Polyvinyl Acetate Manufacturing Plant Project Report 2024: Setup and Cost
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
Introduction
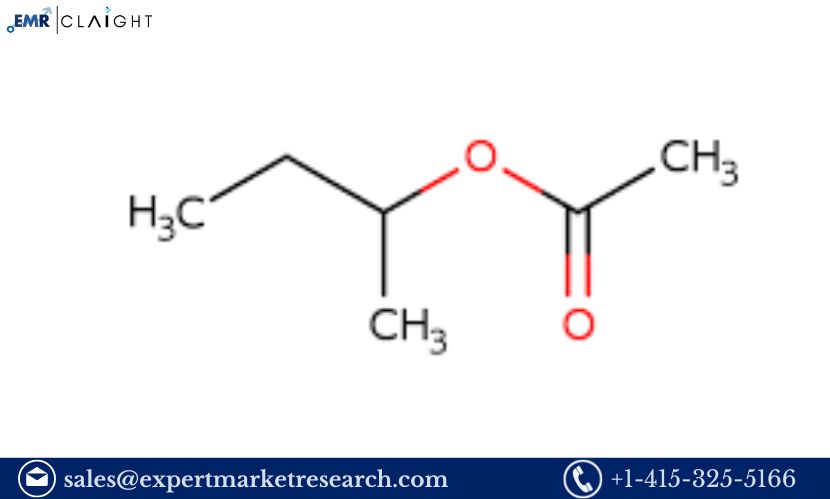
Polyvinyl Acetate (PVA) is a versatile and widely used polymer with applications ranging from adhesives and paints to coatings and textiles. It is known for its excellent adhesion properties, film-forming capabilities, and versatility in formulation. Setting up a Polyvinyl Acetate manufacturing plant requires careful planning and execution, considering market dynamics, technology selection, plant design, and financial analysis. This article provides a comprehensive Polyvinyl Acetate Manufacturing Plant Project Report for establishing a PVA manufacturing facility, offering insights into each crucial aspect of the project.
Overview of Polyvinyl Acetate (PVA)
Polyvinyl Acetate is a synthetic polymer produced by the polymerization of vinyl acetate monomers. It is used in a range of applications due to its adhesive properties and film-forming ability. Common uses of PVA include:
Adhesives: Used in white glue, wood glue, and other adhesives due to its strong bonding capabilities.
Coatings: Applied in paints and coatings to improve film flexibility and durability.
Textiles: Employed in textile finishes and as a binder in nonwoven fabrics.
Packaging: Utilized in coatings for food packaging materials to provide moisture resistance.
Project Scope
The objective of the PVA manufacturing plant project is to develop a facility capable of producing high-quality Polyvinyl Acetate efficiently and economically. The project encompasses several stages, including market analysis, technology selection, plant design, equipment procurement, and financial planning.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents @
https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/prefeasibility-reports/polyvinyl-acetate-manufacturing-plant-project-report/requestsample
1. Market Analysis
Conducting a thorough market analysis is essential to understand the demand for PVA and identify opportunities in the market. Key areas to consider include:
Demand and Applications: Assessing the demand for PVA in various industries such as adhesives, paints, coatings, and textiles. Identifying trends and growth areas can help target the right markets.
Competitive Landscape: Analyzing existing PVA manufacturers, their market share, and product offerings. Understanding the competitive environment can help identify market gaps and potential advantages.
Regulatory Environment: Familiarizing yourself with regulations related to the production, handling, and use of PVA. Compliance with industry standards and safety regulations is crucial.
2. Technology Selection
The production of Polyvinyl Acetate involves polymerization of vinyl acetate monomers. Key technologies and processes include:
Polymerization: The primary method for producing PVA is free-radical polymerization of vinyl acetate monomers in an aqueous medium. The choice of polymerization method (emulsion, suspension, or solution polymerization) can affect the quality and properties of the final product.
Drying and Granulation: After polymerization, PVA is typically in a liquid or paste form. It must be dried and granulated into a powder for ease of handling and use. Technologies such as spray drying or fluidized bed drying are commonly used.
Formulation and Blending: Depending on the intended application, PVA can be formulated with various additives and stabilizers to enhance its properties. This may include adjusting the polymer’s molecular weight or incorporating plasticizers.
