Managing Oral Hematoma
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
Managing Oral Hematoma: Causes, Treatment, and Prevention
Introduction to Oral Hematoma
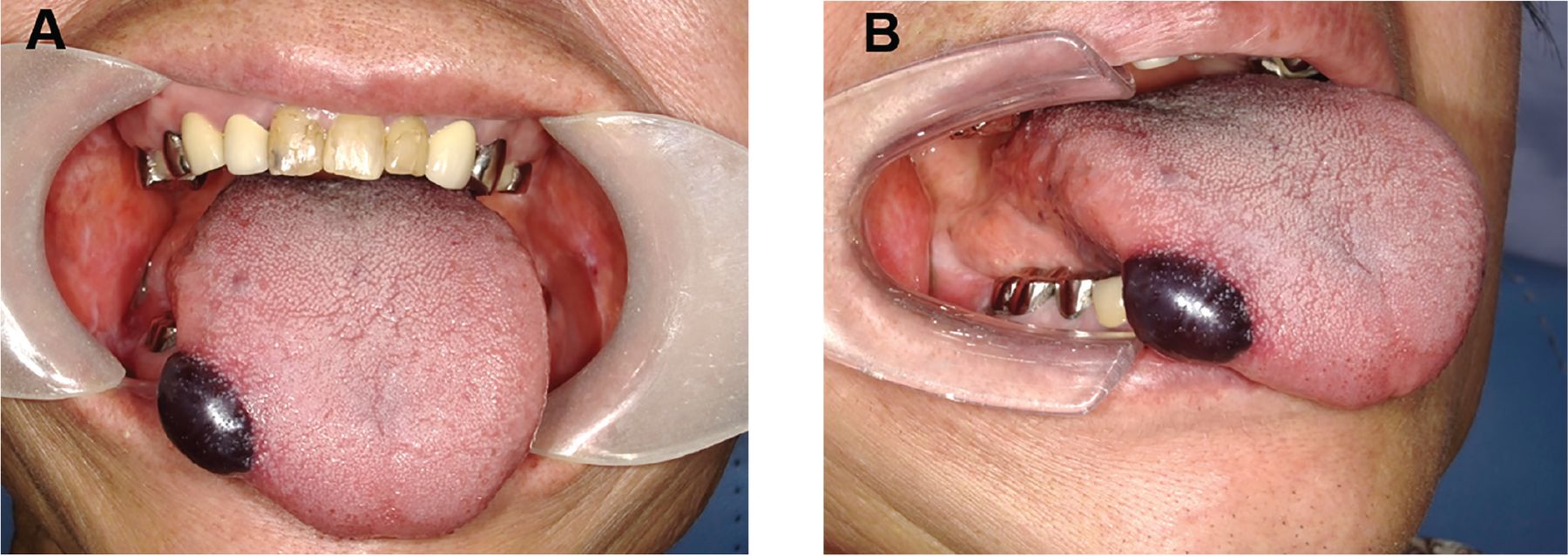
Oral hematoma refers to a localized accumulation of blood in the soft tissues of the mouth in the form of a swollen, painful, or colored lump. It results from the rupture of blood vessels, leading to the accumulation of blood under the skin or mucous membranes, usually on the lips, tongue, cheeks, or gums. Generally precipitated by trauma, oral hematomas can vary from benign to severe based on the causative factor and severity of injury. Although the majority heal on their own, management is essential to reduce pain, avoid complications, and treat underlying conditions. The following article is a comprehensive overview of the causes, medical implications, treatment methods, and prevention of oral hematomas with a focus on preventive oral care.
Causes of Oral Hematoma
Oral hematomas result from different causes, of which trauma is the most prevalent offender:
1 Physical Trauma: Spontaneous biting of cheek, tongue, or lip, falls, athletic injuries, or facial blows have the potential to injure vessels, resulting in the formation of hematomas.
2 Dental Procedures: Interventional procedures such as tooth extraction, root canal procedures, or local anesthesia administration have the possibility of causing minimal vessel rupture leading to hematomas.
3 Dental Appliances: Malfit dentures, ill-aligned braces, or pointed teeth may chronically irritate or traumatize soft tissue, inducing hematomas.
