clinical care.
- Data-Driven Insights: IoT devices generate vast amounts of health data, feeding advanced analytics and research endeavors. These insights can inform new treatment protocols, drug discovery, and public health policies.
- Enhanced Patient Engagement: Wearable devices, mobile apps, and interactive dashboards encourage patients to track their progress, adhere to treatment regimens, and communicate effectively with healthcare providers.
- Reduced Healthcare Costs: Preventive care and remote monitoring help avoid costly emergency interventions. Additionally, streamlined hospital operations and improved asset management further drive down expenses.
Challenges and Considerations of IoT in Healthcare
Despite the clear advantages, implementing IoT in healthcare also presents a set of challenges:
- Data Security and Privacy: Connected devices expand potential attack surfaces for cyber threats. Rigorous encryption, secure networks, and compliance with regulations like HIPAA or GDPR are critical.
- Interoperability Issues: Multiple devices and platforms from different manufacturers may struggle to communicate effectively. Standardized protocols and robust APIs are essential for seamless data exchange.
- Scalability Constraints: As healthcare organizations grow or adopt more devices, existing network infrastructures may become strained, affecting the reliability of real-time data transfers.
- Regulatory Hurdles: The pace of technological innovation sometimes outstrips regulatory frameworks, creating ambiguity. Organizations must stay current with local and international standards.
- User Adoption: Both patients and healthcare staff may be reluctant to embrace new technologies, especially if they lack proper training or if the devices are not user-friendly.
The Role of Healthcare IT Professional Services
Spearheading a successful IoT transformation requires specialized expertise, and that’s where healthcare IT professional services become indispensable. These consulting and development services help hospitals, clinics, and research centers navigate the complexities of integrating IoT solutions into their existing ecosystems.
- Strategic Roadmap and Consulting: IT professionals evaluate an organization’s current infrastructure, regulatory environment, and specific clinical needs. They then propose a tailored roadmap, outlining which IoT solutions align best with clinical objectives and resource limitations.
- Custom Development and Integration: Healthcare IT professional services often include software engineering teams capable of building or customizing IoT platforms. They ensure seamless interoperability with existing EHR systems, billing platforms, and other enterprise tools while adhering to strict security protocols.
- Data Security and Compliance: Expert teams can implement end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication, and advanced firewalls. They also help organizations maintain ongoing compliance with regulations like HIPAA in the U.S. or GDPR in the EU, avoiding hefty fines and reputational damage.
- Ongoing Maintenance and Support: IoT environments evolve rapidly as new devices enter the market and protocols change. Professional IT services offer continuous monitoring, regular software updates, and prompt troubleshooting, ensuring minimal downtime and high system reliability.
- Training and Change Management: Introducing IoT solutions often requires shifting traditional workflows. Healthcare IT service providers offer training programs, user-friendly documentation, and stakeholder engagement strategies to drive successful adoption.
Future Trends in IoT-Driven Healthcare
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: Machine learning algorithms will increasingly parse IoT-generated data, offering predictive analytics and automated decision support, especially in chronic disease management.
- Blockchain for Secure Data Sharing: Blockchain could streamline data transfers between different healthcare entities, providing tamper-proof records and transparent transaction histories.
- Edge Computing: Processing data locally—on devices or edge servers—reduces latency and bandwidth usage, making real-time analytics feasible even in low-connectivity environments.
- Nano and Micro Devices: Miniaturized sensors and ingestible devices could extend IoT monitoring into the gastrointestinal tract or bloodstream, opening new avenues for diagnostics and personalized medicine.
- Advanced Robotics and Telepresence: Surgeons might perform complex procedures remotely using robotic arms guided by real-time imaging. This could democratize access to specialized care across vast distances.
Conclusion
The transformative potential of IoT in Healthcare is undeniable. By leveraging connected devices and data analytics, healthcare systems can shift from reactive care to a more proactive, preventive model. From remote monitoring of chronic conditions to robust hospital asset management, IoT paves the way for safer, more efficient, and more personalized healthcare experiences.
However, realizing this potential requires not just the right devices and software, but also the strategic insight and technical capabilities offered by healthcare IT professional services. Through careful planning, rigorous security measures, and comprehensive training, these specialized services ensure that IoT initiatives not only excel in pilot phases but also scale sustainably over the long term.
As technology continues to advance, the Internet of Things in healthcare will likely expand its reach, unlocking innovations once deemed futuristic. Organizations prepared to integrate and embrace these solutions stand to lead the next wave of medical breakthroughs, shaping a future where patient well-being, operational efficiency, and data-driven insights converge harmoniously.
FAQ
1. What is IoT in Healthcare?
IoT in healthcare refers to the use of interconnected devices—like wearables, sensors, and medical equipment—that communicate health data in real time. This system aims to enhance patient monitoring, streamline clinical workflows, and support data-driven decision-making.
2. Why is data security essential for IoT in healthcare?
Healthcare data is extremely sensitive, governed by strict regulations like HIPAA and GDPR. Connected devices can become targets for cyberattacks, so robust security measures are necessary to protect patient privacy and maintain trust.
3. How do healthcare IT professional services support IoT adoption?
These services offer end-to-end support, including strategy development, system integration, data security, compliance, and ongoing maintenance. They ensure IoT solutions align with clinical and operational objectives while minimizing risks.
4. Can smaller clinics benefit from IoT in healthcare?
Absolutely. Scalable IoT solutions exist for both large hospitals and smaller clinics. Wearable devices for remote patient monitoring or basic asset management tools can significantly improve efficiency and patient outcomes in smaller settings.
5. What are the main challenges when implementing IoT in healthcare?
Challenges include ensuring data privacy, achieving device interoperability, managing scalability, meeting regulatory requirements, and overcoming user adoption barriers. Partnering with specialized IT services can help navigate these complexities.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.