Solenoid Motor Starters: Essential Components for Efficient Engine Ignition

Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
Solenoid motor starters are critical components in various engines, from automobiles to industrial machinery, playing a pivotal role in initiating the ignition process. These devices combine electrical and mechanical functions to bridge the gap between the battery and the engine, ensuring a smooth and reliable start every time. Understanding how they work, their key features, and maintenance requirements can help users optimize performance and extend their lifespan.
The Evolution of Solenoid Motor Starters
The development of solenoid motor starters is closely linked to the evolution of internal combustion engines. In the early days of automobiles, starting an engine was a labor-intensive task that required hand-cranking—a process that was not only physically demanding but also dangerous, as the crank could kick back and cause serious injuries. The first electric starters, introduced in the early 20th century, revolutionized this process, and solenoid technology quickly became an integral part of these systems.
Early electric starters lacked the solenoid component, relying instead on direct mechanical linkage to engage the starter motor with the flywheel. However, these designs had limitations, including inconsistent performance and a higher risk of damage to the starter or engine. The integration of solenoids addressed these issues by providing a more precise and reliable way to control the engagement and disengagement of the starter motor. Over time, advancements in materials science and electrical engineering have led to more efficient solenoid designs, with improved durability, higher current-handling capabilities, and enhanced compatibility with modern engine systems.
