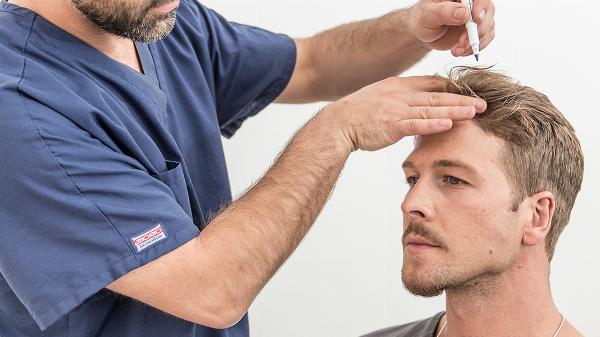
The Science Behind Hair Transplants: How They Work
Hair loss is a common concern for many people around the world. While various treatments and remedies claim to restore hair, one of the most effective and sought-after solutions is hair transplantation. This article delves into the science behind Hair Transplant in Dubai, exploring how they work, the techniques used, and what individuals can expect from the procedure.
Understanding Hair Loss:
Before diving into the mechanics of hair transplants, it's essential to understand the causes of hair loss. The most common type is androgenetic alopecia, often referred to as male or female pattern baldness. This genetic condition leads to hair follicles shrinking, resulting in thinner and shorter hair until the follicle eventually stops producing hair altogether.
Other factors contributing to hair loss include hormonal changes, medical conditions, stress, and certain medications. Understanding these underlying causes is vital for individuals considering hair transplants, as it helps set realistic expectations for the procedure's outcome.
What Is a Hair Transplant?
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure that involves moving hair follicles from one part of the body (known as the donor site) to a bald or thinning area (the recipient site). The hair follicles are typically taken from areas where hair is more resistant to balding, such as the back or sides of the head.
Hair transplants can be performed using two primary techniques: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). Understanding these techniques is crucial for potential patients.
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT):
FUT, also known as the strip method, involves removing a strip of skin from the donor area. The strip is then dissected into individual follicular units, which typically contain one to four hair follicles. This method allows for the transplantation of a large number of hair follicles in a single session.
Advantages of FUT:
Higher Graft Yield: FUT can yield a considerable number of grafts in a single procedure, making it suitable for patients with significant hair loss.
Cost-Effectiveness: Generally, FUT is less expensive than FUE due to the efficiency of the technique.
Disadvantages of FUT:
Scarring: FUT leaves a linear scar at the donor site, which may be noticeable if the hair is cut short.
Longer Recovery Time: Patients may experience a longer recovery period due to the surgical nature of the procedure.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE):
FUE is a more advanced technique that involves harvesting individual hair follicles directly from the donor area using a specialized extraction tool. This method does not require the removal of a strip of skin, resulting in minimal scarring.
Advantages of FUE:
Minimized Scarring: FUE leaves tiny, dot-like scars that are less noticeable compared to the linear scar from FUT.
Faster Recovery: Patients typically experience less pain and a quicker recovery time with FUE.
Disadvantages of FUE:
Lower Graft Yield: FUE may yield fewer grafts in a single session compared to FUT, which may necessitate multiple sessions for extensive hair restoration.