Selecting the right technology involves evaluating factors such as efficiency, cost, scalability, and the specific requirements of the end applications.
3. Plant Design and Layout
Designing the plant involves creating a layout that maximizes production efficiency, safety, and compliance with industry standards. Key components include:
Raw Material Storage: Facilities for storing vinyl acetate monomers and other raw materials. Proper storage conditions are essential to maintain material quality and safety.
Production Units: Equipment for polymerization, drying, and granulation. This includes reactors, dryers, and granulators.
Quality Control Lab: A laboratory for testing PVA samples to ensure they meet quality standards and regulatory requirements. Regular testing is crucial for maintaining product consistency.
Packaging and Storage: Facilities for packaging PVA powder in various forms, such as bags or bulk containers, and storing them until distribution.
The plant layout should also account for future expansion and the integration of new technologies.
4. Raw Materials and Supply Chain
Effective management of raw materials and the supply chain is critical for smooth operations. Key considerations include:
Raw Material Sourcing: Establishing reliable suppliers for vinyl acetate monomers and other additives. Strong supplier relationships ensure a steady supply of high-quality materials.
Storage and Handling: Implementing proper storage and handling procedures to prevent contamination and maintain material quality.
Logistics: Planning for transportation and inventory management to minimize delays and reduce costs. Efficient logistics are essential for maintaining production schedules and meeting customer demands.
5. Environmental and Safety Considerations
Addressing environmental and safety considerations is crucial for operating a PVA manufacturing plant. Key aspects include:
Waste Management: Implementing systems for managing and disposing of waste products, such as residual monomers and solvents, in an environmentally responsible manner.
Energy Efficiency: Using energy-efficient technologies and practices to minimize energy consumption and reduce operational costs. This includes optimizing heating, cooling, and power systems.
Safety Protocols: Developing safety protocols to protect workers and the community from potential hazards associated with the production process, such as handling chemicals and operating machinery.
6. Financial Analysis
A detailed financial analysis is essential for assessing the feasibility and profitability of the project. Key components include:
Capital Investment: Initial costs for setting up the plant, including construction, equipment, and installation. This also includes costs for obtaining permits and meeting regulatory requirements.
Operating Costs: Ongoing expenses such as raw materials, labor, utilities, maintenance, and quality control. Effective cost management is crucial for maintaining profitability.
Revenue Projections: Estimating income from the sale of PVA products based on production capacity, market prices, and customer contracts. Accurate revenue projections help assess the project’s financial viability.
Profitability Analysis: Calculating the return on investment (ROI) and payback period to evaluate the project’s financial performance. This helps in making informed investment decisions.
FAQ
What is Polyvinyl Acetate (PVA)?
Polyvinyl Acetate is a synthetic polymer produced by polymerizing vinyl acetate monomers. It is known for its adhesive properties and is used in various applications including adhesives, coatings, and textiles.
How is PVA manufactured?
PVA is manufactured through the polymerization of vinyl acetate monomers using processes such as emulsion or suspension polymerization. The polymer is then dried and granulated into a powder or formulated into a liquid for different applications.
What are the primary uses of PVA?
PVA is used in a wide range of applications including adhesives (such as white glue), paints and coatings, textile finishes, and as a binder in nonwoven fabrics. Its versatility and strong bonding capabilities make it valuable in many industries.
What are the environmental concerns related to PVA production?
Environmental concerns include waste management, energy consumption, and the use of chemicals. Implementing effective waste management systems, using energy-efficient technologies, and adhering to environmental regulations can help mitigate these impacts.
How long does it take to set up a PVA manufacturing plant?
Setting up a PVA manufacturing plant typically takes between 12 to 18 months. This includes time for construction, equipment installation, and regulatory approvals.
What factors should be considered in the financial analysis of a PVA plant?
Key factors include initial capital investment, operating costs, revenue projections, and profitability analysis. It is important to evaluate both direct costs (e.g., raw materials, labor) and indirect costs (e.g., utilities, maintenance) to assess the project's financial feasibility.
Related Reports
https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/reports/animal-health-market
https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/reports/sauces-market
https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/reports/fraud-detection-and-prevention-market
Media Contact:
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: [email protected]
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.