Today, solenoid motor starters are sophisticated devices that incorporate advanced features such as overcurrent protection, thermal shielding, and corrosion-resistant materials. These improvements have made them indispensable in a wide range of applications, from compact passenger cars to large industrial generators.
How Solenoid Motor Starters Work: A Detailed Breakdown
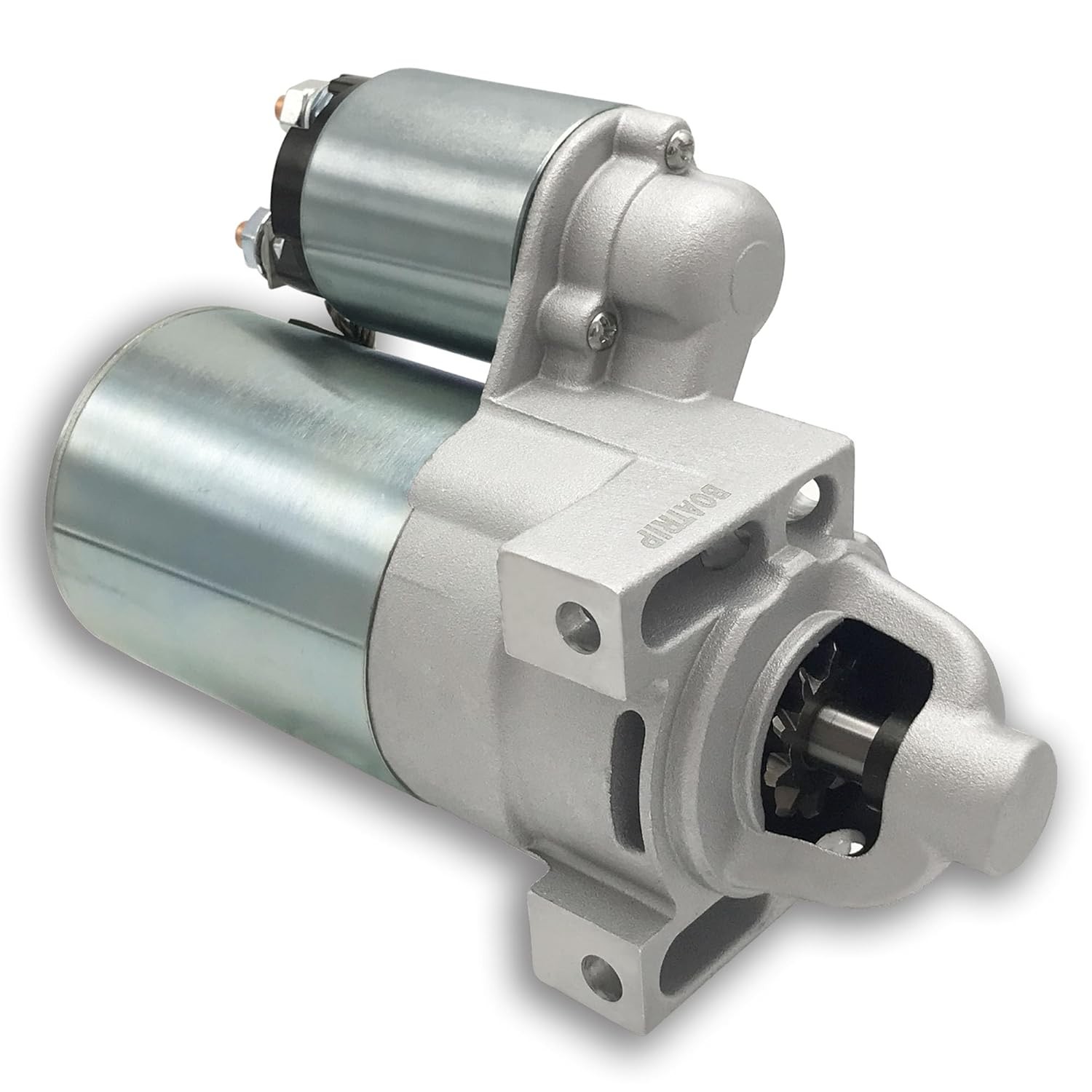
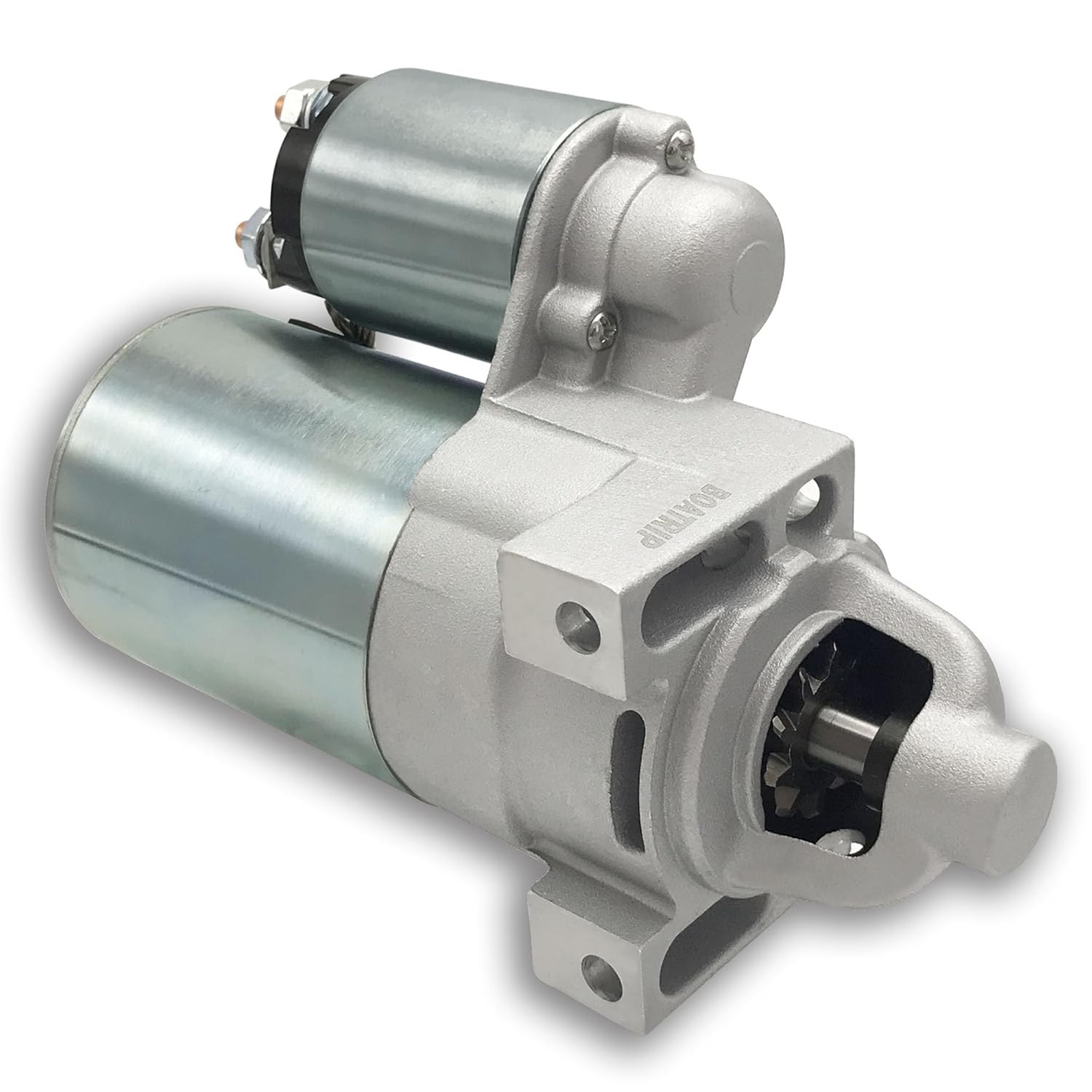
At the core of a solenoid motor starter is an electromagnet, which consists of a coil of wire wrapped around a movable iron core, known as a plunger. When an electric current flows through the coil—typically triggered by turning the ignition key or pressing a start button—the electromagnet generates a magnetic field. This magnetic force pulls the plunger forward, which in turn pushes a gear (called the pinion gear) to engage with the engine’s flywheel.
The pinion gear is designed to match the teeth of the flywheel, ensuring a secure and precise connection. The flywheel, a large rotating disc attached to the engine’s crankshaft, stores rotational energy and helps to maintain the engine’s momentum once it starts. When the pinion gear engages with the flywheel, the starter motor’s rotation is transferred to the crankshaft, which begins to turn, initiating the combustion process.
Simultaneously, the movement of the plunger closes a set of heavy-duty contacts, allowing a large current from the battery to flow directly to the starter motor, which then cranks the engine. These contacts are made from high-conductivity materials such as copper or silver, which minimize resistance and ensure efficient current transfer. The contacts are also designed to withstand the high electrical arcing that occurs when they close, which can otherwise cause wear and damage over time.
Once the engine starts and the ignition key is released, the current to the coil is cut off, the magnetic field collapses, and a spring pushes the plunger and pinion gear back to their original positions, disconnecting the starter motor from the flywheel. This disengagement is crucial, as leaving the starter motor connected to the running engine would result in damage to both components, due to the significant difference in rotational speed between the starter motor and the flywheel.
Key Features and Advantages
One of the primary advantages of solenoid motor starters is their ability to handle high electrical currents efficiently. The solenoid acts as a switch, using a small control current to activate a much larger current for the starter motor, which is essential because the starter motor requires a significant amount of power to crank the engine. This design not only protects the ignition switch from the high current but also ensures that the current flows only when needed, preventing unnecessary power drain from the battery.
Another key feature is their fast response time. Solenoids can engage the starter motor in a fraction of a second, which is critical for ensuring a quick start. This rapid response is achieved through the use of high-quality materials in the coil and plunger, as well as precise engineering of the magnetic field.
Solenoid motor starters are also highly durable, with many models designed to withstand harsh operating conditions such as extreme temperatures, vibration, and moisture. This durability is achieved through the use of rugged materials such as stainless steel for the plunger and housing, and corrosion-resistant coatings for the electrical contacts.