4 Medical Conditions: Blood clotting conditions (e.g., hemophilia, thrombocytopenia) or medications (e.g., anticoagulants such as aspirin, warfarin) enhance bleeding tendencies, predisposing to hematomas.
5 Vascular Fragility: Ageing, hypertension, or deficiencies (e.g., vitamin C or K) reduce blood vessel strength, enhancing rupture risk.
6 Oral Infections or Ulcers: Traumatic ulcers, infections, or inflammatory conditions may compromise tissues, leading to blood pooling.
The extent of a hematoma varies based on the severity of the injury or the underlying conditions, some healing rapidly while others need to be treated.
Health Impacts and Risks
Most oral hematomas are harmless but can be extremely painful and complicated if not handled properly:
1 Pain and Swelling: Swelling and tenderness caused by hematomas render eating, speech, or brushing painful and difficult.
2 Infection Risk: If the hematoma is part of an open ulcer or wound, bacteria can enter the hematomas, which may cause abscesses or systemic infection.
3 Aesthetic Concerns: Hematomas that become visible on the lips or the cheeks can be aesthetically distressing and affect self-esteem and social functioning.
4 Functional Impairment: Big hematomas can disrupt chewing, swallowing, or oral hygiene, predisposing to secondary dental conditions such as cavities or periodontal disease.
5 Underlying Conditions: Frequent or chronic hematomas can reflect severe conditions, including clotting disorders, vascular disorders, or, in a small number of cases, oral malignancy, and require detailed medical assessment.
Early treatment and follow-up are crucial to avoid these complications and promote healing.
Health Impacts and Risks
Most of the oral hematomas resolve on their own within one to two weeks, but certain steps can help speed recovery and minimize discomfort:
1 Cold Compress: Place a cold pack wrapped in a towel over the hemotoma 10-15 minutes several times a day to decrease swelling, pain, and inflammation.
2 Pain Relief: Take over-the-counter pain medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen to help control pain. Consult a doctor if on blood thinners to prevent complications.
3 Oral Hygiene: Gently rinse with a saltwater solution (1 tsp salt in a glass of warm water) two to three times a day to clean the area and reduce risk of infection.
4 Avoid Irritation: Do not touch, press, or pick at the hematoma, and stay away from spicy, hot, or hard foods that can irritate the area.
5 Monitor Symptoms: If the hematoma does not resolve after two weeks, increases in size, or is associated with fever, severe pain, or unusual symptoms such as numbness, dental or medical treatment is warranted.
6 Professional Intervention: For large, painful, or recurrent hematomas, a dentist can attempt drainage or a biopsy to eliminate more serious conditions. Blood work or imaging might be advised for underlying systemic conditions.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing oral hematomas involves minimizing trauma and maintaining optimal oral and overall health:
1 Protective Gear: Wear mouthguards during sports, physical activities, or if prone to teeth grinding (bruxism) to reduce the risk of oral injuries.
2 Regular Dental Care: Schedule dental checkups to ensure properly fitting dentures, smooth sharp teeth, and well-adjusted orthodontic appliances to prevent tissue irritation.
3 Healthy Diet: Steer clear of hard or sharp foods (e.g., popcorn kernels, hard candies) that can damage soft tissues. Eat foods high in vitamins C and K to promote vascular health.
4 Manage Medical Conditions: Collaborate with a healthcare provider to manage clotting disorders, hypertension, or other conditions that raise bleeding risk.
5 Gentle Oral Hygiene: Brush and floss gently with a soft-bristled toothbrush to prevent damaging gums or soft tissues.
Lifestyle Changes: Abstain from habits such as chewing hard things (e.g., ice, pens) which can lead to inadvertent trauma.
Conclusion
Oral hematomas, while usually benign, need to be managed with care to provide comfort, avoid complications, and treat possible underlying causes. By knowing their causes, receiving timely treatment, and practicing preventive measures, individuals can have healthy mouths and reduce risks. Proper dental care, protective behavior, and consideration of recurring symptoms are essential to effectively manage oral hematomas, having a healthy, pain-free mouth and promoting overall well-being.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.


