Valve Seal Installation and Maintenance

Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
Comprehensive Guide to Valve Seals: Functions, Installation, Maintenance, and Troubleshooting
China-Based Industrial Valve Seal Kit Manufacturer Provides Low-Emission Valves, High-Performance Valve Packing, and Advanced Seal Materials for Demanding Applications.
Valve seals are critical components in fluid control systems, playing a key role in maintaining tight seals, preventing fluid leakage, and ensuring system reliability. Proper installation and maintenance of these seals are essential for extending valve lifespan, enhancing efficiency, and ensuring smooth operation under various working conditions. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the purpose, installation, precautions, common problems, and maintenance procedures associated with valve seals.
1. Importance and Function of Valve Seals
Valve seals are located between the valve seat and disc, or between the valve stem and packing gland. Their primary purpose is to ensure leak-tight operation and maintain pressure integrity in the system. This is particularly important in high-pressure, high-temperature, or chemically aggressive environments.
Key Functions:
Leak Prevention: The primary function of valve seals is to block fluid from escaping through the valve disc, seat, or packing gland when the valve is closed. This is crucial for system safety and environmental protection.
Pressure and Temperature Stability: In high-performance applications such as petrochemical or gas transmission systems, seals help maintain constant pressure and temperature, even under extreme conditions.
Component Protection and Longevity: Proper sealing reduces erosion, corrosion, and wear of valve components, significantly increasing valve service life and reducing maintenance costs.
2. Common Seal Materials and Types
The choice of seal material greatly influences valve performance. Seals must be compatible with the fluid medium, pressure, and temperature conditions of the application.
Typical Materials:
Metal Seals: Ideal for high-pressure, high-temperature environments such as oil and gas pipelines. They offer excellent strength and thermal resistance.
Rubber Seals: Best suited for general-purpose applications with water or gas at moderate pressures and temperatures. Known for their elasticity and low cost.
PTFE (Teflon) Seals: Suitable for corrosive or high-temperature environments. PTFE offers excellent chemical resistance and can withstand a broad range of operating conditions.
Composite Seals: Made from combinations of metals and non-metals, these seals offer a balance of strength, flexibility, and sealing performance, ideal for demanding applications.
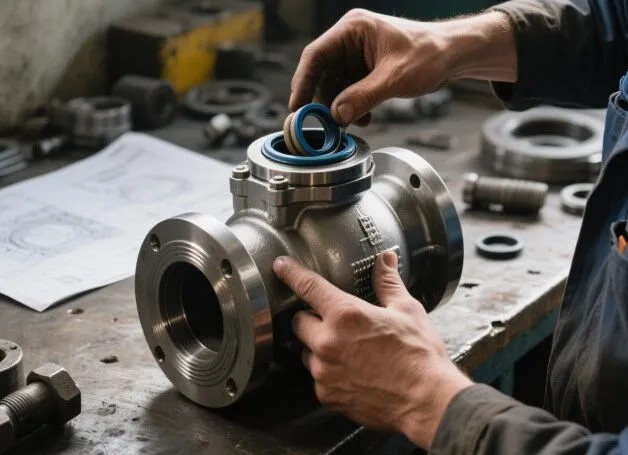
3. Valve Seal Installation Guidelines
Proper installation is key to achieving optimal sealing performance. Follow these steps to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Preparation:
Select the Right Material: Match the seal to the system’s operating pressure, temperature, and medium (e.g., corrosive or abrasive fluids).
Inspect for Defects: Examine seals for cracks, deformation, or aging. Do not install damaged seals.
Clean All Surfaces: Ensure the valve seat, disc, and sealing surfaces are free from dust, grease, and debris.
Apply Lubricant: For rubber or PTFE seals, use a compatible lubricant to reduce friction and avoid installation damage.
Installation Steps:
Correct Placement: Fit the seal into the designated position, ensuring it is properly seated without folds, misalignment, or gaps.
Controlled Compression: Avoid over-compressing the seal. Ideal compression is generally 70–80% of the seal’s original thickness to maintain elasticity.
Gradual Tightening: Apply even pressure during assembly to prevent localized stress or distortion.
Secure Valve Components: Tighten the valve seat, disc, and other components as per manufacturer recommendations to maintain structural integrity.
Post-Installation Checks:
Visual Inspection: Confirm proper placement and ensure the seal is undamaged and seated correctly.
Pressure Testing: Conduct a pressure test, usually above the normal operating pressure, to verify seal performance.
Leak Testing: Use soap solution or dedicated leak detection equipment to confirm there are no leaks.
4. Installation Precautions
Avoid Contamination: Do not allow oil, dust, or foreign substances to contact the seal during installation.
Verify Compatibility: Confirm that the seal matches the valve’s material, dimensions, and service requirements.
Temperature Awareness: Avoid installation at extreme temperatures that could alter the seal’s physical properties.
Pay Attention to Orientation: Some seals are directional and must be installed accordingly for effective sealing.
5. Common Valve Seal Issues and Troubleshooting
Understanding typical problems and their causes allows for quicker diagnosis and resolution.
Issue 1: Leakage
Causes: Seal degradation, improper installation, or worn valve components.
Solutions: Inspect and replace the seal. Examine the valve seat and disc for wear and repair or replace them if needed.
Issue 2: Cracking or Damage
Causes: Use of incompatible materials, excessive compression, or temperature spikes.
Solutions: Use seals made for the specific operating conditions. Avoid over-tightening and monitor operating parameters.
Issue 3: Seal Displacement
Causes: Incorrect seal size or improper fitting, or wear in valve seats.
Solutions: Refit the correct size seal. Secure it properly during installation. Inspect for component wear.
6. Regular Maintenance and Inspection
Routine maintenance ensures continued performance and reduces the risk of failure in critical systems.
Maintenance Tasks:
Inspect for Wear and Aging: Regularly check for cracks, hardening, or deformation.
Check Valve Surfaces: Ensure the valve seat and disc remain smooth and intact.
Monitor System Conditions: Regularly observe pressure and temperature levels to avoid seal overloading.
Seal Replacement:
Replace seals showing any signs of aging or damage. Always use the correct size and specification as recommended by the manufacturer.
Conclusion
Valve seals are essential to the safe and efficient operation of any fluid control system. By selecting the appropriate material, ensuring proper installation, and performing regular maintenance, operators can significantly improve valve performance, reduce system downtime, and enhance overall safety. Understanding common issues and how to address them helps ensure long-term reliability and cost-effective operation.Know more about Google SEO Directory
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.