In addition to their durability, solenoid motor starters are also relatively easy to install and maintain. Most models are designed to fit standard engine configurations, and replacement parts are readily available. Regular maintenance tasks, such as cleaning the contacts and lubricating the moving parts, can be performed with basic tools, making them accessible to users with minimal technical expertise.
Applications Across Industries
Solenoid motor starters are used in a wide range of applications, spanning multiple industries. In the automotive sector, they are a standard component in cars, trucks, buses, and motorcycles. Modern vehicles rely on solenoid motor starters to provide reliable ignition, even in extreme weather conditions. For example, in cold climates, where the engine oil thickens and the battery’s performance is reduced, a high-quality solenoid motor starter can still deliver the necessary power to crank the engine.
In the marine industry, solenoid motor starters are used in boats and yachts, where they must withstand the corrosive effects of saltwater and humidity. Marine-grade solenoid motor starters are specially designed with enhanced corrosion resistance to ensure long-term performance in these challenging environments.
The industrial sector also relies heavily on solenoid motor starters. They are used in generators, which provide backup power in case of a mains failure. In construction equipment, such as excavators, bulldozers, and cranes, solenoid motor starters are essential for ensuring that the machinery can be started quickly and reliably, minimizing downtime on the job site.
In agriculture, solenoid motor starters are used in tractors, combines, and other farm equipment. These machines often operate in dusty, dirty environments, and solenoid motor starters must be able to withstand these conditions while providing consistent performance. They are also used in irrigation systems, where they help to start pumps that deliver water to crops.
Solenoid motor starters are also found in small engines, such as those used in lawnmowers, chainsaws, and generators. These devices require a compact and lightweight starter, and solenoid motor starters are ideal for this purpose, as they provide high power in a small package.
Types of Solenoid Motor Starters
There are several different types of solenoid motor starters, each designed for specific applications. The most common type is the linear solenoid motor starter, which uses a plunger that moves in a straight line to engage the pinion gear with the flywheel. This type is widely used in automotive and small engine applications.
Rotary solenoid motor starters, on the other hand, use a rotating plunger to engage the pinion gear. These starters are often used in industrial machinery, where a higher torque output is required. The rotating motion of the plunger allows for a more gradual engagement with the flywheel, which reduces wear and tear on the gears.
Another type of solenoid motor starter is the permanent magnet solenoid starter. This design uses a permanent magnet instead of an electromagnet to generate the magnetic field, which reduces the current consumption and increases efficiency. Permanent magnet solenoid starters are often used in hybrid and electric vehicles, where energy efficiency is a key concern.
Comparing Solenoid Motor Starters with Other Starting Systems
While solenoid motor starters are the most common type of starting system used in internal combustion engines, there are other options available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
One alternative is the direct drive starter, which does not use a solenoid. Instead, the starter motor is directly connected to the flywheel via a gear. Direct drive starters are simpler in design and may be less expensive, but they lack the precision and reliability of solenoid motor starters. They are also more prone to damage from kickback, as there is no solenoid to disengage the starter motor quickly.
Another alternative is the inertia starter, which uses a spring-loaded mechanism to engage the starter motor with the flywheel. Inertia starters are lightweight and compact, but they have a slower response time and are less powerful than solenoid motor starters. They are typically used in small engines, such as those found in lawnmowers and chainsaws.
Compared to these alternatives, solenoid motor starters offer a number of advantages, including faster response times, higher power output, greater reliability, and better protection against damage. For these reasons, they are the preferred choice for most applications where a reliable and efficient starting system is required.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Like any mechanical or electrical component, solenoid motor starters require regular maintenance to function properly. Common issues include corrosion on the electrical contacts, which can disrupt the current flow, and wear on the plunger or spring, which can prevent the pinion gear from engaging or disengaging correctly.
