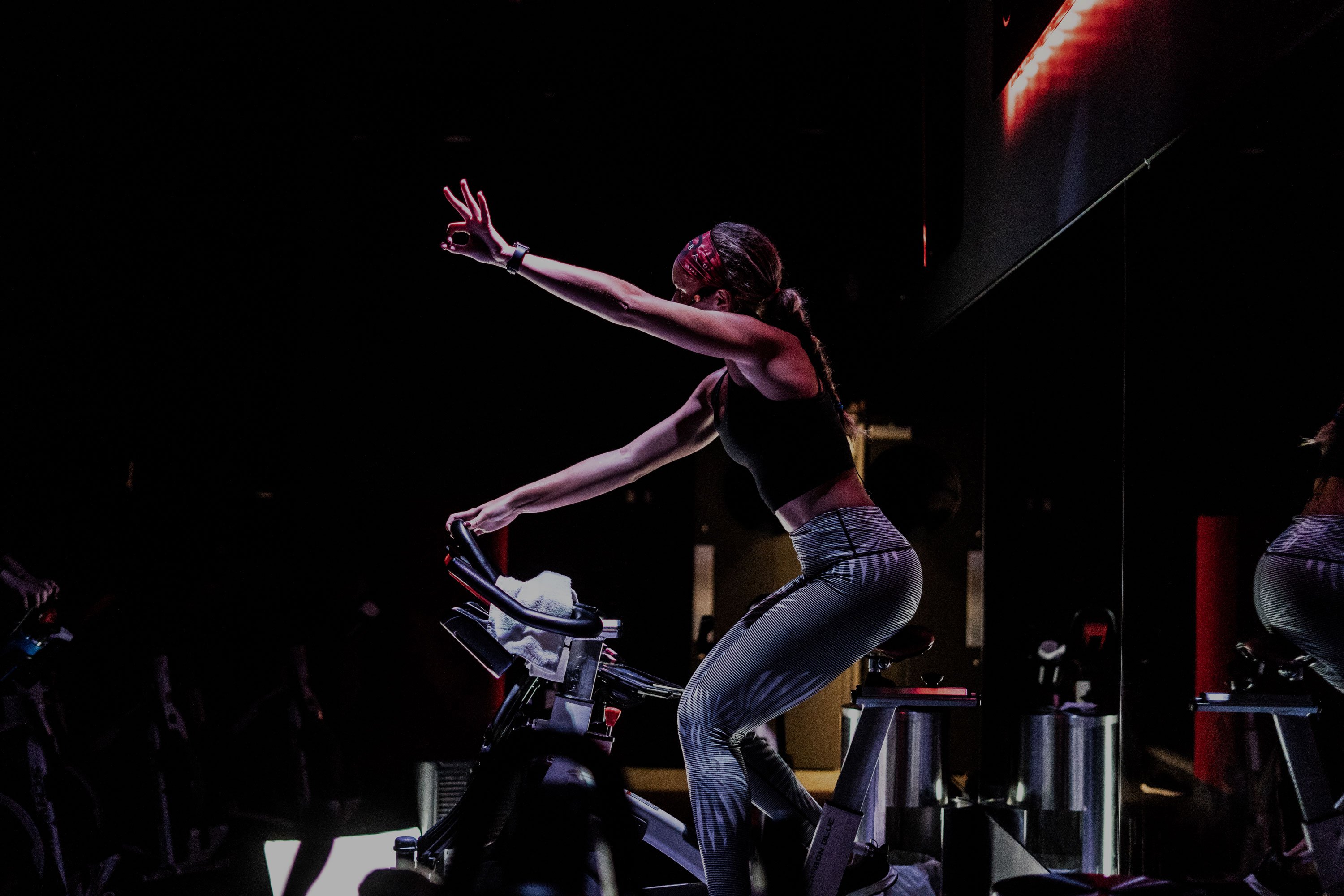The Science Behind Calories Burned During Indoor Cycling

Strong8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
Indoor cycling has become a popular workout choice for fitness enthusiasts looking to burn calories, build muscle, and improve overall cardiovascular health. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced rider, understanding the science behind calories burned during indoor cycling can help you maximize your workout and achieve your fitness goals.
