Zinc Nitrite Manufacturing Plant Project Report 2024: Setup and Cost

Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
Introduction
Zinc nitrite is a specialized chemical compound used in various industrial applications, including in the production of dyes, pigments, and as a corrosion inhibitor. The demand for zinc nitrite is growing in industries that require high-quality chemicals for their processes and products. The Zinc Nitrite Manufacturing Plant Project Report provides a detailed guide for setting up a facility to produce this compound, covering feasibility, regulatory requirements, production processes, and potential benefits and challenges.
What is Zinc Nitrite?
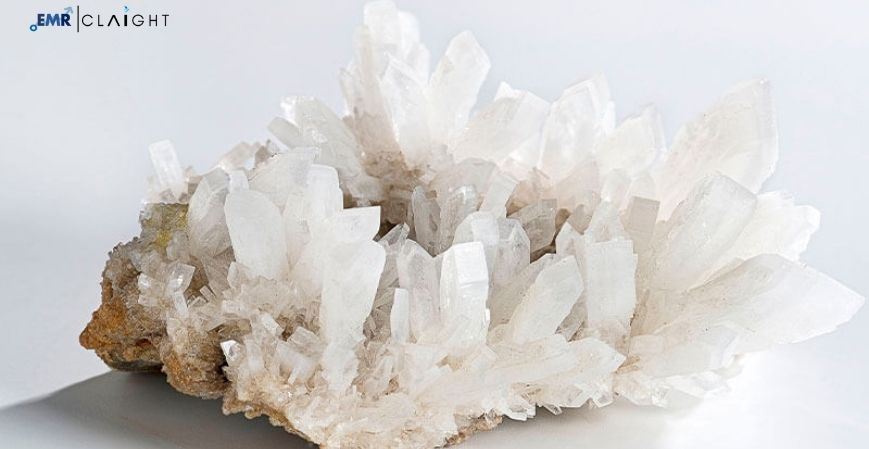
Zinc nitrite (Zn(NO₂)₂) is a chemical compound that appears as a white, crystalline powder. It is utilized in various applications:
Industrial Chemicals: Used as a precursor in the manufacture of other chemicals, including dyes and pigments.
Corrosion Inhibitors: Added to products to prevent corrosion in metals.
Laboratory Reagents: Employed in various chemical reactions and analyses in research settings.
Purpose of the Manufacturing Plant
The main goals of establishing a zinc nitrite manufacturing plant are to:
Produce High-Quality Zinc Nitrite: Meet the demand of industries requiring this compound for their products and processes.
Ensure Efficient Production: Implement advanced manufacturing technologies to enhance production efficiency and reduce costs.
Comply with Regulations: Adhere to safety, environmental, and quality standards to ensure the production of safe and effective products.
Support Economic Growth: Contribute to the local economy by creating jobs and stimulating industrial development.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents @
https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/prefeasibility-reports/zinc-nitrite-manufacturing-plant-project-report/requestsample
Key Components of the Project
Feasibility Study
Conducting a feasibility study is critical for determining the project's viability. Key components include:
Market Analysis: Assessing demand for zinc nitrite, identifying potential customers, and evaluating market trends and competition.
Cost Estimates: Calculating the costs involved in setting up the facility, including construction, equipment, raw materials, and operational expenses.
Financial Projections: Forecasting revenues, profits, and return on investment.
Risk Assessment: Identifying potential risks such as regulatory changes, market fluctuations, and supply chain issues, and developing strategies to address them.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensuring compliance with regulatory standards is essential for operating a zinc nitrite manufacturing plant. Key considerations include:
Safety Regulations: Adhering to safety standards for handling hazardous materials. This includes proper storage, handling, and disposal procedures to protect workers and prevent accidents.
Environmental Regulations: Complying with laws related to emissions, waste management, and environmental impact. Implementing measures to control pollution and manage by-products effectively.
Quality Standards: Ensuring that the zinc nitrite produced meets industry standards and regulatory requirements for purity and performance.
