Species-specific Primary Cells: Advancing Precision Research

Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
Primary cell culture refers to growing cells derived straight from a tissue in a laboratory. The retention of tissue characteristics by these cells has led to an in-depth understanding of cellular events within the tissue in physiological functions, disease pathology, and treatment course. For decades, they have been obtained from different animal models and human tissues. However, research has revealed subtle differences in the species employed for primary cell extraction. Therefore, species-specific primary cells have been gaining value over non-specific cell culture. The benefits of using custom cells have also paved the way for employing species-specific cells for more relevant data.
Animal Models in Research
Due to limitations in conducting research on humans, scientists have employed non-human animal species. These models include mice, rats, rabbits, dogs, pigs, etc. They shared similarities in biochemical processes, genetic profiles, phylogeny, and pathogenesis. These species facilitated the translation of research studies and new therapies on humans. They also have a key role in drug safety and efficacy studies before proceeding with clinical trials. Furthermore, to eliminate variation, they are bred in a controlled environment. Gene editing and development of animal models specific to a disease or study enhanced the precision of research.
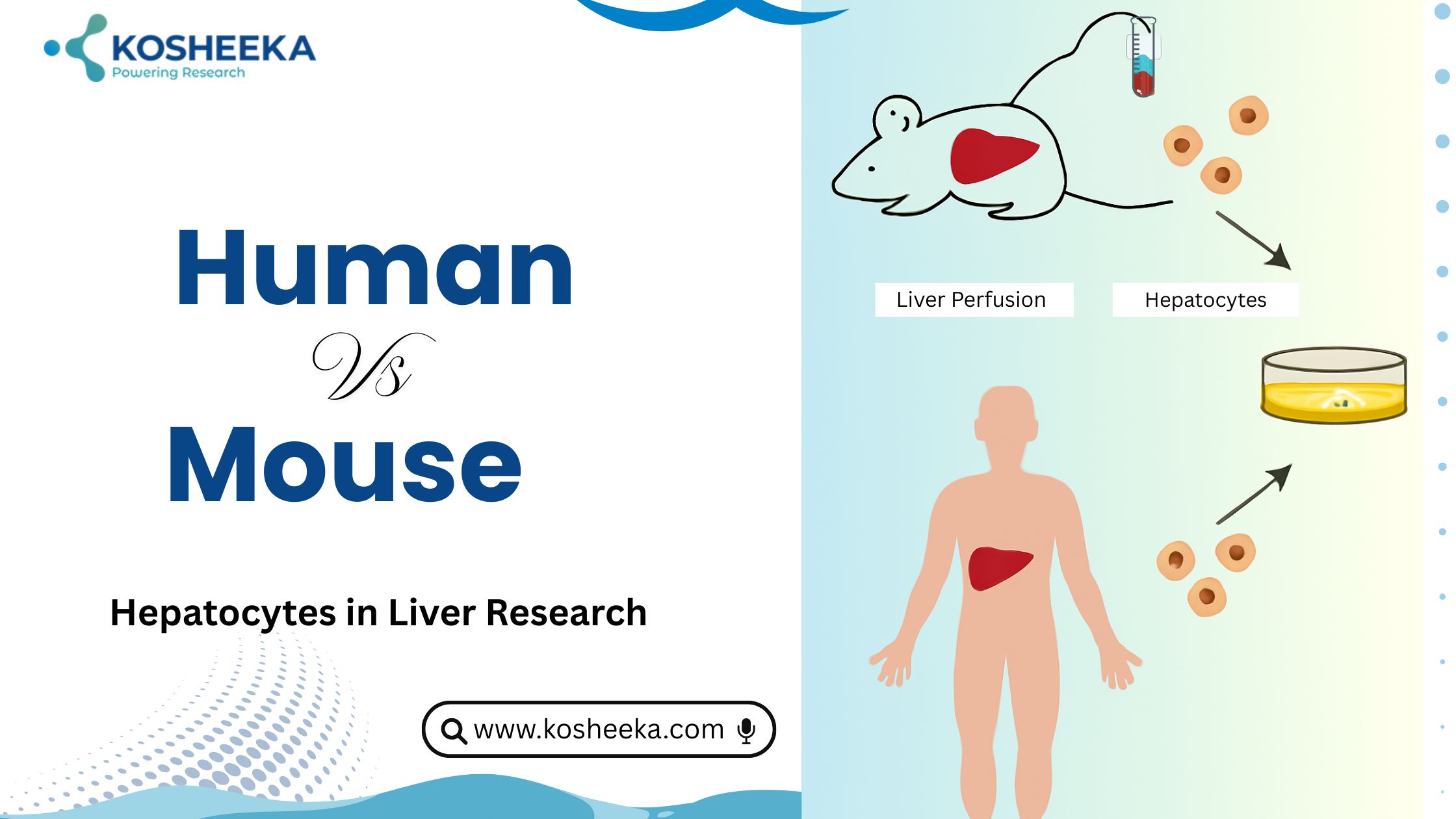
Species-Specific Primary Cells
Primary cells have provided insights into tissue functioning. However, they vary depending on the species they belong to. For example, a study demonstrated two aberrant signaling pathways that lead to the transformation of mice fibroblasts into cancer cells. However, these pathways increased considerably while researching human fibroblasts. Therefore, a research project should account for the species-specific differences in its designing phase. One should carefully select the animal model and cells specific to the study. The availability of various animal models has created the need for diverse species-specific primary cells. The research on these cells can generate data relevant to the species or animal models, thus enabling reproducibility in the in vivo study.
Applications of Primary Cell Culture
Cancer Research
Cancer has become one of the leading causes of mortality. It has spurred substantial research in this area. Several immunotherapies and drugs are under development. The research focuses on discovering the genetic mutations and their impact on downstream signaling that drive tumor transformation. At the beginning of 2025, a team of researchers exploited this information to find a molecular switch that reversed cancer cells into normal cells. The study employed the culture of primary cells obtained from the patient’s cancer and normal tissue. Therefore, in vitro culture research will soon lead to a cure for cancer.
