Why Choose an RS-485 Modbus Gateway with 5 Digital Inputs for Your PLC Network?
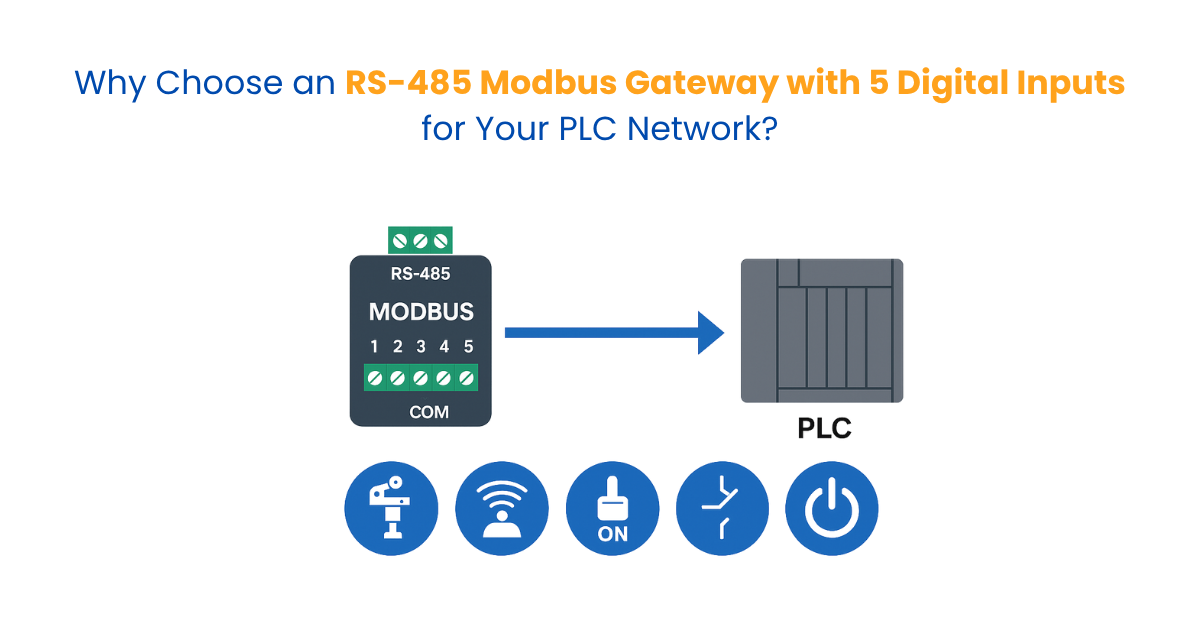
In industrial automation and control systems, the need for reliable, real-time data transmission between field devices and PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) is paramount. A key component that enables seamless communication in such environments is the RS-485 Modbus Gateway—particularly those with 5 digital inputs (DI).
This blog will explore the advantages of using an RS-485 Modbus Gateway with 5 digital inputs in your PLC network, including how it enhances system scalability, input flexibility, and communication reliability across various industrial applications.
What is an RS-485 Modbus Gateway?
An RS-485 Modbus Gateway is a communication bridge that converts Modbus signals (usually RTU or ASCII) over RS-485 to other protocols or devices. It allows data exchange between Modbus field devices (sensors, actuators, meters) and higher-level control systems like PLCs, HMIs, or SCADA systems.
Key Features of a Typical RS-485 Modbus Gateway:
- Supports Modbus RTU/ASCII protocols
- Connects multiple slave devices on a single bus
- Long-distance transmission over twisted-pair cables
- Noise immunity in harsh environments
- Often DIN-rail mountable for industrial cabinets
Why Digital Inputs Matter
Digital inputs (DIs) are used to detect binary states—typically ON/OFF, HIGH/LOW, or 1/0 signals—from external devices. Integrating 5 digital inputs into the Modbus gateway provides local input detection, reducing the need for additional I/O modules or PLC cards.
Examples of Digital Input Signals:
- Switches (limit, pressure, float)
- Relay contacts
- Motion detectors
- Door open/close states
- Alarm signals from machines
Key Benefits of Choosing a RS-485 Modbus Gateway with 5 Digital Inputs
1. Simplified Wiring and Infrastructure
In traditional setups, each sensor or switch must be hardwired directly to the PLC’s digital input modules. This not only increases wiring complexity but also introduces multiple points of failure.
With an RS-485 Modbus Gateway that includes 5 built-in digital inputs, you can directly wire those signals into the gateway, which then sends their status over a single RS-485 line to the PLC.
Benefits:
- Fewer Cables: One communication cable replaces multiple signal wires.
- Tidier Panels: Cleaner installation inside control cabinets.
- Faster Commissioning: Reduced wiring time and labor costs.
- Easier Maintenance: Fault isolation is quicker when fewer wires are involved.
2. Distributed I/O for Better Scalability
Distributed I/O refers to placing input/output modules closer to field devices rather than at a centralized PLC panel. An RS-485 Modbus Gateway with 5 digital inputs can act as a local I/O module, ideal for this architecture.
Example:
If you have sensors placed 100 meters away from the PLC, placing a gateway near them allows you to:
- Avoid running long individual wires back to the main cabinet.
- Add additional devices by daisy-chaining another RS-485 gateway on the same line.
- Scale the network modularly, adding more devices as the system grows.
This approach reduces signal degradation and is far more manageable in large-scale plants, factories, or remote installations.
3. Enhanced Communication Reliability
RS-485 is a differential signaling protocol that excels in electrically noisy environments (e.g., industrial motors, generators, high-voltage systems). Pairing it with the Modbus RTU/ASCII protocol ensures robust, predictable, and widely supported communication.