Understanding Calories and Energy Expenditure
Before diving into the specifics of indoor cycling, it is important to understand what calories are and how they relate to energy expenditure. A calorie is a unit of energy that your body uses to perform various functions, including breathing, digesting food, and exercising. The number of calories you burn during any activity depends on several factors, including your weight, age, gender, and intensity of the exercise.
How Indoor Cycling Burns Calories
Indoor cycling is a high-intensity cardiovascular workout that involves pedaling on a stationary bike, often with varying levels of resistance and speed. The intensity of the workout can vary depending on the cycling class or your personal goals, but the primary focus is on increasing heart rate and burning calories of Calories Burned Indoor Cycling.
Cardiovascular Endurance and Calorie Burn
Research has shown that a typical indoor cycling session can burn anywhere from 400 to 600 calories per hour, depending on factors such as your weight, intensity, and duration of the workout. For example, a person weighing 155 pounds can burn approximately 520 calories during a 60-minute indoor cycling session at a moderate intensity. If the intensity is increased to a vigorous level, the calorie burn can rise to around 670 calories per hour.
The Role of Resistance in Calorie Burn
Another factor that influences the number of calories burned during indoor cycling is resistance. Most indoor cycling bikes come with adjustable resistance levels, allowing you to simulate climbing hills or sprinting on flat terrain. When you increase the resistance, your muscles have to work harder to push the pedals, which in turn increases the amount of energy your body expends.
The Science of Muscle Building During Cycling
While indoor cycling is primarily known for its cardiovascular benefits, it also plays a significant role in Muscle Building Cycling Workout. The repetitive motion of pedaling, combined with resistance, helps strengthen and tone the lower body muscles. But how exactly does this process work?
Muscle Hypertrophy and Cycling
Muscle Building Cycling Workout hypertrophy refers to the growth and increase in the size of muscle cells. This process occurs when the muscles are subjected to repeated stress, such as during resistance training or high-intensity workouts like indoor cycling. As you pedal against resistance, micro-tears form in the muscle fibers. During the recovery phase, the body repairs these tears by fusing muscle fibers together, resulting in increased muscle mass.
Factors That Influence Calorie Burn During Indoor Cycling
While Calories Burned Indoor Cycling, several factors can influence the exact number of calories you burn during a session. Understanding these factors can help you tailor your workouts to achieve the best results.
Body Weight and Composition
Your body weight plays a significant role in determining how many calories you burn during exercise. Generally, the more you weigh, the more calories you will burn during physical activity. This is because your body requires more energy to move a larger mass. For example, a person weighing 185 pounds will burn more calories during the same indoor cycling session than a person weighing 155 pounds.
Tips to Optimize Your Indoor Cycling Workout
Now that you understand the science behind calories burned during indoor cycling, here are some tips to help you optimize your workout for maximum results:
1. Use a Heart Rate Monitor
Tracking your heart rate during indoor cycling can help you stay within your target heart rate zone, ensuring that you’re working at an intensity that maximizes calorie burn. Aim to stay within 70-85% of your maximum heart rate for the best results.
2. Vary the Resistance
Incorporating different resistance levels throughout your workout can help engage different muscle groups and prevent your body from adapting to a single intensity level. This variation not only enhances calorie burn but also promotes muscle growth.
3. Incorporate Interval Training
As mentioned earlier, High-Intensity Interval Training is an effective way to increase calorie burn and build muscle. Try alternating between short bursts of maximum effort and longer periods of moderate effort during your indoor cycling session.
Conclusion
Indoor cycling is a powerful workout that not only burns calories but also builds muscle and improves cardiovascular health. By understanding the science behind calories burned during indoor cycling and implementing strategies to optimize your workout, you can achieve your fitness goals more effectively. Remember to vary your intensity, incorporate resistance, and stay consistent with your routine to see the best results over time.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.