Regular inspection is the first step in maintaining a solenoid motor starter. This should include checking the electrical connections for signs of corrosion or looseness, inspecting the plunger and pinion gear for wear, and ensuring that the spring is functioning properly. If any issues are detected, they should be addressed promptly to prevent further damage.
Cleaning the electrical contacts is an important maintenance task. Over time, dirt, grease, and corrosion can build up on the contacts, reducing their conductivity. This can be cleaned using a wire brush or sandpaper, followed by a application of electrical contact cleaner to remove any remaining debris.
Lubricating the moving parts is also essential. The plunger and pinion gear should be lubricated with a high-quality lubricant that is compatible with the materials used in the starter. This will reduce friction and wear, ensuring smooth operation.
If a solenoid motor starter fails, there are several symptoms to look out for. A clicking sound when trying to start the engine is a common indication that the solenoid is activating but not engaging the starter motor properly. This could be due to a worn pinion gear, a weak spring, or a faulty connection between the solenoid and the starter motor.
No response at all when turning the ignition key could indicate a more serious problem, such as a faulty coil, a broken spring, or a damaged plunger. In some cases, the issue may be with the battery or the ignition switch, so it is important to rule out these possibilities before replacing the solenoid.
Testing a solenoid motor starter can be done using a multimeter. This involves checking the resistance of the coil to ensure that it is within the manufacturer’s specifications, and testing the continuity of the electrical contacts. If the coil resistance is too high or too low, or if the contacts do not have continuity, the solenoid should be replaced.
Choosing the Right Solenoid Motor Starter
When selecting a solenoid motor starter, it is important to consider several factors to ensure that it is compatible with the engine or equipment it will be used with. The voltage rating is one of the most important considerations, as solenoid motor starters are designed to operate at specific voltages (typically 12V or 24V). Using a solenoid with the wrong voltage rating can result in poor performance or damage to the starter or engine.
The current capacity is another important factor. The solenoid must be able to handle the current required by the starter motor. This information can usually be found in the engine or starter motor’s specifications.
Compatibility with the engine’s flywheel is also crucial. The pinion gear on the solenoid must match the teeth of the flywheel to ensure proper engagement. Using a solenoid with the wrong pinion gear can result in damage to both the starter and the flywheel.
In addition to these technical considerations, it is also important to choose a high-quality solenoid motor starter from a reputable manufacturer. This will ensure that the starter is reliable and durable, and that replacement parts are readily available. Reading reviews and seeking recommendations from professionals in the industry can help in making an informed decision.
For those in need of replacement parts or more information, resources like the starter motor can provide a wide range of options and expert guidance. These resources often offer detailed product specifications, compatibility information, and customer reviews, making it easier to find the right solenoid motor starter for a specific application.
Future Trends in Solenoid Motor Starter Technology
As technology continues to advance, solenoid motor starters are also evolving to meet the changing needs of the industry. One trend is the development of more efficient solenoid designs that consume less power while delivering the same or higher performance. This is being achieved through the use of advanced materials in the coil and plunger, as well as optimized magnetic field designs.
Another trend is the integration of smart technology into solenoid motor starters. This includes features such as built-in sensors that can monitor the starter’s performance and detect potential issues before they cause a failure. These sensors can send data to a vehicle’s onboard computer or a remote monitoring system, allowing for proactive maintenance and troubleshooting.
The use of environmentally friendly materials is also becoming more important in solenoid motor starter design. Manufacturers are increasingly using recycled materials and reducing the use of hazardous substances, such as lead and mercury, to minimize the environmental impact of their products.
In conclusion, solenoid motor starters are indispensable components that enable the efficient and reliable ignition of engines across various applications. Their innovative design, which combines electromagnetism and mechanical action, ensures that engines start quickly and safely, while their durability and versatility make them suitable for everything from everyday vehicles to heavy-duty machinery. By understanding how they work and maintaining them properly, users can ensure that their solenoid motor starters continue to perform effectively, keeping engines running smoothly for years to come.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.