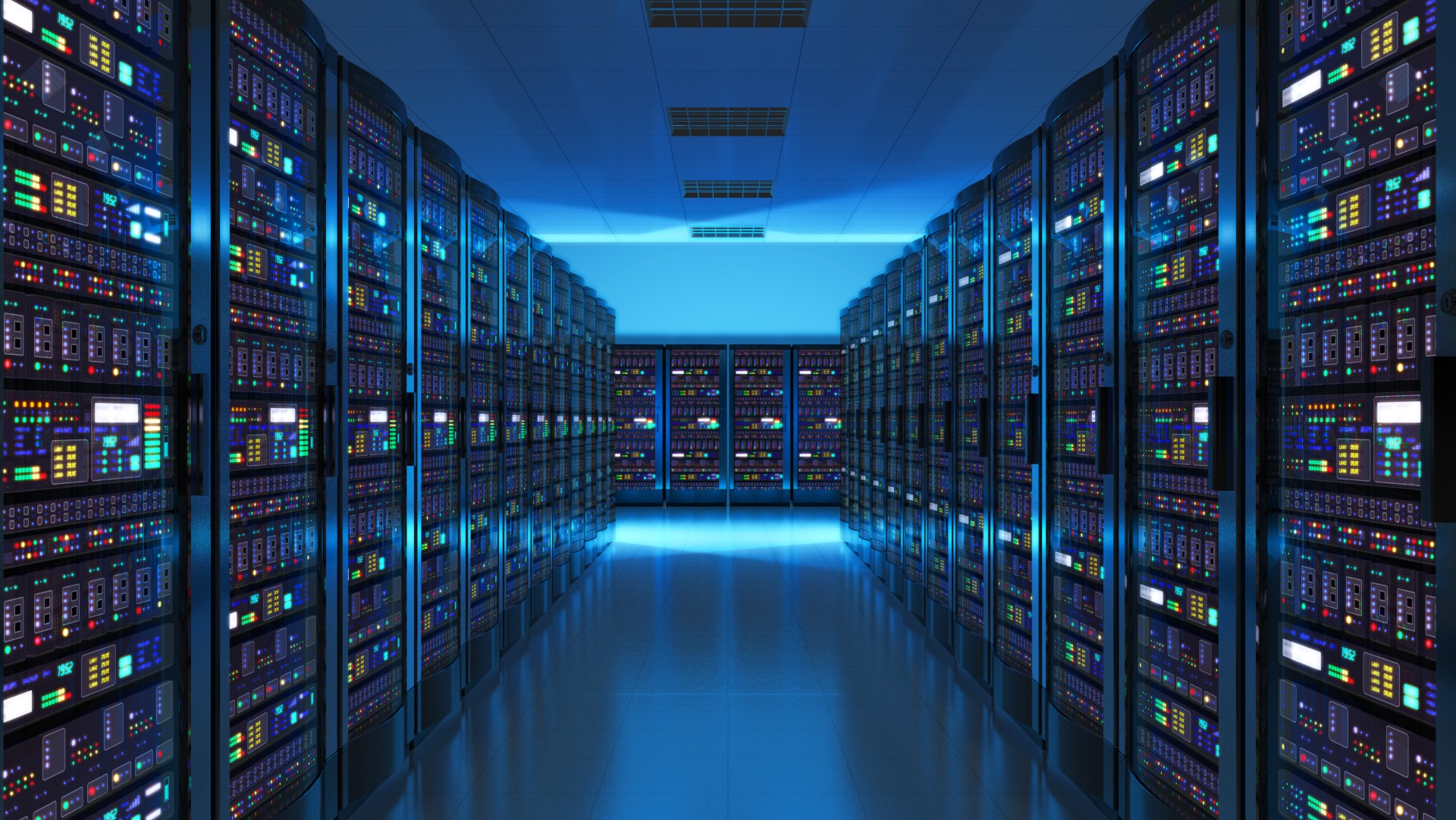
How Are Amazon, IBM, and Microsoft Redefining the Data Center Industry? Here's Why

Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
Introduction:
The data center industry is undergoing a dramatic transformation. As the demand for cloud services, artificial intelligence (AI), Machine Learning, and big data analytics accelerates, the tech giants that dominate this space—Amazon, IBM, and Microsoft—are leading the charge to reshape the future of data infrastructure. These companies are not just expanding their data center capabilities but are also innovating with cutting-edge technologies to keep up with the increasing volume of data, the need for faster processing, and the imperative of sustainability.
One of the key drivers of this transformation is edge computing. This disruptive technology is changing how data is processed, stored, and distributed, with profound implications for the data center landscape. In this article, we explore how Amazon, IBM, and Microsoft are embracing edge computing and its impact on data center strategies.
The Rise of Edge Computing
Edge computing is the practice of processing data closer to its source, rather than relying solely on centralized cloud data centers. This approach reduces latency, improves speed, and enhances the performance of applications that require real-time data processing. With the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), 5G networks, and AI applications, edge computing is becoming essential for businesses and consumers alike.
Amazon: AWS and the Move Toward Edge Computing
Amazon’s cloud computing division, Amazon Web Services (AWS), is a pioneer in embracing edge computing technologies. AWS is known for its global network of data centers, providing cloud-based computing, storage, and analytics services to businesses of all sizes. However, Amazon has recognized the growing importance of edge computing and has made substantial investments to incorporate it into its offerings.
