Technology Innovations & Opportunities in the India Zero Trust Architecture Market
Strong 8k brings an ultra-HD IPTV experience to your living room and your pocket.
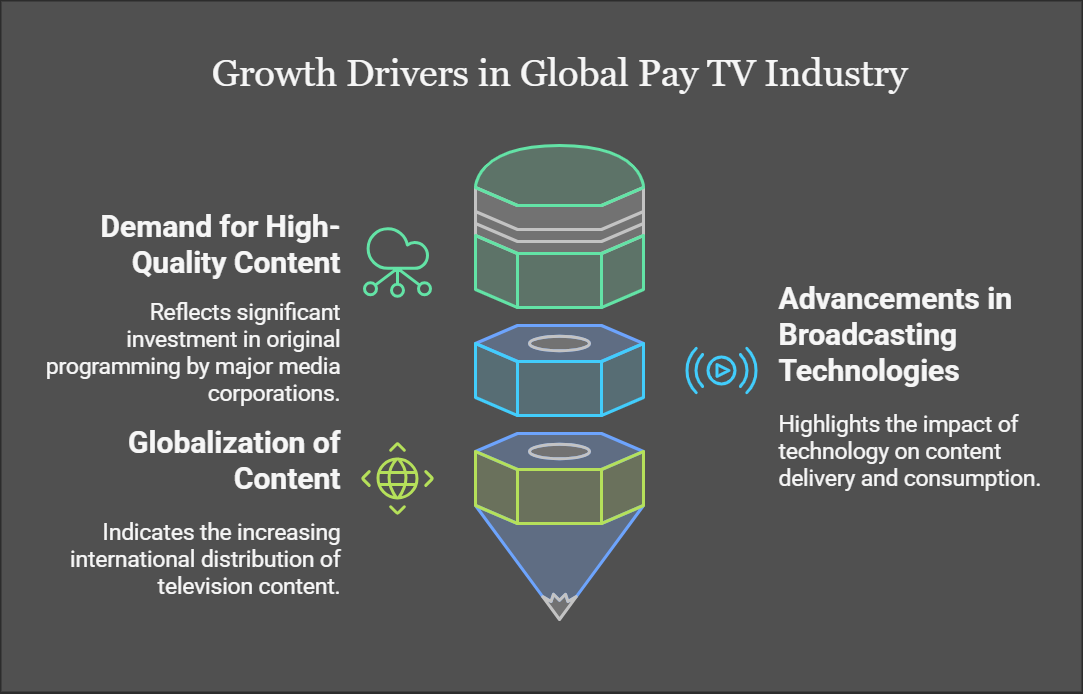
As cyber threats evolve in sophistication, the India Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) Market is experiencing a wave of technological innovations to address these challenges. The Zero Trust model operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify," mandating strict authentication and granular access control for users, devices, and applications, irrespective of their location. With India rapidly embracing digital transformation, organizations across industries are adopting advanced Zero Trust solutions to secure their networks. Get the India Zero Trust Architecture Industry Overview.
Key Technology Innovations in India’s Zero Trust Architecture Market
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML): AI and ML are transforming how organizations implement Zero Trust strategies by enabling real-time threat detection, behavioral analytics, and predictive security measures.
- Behavioral Analytics: AI-powered solutions analyze user behavior and flag anomalies, such as unusual login times or access to sensitive files, to prevent potential breaches.
- Automated Threat Detection: Machine learning algorithms identify and mitigate cyber threats in real-time, enhancing response times and reducing human error.
- Adaptive Authentication: AI-driven adaptive authentication dynamically adjusts security requirements based on user behavior and risk levels.
2. Identity and Access Management (IAM): IAM solutions are at the core of Zero Trust Architecture, enabling organizations to enforce strict authentication and access policies.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Advanced MFA solutions, including biometrics and token-based authentication, provide an additional layer of security.
- Single Sign-On (SSO): SSO technology simplifies user access while maintaining stringent authentication protocols.
- Identity Federation: Integrating IAM with cloud platforms allows seamless access control across hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
3. Cloud-Native Security Solutions: The rise of cloud computing in India has necessitated the development of Zero Trust solutions tailored for cloud environments.
- Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs): CASBs monitor and secure data flow between users and cloud applications, ensuring compliance and data security.
- Microsegmentation: This technology isolates workloads in the cloud, preventing lateral movement in the event of a breach.
- Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Security: Advanced Zero Trust solutions provide unified security across diverse cloud platforms, ensuring consistent policies and visibility.
4. Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA): ZTNA is a key innovation in securing remote work and hybrid environments by providing secure, granular access to applications without exposing the entire network.
- Software-Defined Perimeters (SDP): SDP technology hides network resources from unauthorized users, ensuring only authenticated users can access applications.
- Endpoint Security: ZTNA solutions enforce device compliance checks before granting access, ensuring secure endpoints.
- Dynamic Access Control: Access policies adapt in real-time based on user identity, device posture, and location.
5. Blockchain for Identity and Data Security: Blockchain technology is gaining traction in India’s Zero Trust market for its ability to enhance identity verification and data integrity.
- Decentralized Identity Management: Blockchain enables secure, tamper-proof digital identities, reducing reliance on centralized databases.
- Secure Data Sharing: Blockchain’s distributed ledger technology ensures secure and transparent data sharing across networks.
- Immutable Logs: Blockchain records provide tamper-proof logs for auditing and compliance purposes.
6. Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT): As IoT adoption grows in India, integrating AI with IoT devices in Zero Trust Architecture ensures enhanced security and real-time threat detection.
- IoT Device Authentication: AIoT solutions authenticate and monitor IoT devices, ensuring compliance with Zero Trust principles.
- Anomaly Detection: AI-powered IoT systems detect unusual device behavior and isolate compromised devices to prevent network-wide threats.
- Dynamic Device Policies: Security policies adapt dynamically based on device type, location, and usage patterns.
7. Data-Centric Security: With data breaches becoming more prevalent, Zero Trust models are increasingly incorporating data-centric security approaches.
- Data Encryption: Advanced encryption technologies ensure that sensitive data remains secure during transit and at rest.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP tools monitor and control data flow to prevent unauthorized access or sharing.
- Tokenization: Tokenization replaces sensitive data with unique identifiers, ensuring secure data usage in applications.
8. Secure Access Service Edge (SASE): SASE combines network security functions with wide-area networking (WAN) capabilities, aligning perfectly with Zero Trust principles.
- Unified Security Framework: SASE integrates ZTNA, CASBs, firewalls, and secure web gateways into a single framework.
- Scalability: SASE solutions are highly scalable, catering to the needs of large enterprises and SMBs alike.
- Cloud-First Approach: Designed for cloud-first organizations, SASE ensures secure access to cloud-based resources.
Opportunities in the Indian Zero Trust Market
Adoption by SMEs
The increasing adoption of digital tools by small and medium enterprises (SMEs) in India creates opportunities for cost-effective and scalable Zero Trust solutions.
Government Initiatives
Policies like Digital India and Data Localization Laws drive demand for advanced cybersecurity frameworks, including Zero Trust.
Focus on Critical Infrastructure
Sectors like energy, healthcare, and financial services are adopting Zero Trust to protect critical infrastructure from cyber threats.
Remote Work and Hybrid Environments
The shift to remote and hybrid work environments post-pandemic has accelerated the adoption of Zero Trust technologies to secure distributed workforces.
AI-Driven Innovation
Integrating AI with Zero Trust solutions will unlock new possibilities for real-time threat detection and adaptive security.
Conclusion
The India Zero Trust Architecture Market is witnessing a technological revolution, with innovations like AI/ML, ZTNA, SASE, and blockchain shaping its future. These advancements are not only enhancing security but also addressing the unique challenges faced by Indian organizations in a rapidly digitizing economy.
As cybersecurity threats continue to evolve, embracing these technologies will be crucial for businesses to safeguard their digital assets and maintain trust in a connected world. The Zero Trust model, underpinned by these innovations, is set to become the cornerstone of cybersecurity in India.
Note: IndiBlogHub features both user-submitted and editorial content. We do not verify third-party contributions. Read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policyfor details.