Scientific Research
Basic research has contributed considerably to our understanding of biochemical processes and genetic makeup. In vitro culture has become the foundation of this basic research, revealing the cellular-level changes and their implications at the tissue level. This research has unraveled DNA replication, transcription, translation, genetic code, etc. Additionally, primary cells are responsible for the discovery of several RNAs, histones, chaperones, and other macromolecules. This research has proved vital to finding therapeutic targets and designing pharmacological therapies around them.
Genetic Engineering
Since its development, gene editing has become a vital research tool. Primary cell culture, as opposed to other alternatives like animal models, provides an efficient platform for genetic engineering. Such studies have established the function of genes in the overall cell function or revealed additional functional value. For example, cell culture demonstrated that lncRNAs, previously considered redundant, have an essential role in transcription.
Drug Development
Before establishing in vitro culture, drug testing utilized animals, a laborious process with ethical implications. However, primary cells specific to species have notably reduced the efforts, time, and money required to conduct drug discovery and validation. The drug development process has accelerated as a result of their ability to screen numerous medicines at once using high-throughput methods. The information about the drug-induced cellular processes also made it clear what formulation modifications were required to enhance efficacy and safety profiles.
Personalized Medicine
There is sufficient evidence that individuals vary in their response to drugs. As a result, personalized medicine has emerged, in which medical interventions are customized based on a patient's biology and response. The same concept is also included in in vitro culture with cells belonging to relevant species, with further customization of traits like age and gender.
Key Takeaways
The value of primary cells in preclinical investigations cannot be undermined. It has widened the scope of research by offering a tremendous amount of data. The low efforts and lack of ethical implications in comparison to animal alternatives have driven their routine use in research. With the advancing technology, the demand for cells belonging to particular species has grown. They enhance the reproducibility of results in the in vivo studies, adding reliability to the data. The uses of primary cell culture are numerous but it also requires their careful application. Kosheeka delivers species-specific primary cells after isolating them under aseptic conditions, characterizing them by robust techniques and stringent testing.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.