AWS Outposts and Local Zones
One of the ways Amazon is integrating edge computing into its data center strategy is through the introduction of AWS Outposts and AWS Local Zones. These solutions bring AWS’s infrastructure closer to end users, enabling low-latency, high-performance computing for applications that need it the most.
AWS Outposts extend AWS infrastructure to on-premises locations, allowing businesses to run applications and workloads locally while still being connected to the AWS cloud. This hybrid approach allows organizations to leverage the benefits of edge computing without sacrificing the scalability, reliability, and security offered by AWS data centers.
Meanwhile, AWS Local Zones are physical locations strategically placed closer to population centers to improve the performance of latency-sensitive applications. Local Zones offer compute, storage, and database services that are optimized for edge computing, enabling businesses to provide real-time services to customers across industries like gaming, media, entertainment, and healthcare.
These investments signal Amazon’s commitment to edge computing and its recognition of the critical role it will play in future data center operations. By pushing computing resources closer to the edge, Amazon is positioning AWS to meet the demands of emerging technologies that require faster and more efficient data processing.
Amazon’s IoT Edge Solutions
Amazon is also leveraging its IoT platform, AWS IoT, to bring the power of edge computing to the Internet of Things (IoT). With IoT devices generating vast amounts of data, processing that data locally at the edge is essential for real-time decision-making. Amazon’s IoT solutions, such as AWS IoT Greengrass, allow devices to run edge computing workloads, manage data locally, and only send relevant information to the cloud.
IBM: Edge Computing Meets AI and Hybrid Cloud
IBM has a rich history of enterprise computing, and as the company pivots toward cloud and AI technologies, edge computing is playing a significant role in its transformation. IBM’s vision for the future of data centers incorporates AI, quantum computing, and edge computing to enable businesses to process data in real time, optimize workflows, and create smarter systems.
AI-Powered Edge Computing
IBM’s data center strategy places a strong emphasis on artificial intelligence and how it can be integrated with edge computing to enhance business operations. IBM’s edge computing solutions, powered by AI, are designed to optimize data processing at the edge and enable more intelligent decision-making.
For example, IBM’s Edge Application Manager uses AI to manage edge devices, allowing organizations to deploy applications at scale while ensuring optimal performance. By combining edge computing with AI, IBM is helping businesses automate processes, improve customer experiences, and reduce the need for constant connectivity to centralized cloud data centers.
Hybrid Cloud and Edge Computing
IBM’s hybrid cloud strategy is also a significant factor in its data center innovations. With the rise of edge computing, businesses need a flexible and scalable way to integrate edge data with cloud infrastructure. IBM’s hybrid cloud solutions allow businesses to combine the best of on-premises, private, and public cloud resources, offering the flexibility needed to handle edge computing workloads efficiently.
Microsoft: Leading with Azure and a Global Edge Network
Microsoft’s Azure cloud platform is another major player in the cloud and data center market, and the company is deeply invested in the potential of edge computing. Microsoft has been rapidly expanding its Azure Edge services to meet the growing demand for low-latency data processing and real-time analytics.
Azure Stack and Edge Computing Solutions
One of Microsoft’s primary edge computing offerings is Azure Stack, which allows businesses to run Azure services in remote or edge locations. Azure Stack is an extension of Microsoft’s Azure cloud and enables businesses to deploy applications and services locally, reducing latency and ensuring continuous operations even when connectivity to the main data center is limited.
The Role of 5G and Azure Edge Zones
Microsoft is also investing heavily in 5G networks, recognizing that the combination of 5G and edge computing will enable transformative business models. With ultra-fast 5G connectivity, edge devices can process data with near-instantaneous response times. Microsoft’s Azure Edge Zones are designed to leverage 5G connectivity to deliver low-latency, high-performance services to end users.
How Edge Computing is Changing Data Center Strategies
The impact of edge computing on data center strategies is profound. Amazon, IBM, and Microsoft are all actively incorporating edge computing into their data center ecosystems, allowing businesses to process data closer to its source and improve the performance of latency-sensitive applications. By investing in edge technologies, these companies are addressing the need for faster processing, reduced latency, and more efficient use of resources.
Edge computing is also reshaping how organizations think about cloud infrastructure. Traditionally, data centers have been centralized, with businesses relying on large-scale facilities to process and store data. However, with edge computing, businesses are increasingly looking to distribute computing resources closer to the user, reducing the strain on centralized data centers and improving efficiency.
Conclusion
The integration of edge computing into data center strategies is one of the most significant shifts in the tech industry. Amazon, IBM, and Microsoft are leading the way in this transformation, investing heavily in edge computing technologies and building ecosystems that can support low-latency, real-time data processing. As these companies continue to innovate and expand their edge offerings, we can expect to see even greater advancements in data center operations, cloud services, and the broader digital economy.
With edge computing becoming an integral part of data center strategies, businesses can look forward to more agile, responsive, and scalable solutions that cater to the growing demands of modern technology. The future of data centers is edge-driven, and Amazon, IBM, and Microsoft are at the forefront of this revolution, reshaping how data is processed, stored, and delivered.
Read the full blog
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.