Technical Advantages:
- Up to 1200 meters communication distance
- Multiple slave devices (up to 32 or more) on a single twisted-pair cable
- Error checking via CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check)
- Immunity to electrical noise
When the gateway receives digital input signals, it transmits the state over RS-485 with reliable error handling, which is critical for PLC decision-making and control.
4. Real-Time Digital Signal Monitoring
In many industrial processes, binary signals such as “Valve Open,” “Emergency Stop Pressed,” or “Pump Fault” must be instantly detected by the PLC or SCADA system to ensure safety and performance.
A Modbus Gateway with 5 digital inputs captures these states in real time and communicates them to your control system at polling intervals as short as a few milliseconds.
Use Cases:
- Alarms and alerts
- Triggering backup systems
- Safety interlocks
- System status dashboards
This event-driven architecture improves system responsiveness and minimizes downtime due to delayed signal recognition.
5. Cost Efficiency
Industrial automation budgets are often tight, especially in mid-sized operations or retrofitting projects. Instead of purchasing:
- Additional PLC digital input modules,
- Long lengths of signal wire,
- And I/O expansion racks,
- you can deploy a Modbus gateway with 5 digital inputs as a cost-effective alternative.
Cost-Saving Areas:
- Hardware: Lower number of PLC cards or expansion modules needed.
- Installation: Less wiring, smaller cabinets, fewer terminals.
- Maintenance: Fewer connections = fewer points of failure.
Over time, the total cost of ownership (TCO) is significantly reduced, while system flexibility remains high.
Typical Applications in PLC Networks
Here are detailed use cases for various industries:
➤ Factory Automation
- Detect if a machine guard is open (safety interlock)
- Check if a conveyor end-limit switch is triggered
- Monitor manual pushbutton status for operator panels
➤ Building Management Systems (BMS)
- Receive door-open/close status
- Trigger fire/smoke alarms via relay inputs
- Monitor lighting control relays
➤ Water/Wastewater Plants
- Monitor float switches for tank levels
- Detect pump fault or thermal overloads
- Get remote status of valve positions
➤ Energy Systems
- Receive trip signals from circuit breakers
- Monitor dry contact outputs of energy meters
- Detect solar inverter fault status
These systems benefit from the fast binary feedback and remote monitoring enabled by the gateway’s digital inputs.
Integration with PLCs – How It Works
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how a gateway with digital inputs integrates with a PLC:
Step 1: Gateway Configuration
- Assign a unique Modbus slave ID.
- Set baud rate and parity to match your PLC's RS-485 settings.
Step 2: Digital Input Wiring
- Connect switches, sensors, or relay contacts to the DI terminals.
- Ensure voltage levels are within the accepted range (typically 5–30V DC).
Step 3: PLC Setup
- Program your PLC to poll specific Modbus registers (usually discrete input registers).
- Use function codes (e.g., FC02) to read digital input states.
Step 4: Logic Implementation
Use the digital states in your ladder logic or structured text to:
- Start/stop motors
- Raise alarms
- Record timestamps
- Trigger output actions
The system continuously monitors these inputs, often at polling intervals between 10ms to 500ms, depending on network traffic.
Choosing the Right Gateway: Key Considerations
Selecting the right RS-485 Modbus Gateway with 5 DIs ensures compatibility and longevity.
| Specification
|
Why It Matters
|
| Modbus Protocols
|
Must support RTU/ASCII based on PLC or SCADA used
|
| Input Voltage Range
|
Matches field devices (e.g., 5–30V DC typical)
|
| Optical Isolation
|
Protects gateway from high-voltage or surge events
|
| DIN Rail Mounting
|
Ensures clean industrial panel integration
|
| Certifications
|
Necessary for compliance in regulated environments
|
| Power Input Range
|
Ensures reliable performance despite voltage dips
|
Always cross-check the Modbus address mapping, configuration tools, and documentation before integration.
Real-World Example – Wastewater Plant
Scenario:
A wastewater plant had float switches, pressure switches, and emergency buttons distributed across a 200-meter facility. The old setup required:
- Over 1.5 km of signal cabling
- Multiple terminal blocks
- Higher maintenance costs
Solution:
They installed four RS-485 Modbus Gateways with 5 digital inputs each, placed close to field sensors.
Outcome:
- Reduced wiring by 60%
- Faster troubleshooting
- Improved PLC response time
- Ease of expansion for future digital sensors
Final Thoughts
An RS-485 Modbus Gateway with 5 Digital Inputs is a smart investment for automation engineers looking to:
- Expand PLC input capabilities without overloading I/O cards
- Deploy distributed sensor networks with minimal wiring
- Monitor binary signals reliably in real-time
- Build scalable, modular, and cost-effective control systems
This solution is especially valuable in industrial, building, and energy sectors that rely on robust, flexible field connectivity.
FAQs
Q1: Can I connect analog signals to digital inputs?
No. Digital inputs only detect binary ON/OFF signals. Use analog input modules for voltage or current-based sensors.
Q2: How many gateways can I connect on one RS-485 bus?
Up to 32 devices (including the master) can typically be connected. Use repeaters or RS-485 hubs for larger networks.
Q3: Are digital inputs isolated from the RS-485 line?
Yes, most industrial-grade gateways include opto-isolation to prevent signal interference and electrical damage.
Q4: Do I need to configure each digital input separately?
Not necessarily. Most devices assign Modbus registers automatically, but you can customize mapping using vendor software or DIP switches.
Q5: Can this be used in outdoor environments?
Yes, if the device has proper IP rating (like IP65/IP67) and is housed in weatherproof enclosures.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.