Six Sigma: A Comprehensive Blueprint for Triumph in 2025
Dive into the transformative potential of Six Sigma in 2025, a data-driven approach to streamline processes. This detailed guide,, explores the DMAIC methodology, skill levels, and its role in reducing defects and boosting efficiency. Perfect for professionals and businesses seeking operational excellence.
Unveiling the Principles of Six Sigma
Six Sigma has redefined business success, with Motorola achieving 99.99966% defect-free quality and General Electric realizing $12 billion in savings over five years. The term “Sigma,” derived from the Greek alphabet, represents standard deviation, indicating a process where variation is so minimal that the specification limit is six standard deviations from the mean. This data-reliant method detects and eliminates defects, inefficiencies, and errors, enhancing the reliability, speed, and scalability of processes, products, and services. It serves as a philosophy for relentless improvement, a metric for performance monitoring, and a structured process using DMAIC to address key business challenges.
Analyzing the DMAIC System in Six Sigma
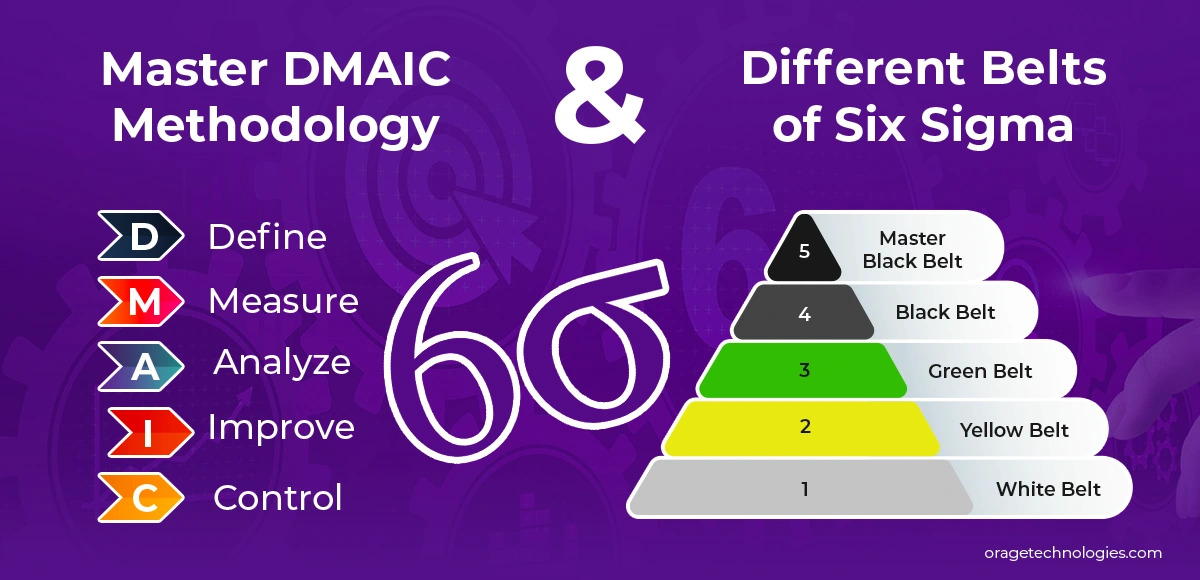
Define Phase: Setting the Course
The Define phase initiates the Six Sigma process by clearly defining the problem and aligning it with business goals. As Charles Kettering wisely noted, “A problem well stated is a problem half solved.” This stage involves establishing the project’s objective, its significance, success criteria, key participants, and deadlines. Essential steps include developing SMART problem and goal statements, creating a project charter with metrics, benefits, scope, milestones, and approvals, and building a SIPOC diagram to map suppliers, inputs, processes, outputs, and customers for a broad process view.
Measure Phase: Assessing the Current Landscape
With the problem identified, the Measure phase quantifies its scale using data. The goal is to establish a baseline by evaluating existing performance. This includes designing a data collection plan, mapping the process to identify bottlenecks, conducting measurement analysis for accuracy and repeatability, measuring performance output (Y) against standards and defect rates, and determining process capability with metrics like Upper Specification Limit (USL), defect rate, yield, and Sigma level.
Analyze Phase: Delving Into Root Causes
The Analyze phase is a critical component of Six Sigma, focusing on uncovering the root causes (X) of issues, where Y = f(X), rather than just symptoms. This stage involves brainstorming potential causes, organizing them with a Cause-Effect or Fishbone diagram, selecting likely causes, preparing a data collection plan with testing details, and validating key causes through hypothesis testing using tools such as bar charts, Pareto charts, histograms, or box plots.
Improve Phase: Implementing Strategic Solutions
The Improve phase turns root causes into actionable improvements for output (Y). It includes generating ideas through techniques like Six Thinking Hats or expert insights, evaluating options with tools like Effort-Impact Matrix or Design of Experiments (DOE), choosing optimal solutions with Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA), applying mistake-proofing (Poka-Yoke) at prevention, facilitation, or detection levels, and deploying solutions via pilot testing and a full-scale plan with communication and training.
Control Phase: Securing Ongoing Success
The Control phase ensures the permanence of Six Sigma enhancements. It involves creating a control plan with performance targets and monitoring methods, using Statistical Process Control (SPC) charts to manage variations, updating procedures, training teams, transferring ownership, and confirming financial benefits like cost savings or waste reduction to verify goal achievement.
Crucial Leadership Roles in Six Sigma Projects
Leadership is essential for Six Sigma effectiveness, with executives and champions fostering a culture of continuous advancement. Leaders such as CEOs, CFOs, COOs, CIOs, Vice Presidents, and Directors align projects with strategic objectives, set selection criteria, approve initiatives, appoint champions, and ensure resource allocation. Champions oversee project execution, securing organizational support and resources.
Tiers of Proficiency in Six Sigma
White Belt: The Initial Stage
The White Belt introduces Six Sigma basics, covering concepts, quality orientation, and process understanding. Designed to spark interest, it prepares individuals to support local efforts and assist small teams with foundational knowledge.
Yellow Belt: Building Essential Skills
Yellow Belts develop expertise through DMAIC training, learning process mapping, Voice of Customer, and root cause analysis. They lead small projects and contribute to larger efforts under Green or Black Belt guidance, improving departmental performance.
Green Belt: Leading with Data Expertise
Green Belts manage part-time DMAIC projects, mastering all phases, statistical tools, and practical problem-solving. They drive moderate improvements while balancing daily responsibilities, enhancing processes within their areas.
Black Belt: Overseeing Major Projects
Black Belts are full-time Six Sigma professionals, leading complex, cross-functional projects with skills in statistics, process evaluation, hypothesis testing, and Design of Experiments (DOE). They manage significant initiatives, mentor Green Belts, and provide technical support.
Master Black Belt: Steering Organizational Success
Master Black Belts, the highest Six Sigma experts, excel in statistical modeling, change leadership, coaching, and training development. They guide Black Belts, shape project strategies, and maintain program consistency, often serving as internal or external consultants.
Conclusion: The Enduring Influence of Six Sigma
Six Sigma, supported by its DMAIC framework and tiered expertise, provides a solid foundation for process improvement across industries. By reducing defects, enhancing efficiency, and nurturing leadership, it delivers significant financial and operational benefits. With skilled professionals at every level, it ensures sustained progress and innovation.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.