Cost: FUE is generally more expensive due to the time and precision required for the extraction process.
The Hair Transplant Procedure:
The hair transplant procedure typically involves several key steps:
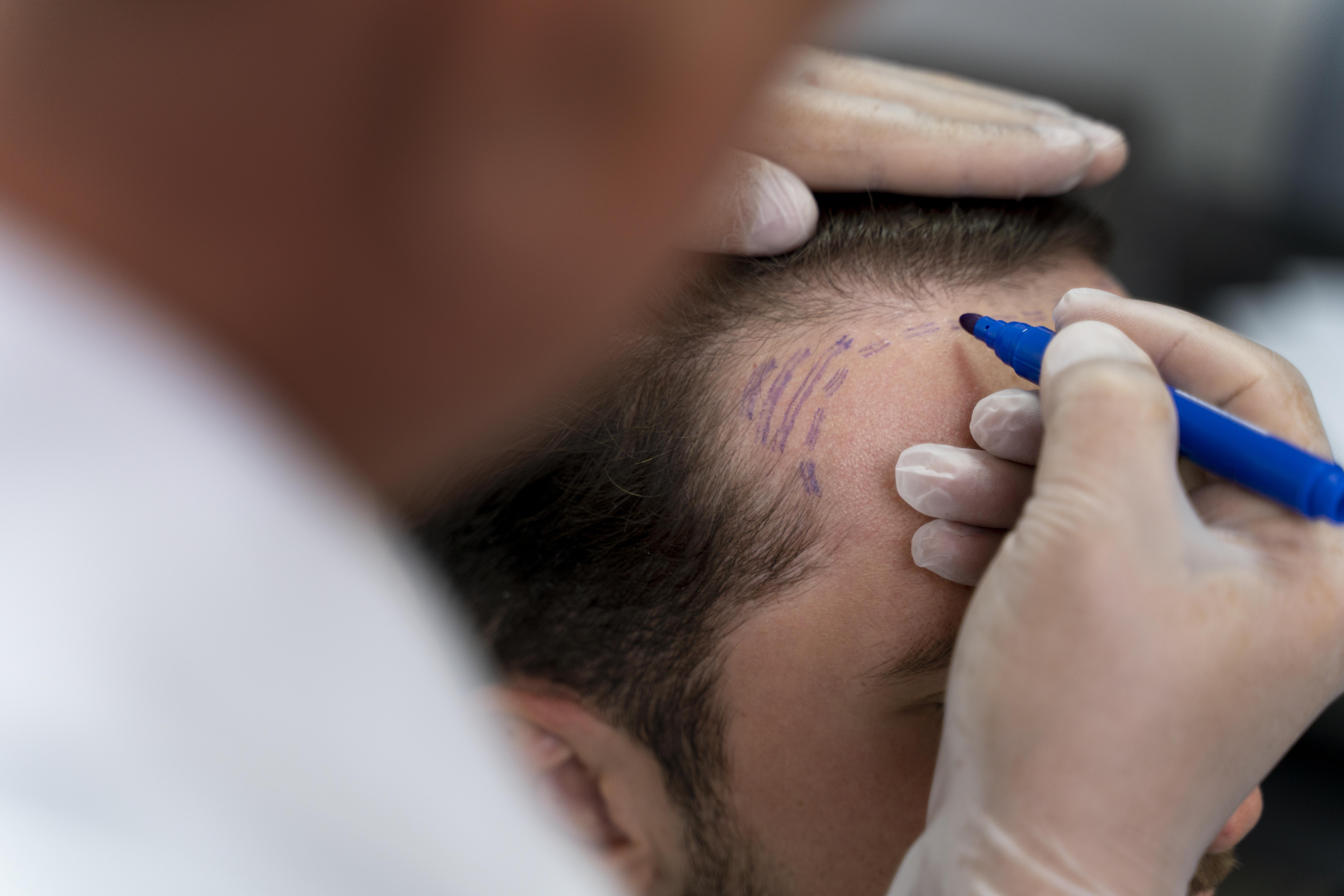
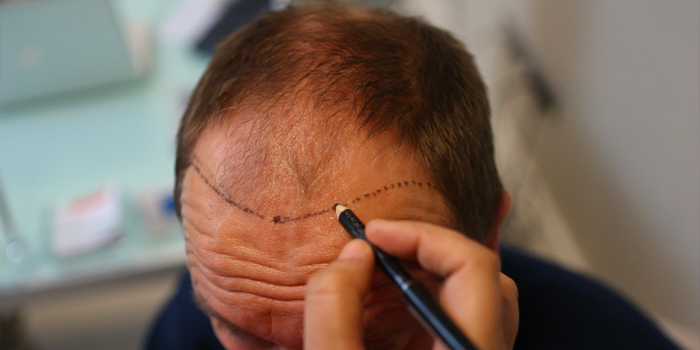
Consultation:
The process begins with a consultation where the surgeon evaluates the patient's hair loss, discusses goals, and creates a personalized treatment plan. The surgeon will also assess the donor area to ensure sufficient hair for transplantation.
Preparation:
On the day of the procedure, the patient is given local anesthesia to numb the donor and recipient areas. This step ensures the patient remains comfortable throughout the process.
Harvesting:
Depending on the chosen technique, the surgeon will either remove a strip of skin (FUT) or extract individual follicular units (FUE) from the donor area.
Graft Preparation:
In the case of FUT, the strip is dissected into individual follicular units. In FUE, the extracted follicles are prepared for implantation immediately.
Transplantation:
The prepared grafts are then implanted into the recipient area. The surgeon makes tiny incisions in the scalp where the grafts will be placed, ensuring they are positioned in a natural pattern.
Recovery:
After the procedure, the patient will receive post-operative instructions, which may include guidelines for caring for the scalp and managing any discomfort. The initial healing process takes about a week, after which the transplanted hair will begin to shed, making way for new growth.
The Science of Hair Growth:
The effectiveness of hair transplants lies in the science of hair growth. Hair follicles go through cycles, including the anagen (growth), catagen (transitional), and telogen (resting) phases. When transplanted hair follicles are taken from a donor area, they retain their genetic characteristics and continue to grow in their new location.
Research shows that transplanted hair follicles typically begin to grow in about three to four months post-surgery, with full results visible within 9 to 12 months. The newly transplanted hair blends with existing hair, creating a natural look.
Potential Risks and Considerations:
Like any surgical procedure, hair transplants come with risks. Some potential side effects include:
Infection
Bleeding
Scarring
Poor growth of transplanted hair
It's crucial for individuals considering a hair transplant to choose a qualified and experienced surgeon to minimize these risks and achieve the best possible outcome.
Conclusion:
Hair transplants have become a popular solution for individuals experiencing hair loss, offering a permanent and effective way to restore hair. By understanding the science behind hair transplants, including the techniques used and the hair growth process, individuals can make informed decisions about their hair restoration options. Whether opting for FUT or FUE, a hair transplant can significantly improve one’s appearance and boost self-confidence, helping people regain not only their hair but also their sense of self.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.