Affiliate Blog Copy – Sell Without Selling. Earn More Now!
Affiliate Blog Copy – Sell Without Selling. Earn More Now!
The Future of Dental Implants: Emerging Trends and Technologies
Written by anaya george » Updated on: June 17th, 2025

Dental implants have revolutionized the field of restorative dentistry, offering a durable and aesthetically pleasing solution for missing teeth. Over the years, advancements in implant technology have significantly improved success rates, comfort, and overall patient satisfaction. As we look to the future, several emerging trends and technologies promise to further enhance the field of Best Dental Implants Clinic in Dubai, making them more accessible, efficient, and effective. This article explores some of the most exciting developments in dental implant technology and what they mean for the future of oral health.
1. 3D Printing and Customization:
The Current State:
3D printing technology is already making waves in dentistry, particularly in the creation of custom dental implants. This technology allows for the precise fabrication of implants tailored to the patient’s unique anatomy, ensuring a perfect fit and optimal function.
The Future:
As 3D printing technology advances, we can expect even greater customization of dental implants, leading to improved outcomes. In the future, entire implant-supported prosthetics, such as crowns and bridges, could be printed on-site in dental offices, reducing the time and cost associated with traditional methods. Additionally, biocompatible materials will continue to evolve, further enhancing the integration and longevity of implants.
2. Smart Implants:
The Current State:
Smart implants are an emerging technology that incorporates sensors and connectivity features into the implant structure. These sensors can monitor various parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and bone integration, providing real-time data to both patients and dentists.
The Future:
Smart implants have the potential to revolutionize post-operative care by providing continuous monitoring of implant health. This technology could alert patients and practitioners to potential issues, such as infection or implant movement, before they become serious problems. In the future, smart implants could also be used to release medication or growth factors directly to the implant site, promoting faster healing and better outcomes.
3. Nano-Enhanced Materials:
The Current State:
Nanotechnology is beginning to influence the materials used in dental implants. Current research is focused on developing nano-enhanced coatings and materials that improve osseointegration, reduce the risk of infection, and enhance the overall durability of implants.
The Future:
In the coming years, we can expect to see widespread use of nano-enhanced materials in dental implants. These materials will be designed to mimic the natural properties of bone, encouraging faster and more robust integration. Additionally, antimicrobial nano-coatings could reduce the risk of peri-implantitis, a common cause of implant failure, by preventing bacterial colonization on the implant surface.
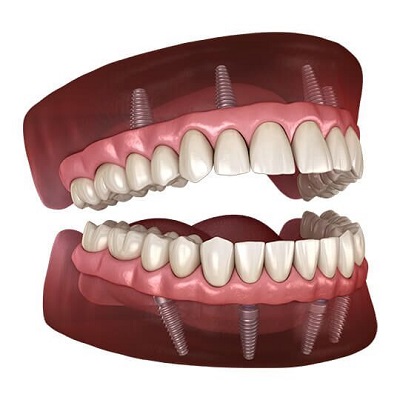
4. Regenerative Medicine and Tissue Engineering:
The Current State:
Regenerative medicine and tissue engineering are currently being explored as ways to enhance the success of dental implants, particularly in patients with insufficient bone or gum tissue. Techniques such as bone grafting and soft tissue augmentation are already in use, but they have limitations.
The Future:
The future of dental implants could see the development of fully regenerative solutions, where patients’ own cells are used to grow bone and gum tissue in the lab. These tissue-engineered constructs could then be implanted alongside or in place of traditional dental implants, ensuring better integration and reducing the need for invasive procedures. Additionally, the use of stem cells and growth factors may allow for the natural regeneration of bone and tissue, eliminating the need for synthetic materials altogether.
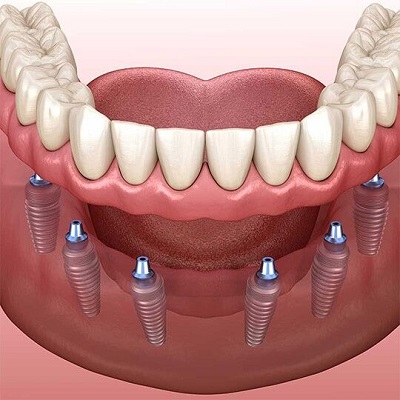
5. Minimally Invasive Implant Procedures:
The Current State:
Minimally invasive techniques for placing dental implants are already being explored, with the goal of reducing patient discomfort and recovery time. Guided implant surgery, which uses digital imaging and computer-aided design, is a step in this direction, allowing for more precise and less traumatic implant placement.
The Future:
The future will likely see the development of even less invasive procedures, possibly involving the use of robotic systems that can place implants with extreme precision. Additionally, advances in imaging technology, such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), could allow dentists to plan and execute implant procedures with unprecedented accuracy, further minimizing trauma and improving patient outcomes.
6. Bioprinting and Organ-on-a-Chip Technology:
The Current State:
Bioprinting and organ-on-a-chip technologies are still in their infancy but hold tremendous potential for the future of dental implants. Bioprinting involves the 3D printing of biological tissues using living cells, while organ-on-a-chip technology creates micro-scale models of human organs to study disease and treatment responses.
The Future:
In the future, bioprinting could be used to create fully functional dental implants that are biologically integrated with the patient’s own tissues. This would eliminate many of the challenges associated with implant rejection and poor osseointegration. Organ-on-a-chip technology could also play a role in personalized medicine, allowing dentists to test how a patient’s tissues might respond to different implant materials and techniques before the actual procedure.
7. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning:
The Current State:
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are beginning to make their mark in dentistry, particularly in diagnostics and treatment planning. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict outcomes, assisting dentists in making more informed decisions.
The Future:
As AI technology continues to evolve, it could become an integral part of the dental implant process. AI-powered tools could help in diagnosing conditions that could affect implant success, predicting the best implant placement strategies, and monitoring long-term implant health. Machine learning algorithms could also be used to develop personalized treatment plans, optimizing implant procedures for individual patients based on their unique anatomy and health profile.
Conclusion:
The future of dental implants is bright, with numerous emerging trends and technologies poised to enhance the effectiveness, comfort, and accessibility of this important dental solution. From 3D printing and smart implants to regenerative medicine and AI, the innovations on the horizon promise to transform the way dental implants are designed, placed, and maintained. As these technologies continue to develop, patients can look forward to even more reliable and personalized care, ensuring that their dental implants provide a lifetime of benefits.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.
Copyright © 2019-2025 IndiBlogHub.com. All rights reserved. Hosted on DigitalOcean for fast, reliable performance.