Facility Design and Construction
Designing and constructing the manufacturing facility are crucial for operational efficiency and safety. Key elements include:
Production Units: Facilities for the chemical synthesis of zinc nitrite, including reactors, mixing tanks, and filtration systems.
Storage Facilities: For raw materials and finished products, equipped with safety features to handle chemicals properly.
Control Systems: Advanced systems for monitoring and controlling the production process to ensure consistency and safety.
Administrative and Support Areas: Offices, laboratories, and maintenance areas to support plant operations and research activities.
Production Process
The production of zinc nitrite involves several key stages:
Raw Material Preparation: Sourcing and preparing raw materials such as zinc salts and nitrite sources.
Chemical Synthesis: Combining raw materials through controlled chemical reactions to produce zinc nitrite. This typically involves reacting zinc salts with nitrite solutions under specific conditions.
Purification: Removing impurities to ensure the final product meets quality standards. This may involve processes such as crystallization or filtration.
Quality Control: Testing the zinc nitrite to ensure it meets industry specifications and regulatory requirements. This includes checking purity, concentration, and other quality parameters.
Quality Control
Quality control is vital to ensure the safety and effectiveness of zinc nitrite. Key aspects include:
Testing for Purity and Composition: Verifying that the product meets required specifications for purity and chemical composition.
Compliance with Standards: Ensuring adherence to industry and regulatory standards for product quality.
Continuous Monitoring: Implementing procedures for ongoing monitoring and testing throughout the production process to maintain consistent quality.
Market Analysis and Distribution
Developing an effective market and distribution strategy is crucial for success. This involves:
Identifying Target Markets: Analyzing the needs of industrial users, chemical manufacturers, and other potential customers.
Building Relationships: Establishing partnerships with distributors, industrial suppliers, and other stakeholders.
Logistics: Developing efficient transportation and storage solutions to ensure timely delivery and maintain product quality.
Potential Benefits
Meeting Industry Demand
The plant will help address the steady demand for zinc nitrite in industrial and laboratory applications, supporting supply chains and improving product availability.
Economic Growth
Establishing the plant can stimulate local economic development by creating jobs, attracting investment, and supporting related industries.
Technological Innovation
The facility can drive technological advancements by incorporating cutting-edge synthesis and purification techniques.
Product Quality
By adhering to stringent quality control measures, the plant can produce high-quality zinc nitrite that meets industry standards and customer expectations.
Sustainability
Implementing sustainable practices, such as efficient resource use and waste management, can enhance the environmental performance of the plant.
Challenges and Risks
High Capital Investment
Setting up a zinc nitrite manufacturing plant requires substantial investment in facility construction, equipment, and operational expenses.
Regulatory Compliance
Navigating complex regulations related to safety, environmental impact, and product quality can be challenging and costly.
Market Fluctuations
Variations in market demand and prices for zinc nitrite and raw materials can impact profitability and financial stability.
Supply Chain Management
Ensuring a consistent supply of high-quality raw materials and managing logistics effectively are crucial for maintaining production efficiency.
Technological Changes
Keeping up with advancements in chemical synthesis and purification technologies requires ongoing investment and adaptation.
FAQ
What is zinc nitrite used for?
Zinc nitrite is used primarily in the manufacture of dyes, pigments, and as a corrosion inhibitor. It is also utilized in laboratory settings for various chemical reactions and analyses.
What are the main stages in the zinc nitrite production process?
The main stages include raw material preparation, chemical synthesis, purification, and quality control. Each stage is crucial for ensuring the final product meets industry standards.
What are the key regulatory requirements for a zinc nitrite manufacturing plant?
The plant must comply with safety regulations for handling hazardous materials, environmental regulations for emissions and waste management, and quality standards for product safety and effectiveness.
How can the plant benefit the local economy?
The plant can create jobs, stimulate economic growth, and attract investment. It also supports local industries by providing a reliable source of zinc nitrite for industrial and laboratory applications.
What challenges might the plant face?
Challenges include managing high capital investment, ensuring regulatory compliance, dealing with market fluctuations, and maintaining an efficient supply chain.
Media Contact:
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: [email protected]
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.