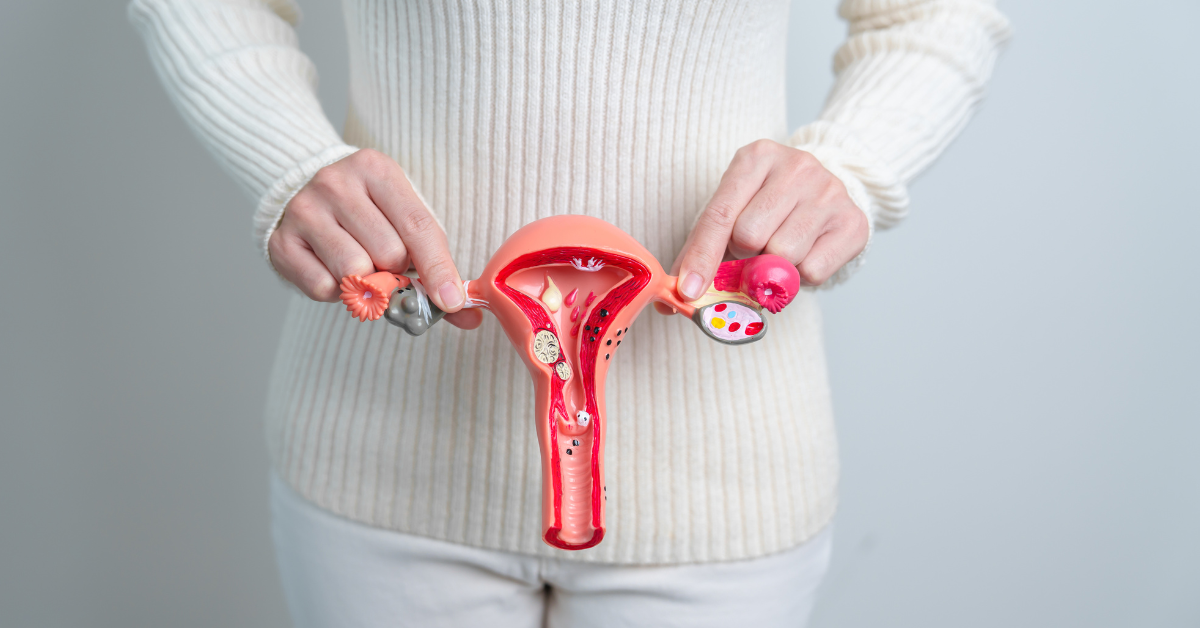
Signs and Symptoms of Cervical Cancer in women

Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
Cervical cancer is one of the most common types of cancer affecting women worldwide. It occurs in the cells of the cervix, which is the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. The primary cause of cervical cancer is persistent infection with high-risk strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV). While cervical cancer develops slowly over time, early detection through awareness of its symptoms can significantly improve treatment outcomes. This blog highlights the key signs and symptoms of cervical cancer that every woman should be aware of.
Early Signs of Cervical Cancer
In the initial stages, cervical cancer may not show noticeable symptoms. This is why regular screenings, such as Pap smears and HPV tests, are crucial for early detection. However, as the disease progresses, some early warning signs may appear, including:
1. Unusual Vaginal Bleeding
One of the most common symptoms of cervical cancer is abnormal vaginal bleeding. This may include:
Bleeding between periods
Bleeding after intercourse
Heavier or longer menstrual periods than usual
Postmenopausal bleeding
Any unexplained bleeding should be evaluated by a healthcare provider, as it could be an early indicator of cervical cancer or other gynecological conditions.
2. Unusual Vaginal Discharge
Women with cervical cancer may notice an unusual vaginal discharge that differs from their normal secretions. The discharge may:
Have a foul odor
Be watery or thick
Contain blood
Any persistent change in vaginal discharge, especially if it is bloody or has a strong odor, should be examined by a doctor.
3. Pain or Discomfort During Intercourse
Pain during sexual intercourse (dyspareunia) can be a symptom of cervical cancer. This discomfort may be due to irritation or growths on the cervix. If this symptom is persistent, it should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
4. Pelvic or Lower Back Pain
Persistent pain in the pelvic region or lower back may be another early sign of cervical cancer. This pain can be dull or sharp and may become more noticeable as the cancer progresses. If pelvic pain is unexplained and persistent, it warrants medical attention.
Advanced Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
As cervical cancer progresses to more advanced stages, the symptoms may become more severe and widespread. These include:
5. Increased Frequency of Urination or Blood in Urine
Women with advanced cervical cancer may experience increased urgency to urinate, difficulty urinating, or notice blood in their urine (hematuria). These symptoms may occur if the cancer spreads to the bladder or affects nearby urinary structures.
6. Leg Swelling and Pain
Advanced cervical cancer can obstruct blood flow, leading to swelling in one or both legs (lymphedema). This swelling may be accompanied by pain, heaviness, or a tingling sensation.
7. Unexplained Weight Loss and Fatigue
Cancer often causes unexplained weight loss due to the body’s increased energy demands. Additionally, persistent fatigue and weakness can indicate the body’s struggle against cancer.
8. Bowel Habit Changes
If cervical cancer spreads to the rectum, it can cause changes in bowel movements, such as constipation, diarrhea, or blood in the stool. Persistent changes in bowel habits should be discussed with a doctor.
Risk Factors for Cervical Cancer
While symptoms are important to recognize, understanding the risk factors can help in prevention. Some major risk factors include:
HPV Infection: High-risk strains of HPV are the leading cause of cervical cancer.
Smoking: Tobacco use increases the risk of developing cervical cancer.
Weak Immune System: Conditions like HIV or immune suppression increase vulnerability.
Multiple Sexual Partners: Increased exposure to HPV raises the risk of cervical cancer.
Long-term Use of Birth Control Pills: Prolonged use of oral contraceptives may slightly increase the risk.
Importance of Regular Screenings
Early detection of cervical cancer significantly improves treatment success. Women should undergo regular screenings such as:
Pap Smear Test: Detects precancerous changes in the cervix.
HPV Test: Identifies high-risk HPV infections.
Colposcopy: A closer examination of the cervix if abnormal cells are detected.
When to See a Doctor
Women should seek medical attention if they experience any of the following:
Persistent abnormal vaginal bleeding
Chronic pelvic or back pain
Unusual vaginal discharge
Painful intercourse
Any other unexplained symptoms related to reproductive health
Conclusion
Cervical cancer is preventable and highly treatable when detected early. Awareness of its signs and symptoms is key to seeking timely medical intervention. Regular screenings, HPV vaccination, and a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of developing cervical cancer. If you or someone you know experiences any of the symptoms mentioned above, consulting a healthcare provider is essential for early diagnosis and treatment.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.